2 - My CCSD
... in 1 mole of H2O molecules there are two moles of H atoms and 1 mole of O atoms (think of a compound as a molar ratio) To find the mass of one mole of a compound –determine the number of moles of the elements present –Multiply the number times their mass (from the periodic table) 17 –add them up f ...
... in 1 mole of H2O molecules there are two moles of H atoms and 1 mole of O atoms (think of a compound as a molar ratio) To find the mass of one mole of a compound –determine the number of moles of the elements present –Multiply the number times their mass (from the periodic table) 17 –add them up f ...
Theoretical study of primary reaction of Pseudozyma
... reactants is very close, 19.1 and 19.7 kcal·mol-1, respectively. This value is in very good agreement with the 20.3 kcal·mol-1, which is the free energy barrier that can be deduced from the experimental catalytic events measure by Berglund and co-workers.15 TS3, associated to the nucleophilic attack ...
... reactants is very close, 19.1 and 19.7 kcal·mol-1, respectively. This value is in very good agreement with the 20.3 kcal·mol-1, which is the free energy barrier that can be deduced from the experimental catalytic events measure by Berglund and co-workers.15 TS3, associated to the nucleophilic attack ...
Scandium and Yttrium - Mercyhurst University
... Much like transition metals ions, scandium(III) and yttrium(III) will coordinate to a variety of ligands, including crown ethers, aza-crown ethers and substituted tris(3,5-pyrazolyl) methane ligands.6, 7 These compounds are interesting because they can be used for competitive binding studies.7 J. Ok ...
... Much like transition metals ions, scandium(III) and yttrium(III) will coordinate to a variety of ligands, including crown ethers, aza-crown ethers and substituted tris(3,5-pyrazolyl) methane ligands.6, 7 These compounds are interesting because they can be used for competitive binding studies.7 J. Ok ...
Chapter 2 power point File
... An element is so small that you need a small unit just to measure them Atomic mass unit (amu) is 1.66 x 10-24 g The atom carbon has a weight of 12 amu Hydrogen has a weight of 1 amu The large number in each square of the periodic table is an element’s average weight in amu The atomic mass has two im ...
... An element is so small that you need a small unit just to measure them Atomic mass unit (amu) is 1.66 x 10-24 g The atom carbon has a weight of 12 amu Hydrogen has a weight of 1 amu The large number in each square of the periodic table is an element’s average weight in amu The atomic mass has two im ...
EARLY ATOMIC THEORY AND STRUCTURE
... - Chapter 5 9. Atomic masses are not whole numbers because: (a) the neutron and proton do not have identical masses and neither is exactly 1 amu. (b) most elements exist in nature as a mixture of isotopes with different atomic masses due to different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass given in th ...
... - Chapter 5 9. Atomic masses are not whole numbers because: (a) the neutron and proton do not have identical masses and neither is exactly 1 amu. (b) most elements exist in nature as a mixture of isotopes with different atomic masses due to different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass given in th ...
Ch 2 Atoms and Elements Student
... properties that distinguish them from atoms of other elements 3. Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. 4. Atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of another element. In a chemical reaction, atoms only change the way that they are bound together with other atoms. ...
... properties that distinguish them from atoms of other elements 3. Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. 4. Atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of another element. In a chemical reaction, atoms only change the way that they are bound together with other atoms. ...
Interim Exam - Review H-Chem 2015
... substances. 4. is formed when wood is heated without the presence of air. 5. can be found in many pure forms. 4. An element is identified most accurately by its ...
... substances. 4. is formed when wood is heated without the presence of air. 5. can be found in many pure forms. 4. An element is identified most accurately by its ...
Unit 8- The Mole
... water molecules are part of the crystalline structure and are weakly bonded to the ions or molecules that make up the compound. Such compounds are known as hydrates, meaning that they contain water. The solid that remains when the water is removed is referred to as the anhydrous salt, or anhydrate. ...
... water molecules are part of the crystalline structure and are weakly bonded to the ions or molecules that make up the compound. Such compounds are known as hydrates, meaning that they contain water. The solid that remains when the water is removed is referred to as the anhydrous salt, or anhydrate. ...
Chapter 2 Elements and Compounds 2.1 The Structure of the Atom
... number (Z) of an element is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. For example, a carbon atom has six protons in its nucleus, and therefore carbon has an atomic number of six (Z = 6). Each element has a unique atomic number, and all atoms of that element have the same number of protons in th ...
... number (Z) of an element is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. For example, a carbon atom has six protons in its nucleus, and therefore carbon has an atomic number of six (Z = 6). Each element has a unique atomic number, and all atoms of that element have the same number of protons in th ...
Characterization of Multi-constituent Substances for REACH
... points, phase transitions and decompositions. Many chemical analytical methods have been developed for measuring specific constituents and can distinguish between, for example, nitrate nitrogen and ammoniacal nitrogen. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION In addition to the actual analytical testing, it is import ...
... points, phase transitions and decompositions. Many chemical analytical methods have been developed for measuring specific constituents and can distinguish between, for example, nitrate nitrogen and ammoniacal nitrogen. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION In addition to the actual analytical testing, it is import ...
Chapter 3
... CaSO4 + 2HF In one process 6.00 kg of CaF2 are treated with an excess of H2SO4 and yield 2.86 kg of HF. Calculate the percent yield of HF. A. B. C. D. ...
... CaSO4 + 2HF In one process 6.00 kg of CaF2 are treated with an excess of H2SO4 and yield 2.86 kg of HF. Calculate the percent yield of HF. A. B. C. D. ...
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context
... following is a trace element that is required by humans and other vertebrates, but not by other organisms such as bacteria or plants? A) nitrogen B) calcium C) iodine D) sodium E) phosphorus 3) Which of the following statements is false? A) Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen are the most abundan ...
... following is a trace element that is required by humans and other vertebrates, but not by other organisms such as bacteria or plants? A) nitrogen B) calcium C) iodine D) sodium E) phosphorus 3) Which of the following statements is false? A) Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen are the most abundan ...
Stoichiometry
... Used to describe a reaction in moles, and particles (molecules, formula units and atoms) but not grams. For example: 2 H2 + O2 2 H2O would be interpreted as 2 molecules of hydrogen react with 1 molecule of water to produce 2 molecules of water OR 2 moles of hydrogen react with 1 mole of oxygen t ...
... Used to describe a reaction in moles, and particles (molecules, formula units and atoms) but not grams. For example: 2 H2 + O2 2 H2O would be interpreted as 2 molecules of hydrogen react with 1 molecule of water to produce 2 molecules of water OR 2 moles of hydrogen react with 1 mole of oxygen t ...
H 2
... compounds combine one Carbonate with water ion. as it isbalance shown above. to form acids. ...
... compounds combine one Carbonate with water ion. as it isbalance shown above. to form acids. ...
Nutri-Shield, Inc. Product Description NS
... Nutri-Shield ’ s proprietary deodorization process eliminates the off-flavors and odors often associated with commercially available sodium benzoate. Nutri-Shield technology, when applied to food preservatives, offers a new generation of products available for formulators to utilize when designing p ...
... Nutri-Shield ’ s proprietary deodorization process eliminates the off-flavors and odors often associated with commercially available sodium benzoate. Nutri-Shield technology, when applied to food preservatives, offers a new generation of products available for formulators to utilize when designing p ...
Metabolic Flux Analysis in Systems Biology of Mammalian Cells
... been applied most often for the analysis of animal cell metabolism. The stoichiometric models used for flux balancing can also be applied for in silico prediction of network characteristics (e.g. maximal yields, optimal pathways, minimum substrate requirements) [48–50] or prediction of optimal genet ...
... been applied most often for the analysis of animal cell metabolism. The stoichiometric models used for flux balancing can also be applied for in silico prediction of network characteristics (e.g. maximal yields, optimal pathways, minimum substrate requirements) [48–50] or prediction of optimal genet ...
Organic Chem, Study Aide
... 2. Halogens are treated like hydrogens except they are written after the H’s; 3. If there are groupings of atoms other than hydrogen attached to a carbon they can be shown using parentheses (and subscript numbers if more than one grouping of the same are present) 4. The hydrogens or other atoms atta ...
... 2. Halogens are treated like hydrogens except they are written after the H’s; 3. If there are groupings of atoms other than hydrogen attached to a carbon they can be shown using parentheses (and subscript numbers if more than one grouping of the same are present) 4. The hydrogens or other atoms atta ...
Chemistry1100 Practice Exam 4 Choose the best answer for
... 11. A compound has an empirical formula CH2- An independent analysis gave a value of 70 for its molar mass. What is the correct molecular formula? a. C2H4 b. C3H6 c. C4O8 d. C5H10 e. C5H11 12. Given the balanced chemical equation, C4H4 + 5 O2 → 4 CO2 + 2 H2O. If 0.3618 moles of C4H4 are allowed to ...
... 11. A compound has an empirical formula CH2- An independent analysis gave a value of 70 for its molar mass. What is the correct molecular formula? a. C2H4 b. C3H6 c. C4O8 d. C5H10 e. C5H11 12. Given the balanced chemical equation, C4H4 + 5 O2 → 4 CO2 + 2 H2O. If 0.3618 moles of C4H4 are allowed to ...
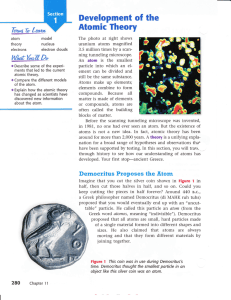
Development of the Atomic Theory
... the nucleus, as shown in the model in Figure tI. This is an atom of the element helium. Building Bigger Atoms You could build a carbon atom using 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons; or you could build an oxygen atom using 8 protons, 9 neutrons, and 8 electrons. You could even build a gold atom w ...
... the nucleus, as shown in the model in Figure tI. This is an atom of the element helium. Building Bigger Atoms You could build a carbon atom using 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons; or you could build an oxygen atom using 8 protons, 9 neutrons, and 8 electrons. You could even build a gold atom w ...
... 6.8 Calculating Empirical Formulas for Compounds • Can we calculate a chemical formula from mass percent composition? • Yes, but it is the empirical formula, not the molecular formula. • An empirical formula only gives the smallest wholenumber ratio of each type of atom in a compound, not the speci ...
File - Science with Mr. Louie
... Example 1: Look at the first number from above: 602 200 000 000 000 000 000 000 To put this number in scientific notation you would move your decimal place until there is one number to the left of the decimal. To do this, we must move our decimal 23 places to the left. When you move the decimal to t ...
... Example 1: Look at the first number from above: 602 200 000 000 000 000 000 000 To put this number in scientific notation you would move your decimal place until there is one number to the left of the decimal. To do this, we must move our decimal 23 places to the left. When you move the decimal to t ...
Chapter 3 – Stoichiometry of Formulas and Equations This chapter
... Chapter 3 – Stoichiometry of Formulas and Equations This chapter addresses two basic concepts: 1) the masses of molecules and salts at both the atomic and macroscopic levels and 2) the number relationship between reacting species. 3.1 The Mole You were introduced briefly to the atomic mass unit in t ...
... Chapter 3 – Stoichiometry of Formulas and Equations This chapter addresses two basic concepts: 1) the masses of molecules and salts at both the atomic and macroscopic levels and 2) the number relationship between reacting species. 3.1 The Mole You were introduced briefly to the atomic mass unit in t ...
Module P8.1 Introducing atoms
... Does the fact that all the known chemical compounds (of which about 810001000 are listed in the chemical literature) can be explained as combinations of just 100 or so elements mean that there are only a hundred or so different sorts of atom? The answer to this depends on what is meant by a ‘sort’ ...
... Does the fact that all the known chemical compounds (of which about 810001000 are listed in the chemical literature) can be explained as combinations of just 100 or so elements mean that there are only a hundred or so different sorts of atom? The answer to this depends on what is meant by a ‘sort’ ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS Chapter 4
... Depict the kind of reactants and products and their relative amounts in a reaction. ...
... Depict the kind of reactants and products and their relative amounts in a reaction. ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.