CHEMISTRY 2202
... Part I – Selected Response (40 marks) Select the letter of the correct response from those provided. EITHER shade the letter on your computer scorable card OR place the letter in the blank provided on your Multiple Choice Answer Sheet, whichever format is being used by your school for this exam. Do ...
... Part I – Selected Response (40 marks) Select the letter of the correct response from those provided. EITHER shade the letter on your computer scorable card OR place the letter in the blank provided on your Multiple Choice Answer Sheet, whichever format is being used by your school for this exam. Do ...
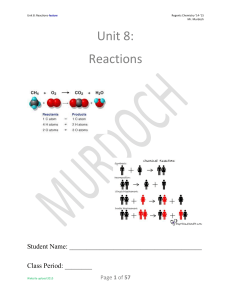
Unit 8: Reactions
... 3. Double Replacement: A solution reaction in which the positive ion of one compound combines with the negative ion of the other compound to form a precipitate, and the other ions remain dissolved in solution. 4. Law of Conservation of Charge: Charge may not be created or destroyed by physical or ch ...
... 3. Double Replacement: A solution reaction in which the positive ion of one compound combines with the negative ion of the other compound to form a precipitate, and the other ions remain dissolved in solution. 4. Law of Conservation of Charge: Charge may not be created or destroyed by physical or ch ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
Phy 211: General Physics I
... Matter can be classified as either Pure or Impure: – Pure • Element: composed of only one type of atom – Composed of either individual atoms or molecules (e.g. O2) ...
... Matter can be classified as either Pure or Impure: – Pure • Element: composed of only one type of atom – Composed of either individual atoms or molecules (e.g. O2) ...
Regents Review Questions
... (2) substance or as a mixture of substances (3) homogenous mixture, only (4) homogenous mixture or as a heterogeneous mixture ...
... (2) substance or as a mixture of substances (3) homogenous mixture, only (4) homogenous mixture or as a heterogeneous mixture ...
Experimental and Computational Evidence of Metal‑O2 Activation
... When PEA was present in a 10-fold excess over the enzyme concentration, reactions were allowed to proceed for 100−200 s before freeze-quenching. Under these conditions, CoII and/or the TPQsq•+ formed at micromolar concentrations, in yields corresponding to ∼1%, should be detectable. The reactive TPQ ...
... When PEA was present in a 10-fold excess over the enzyme concentration, reactions were allowed to proceed for 100−200 s before freeze-quenching. Under these conditions, CoII and/or the TPQsq•+ formed at micromolar concentrations, in yields corresponding to ∼1%, should be detectable. The reactive TPQ ...
Topic 1 Assignment File
... 2) AgNO3 + Ni -‐-‐-‐-‐ Ag + Ni(NO3)2 When 3.3 moles of Ni react with 159.3 grams of AgNO3, which is the limiting and which is the excess reactant? ...
... 2) AgNO3 + Ni -‐-‐-‐-‐ Ag + Ni(NO3)2 When 3.3 moles of Ni react with 159.3 grams of AgNO3, which is the limiting and which is the excess reactant? ...
Spring 2008
... Answer D [H+] = 10-9.097 = 8.0 x 10-10 26. For the reaction: aA(g) + bB(g) cC(g) + heat with a = 1, b=1 and c=1. An increase in total pressure (at const T) A. increases the number of moles of A B. decreases the number of moles of A C. does not change the number of moles of A Answer B There are more ...
... Answer D [H+] = 10-9.097 = 8.0 x 10-10 26. For the reaction: aA(g) + bB(g) cC(g) + heat with a = 1, b=1 and c=1. An increase in total pressure (at const T) A. increases the number of moles of A B. decreases the number of moles of A C. does not change the number of moles of A Answer B There are more ...
Chemical Reactivity as Described by Quantum Chemical Methods
... The failure of classical physics (mechanics and electromagnetism) at the end of the 19th century led to the introduction of the Quantum Concept by Planck, Einstein, Bohr,... culminating in the birth of "modern" quantum mechanics around 1925 due to the work of Schrödinger, Heisenberg, Born, … Schrödi ...
... The failure of classical physics (mechanics and electromagnetism) at the end of the 19th century led to the introduction of the Quantum Concept by Planck, Einstein, Bohr,... culminating in the birth of "modern" quantum mechanics around 1925 due to the work of Schrödinger, Heisenberg, Born, … Schrödi ...
Document
... (b) Electrical - in certain materials, you can remove electrons from one area and send them to another. The area losing the electrons becomes more and ...
... (b) Electrical - in certain materials, you can remove electrons from one area and send them to another. The area losing the electrons becomes more and ...
Redox I
... Mg got oxidized. Fe2+ was the oxidizing agent. •Fe goes from an ion to an element: Fe2+ Fe Fe2+ got reduced. Mg was the reducing agent. ...
... Mg got oxidized. Fe2+ was the oxidizing agent. •Fe goes from an ion to an element: Fe2+ Fe Fe2+ got reduced. Mg was the reducing agent. ...
How do we predict chemical change?
... thermodynamic stability and kinetic stability. Thermodynamic stability is a measure of how stable a system is with respect to changes in the surroundings, such as changes in temperature and pressure, or to the addition of new components. The greater the thermodynamic stability of a substance, the le ...
... thermodynamic stability and kinetic stability. Thermodynamic stability is a measure of how stable a system is with respect to changes in the surroundings, such as changes in temperature and pressure, or to the addition of new components. The greater the thermodynamic stability of a substance, the le ...
Follow Along Notes - Jackson County School System
... Given the equilibrium reaction ZnCO3(s) ZnO(s) + CO2(g). Which one of the following statements is true? a. Equal concentrations of ZnO(s) and CO2(g) would result from the decomposition of a given amount of ZnCO3(s). b. The same equilibrium condition would result if we started with only pure ZnCO3(s) ...
... Given the equilibrium reaction ZnCO3(s) ZnO(s) + CO2(g). Which one of the following statements is true? a. Equal concentrations of ZnO(s) and CO2(g) would result from the decomposition of a given amount of ZnCO3(s). b. The same equilibrium condition would result if we started with only pure ZnCO3(s) ...
Unit 8: Reactions - Mark Rosengarten
... will be the ones that happen. After all, when you let go of a bowling ball, it falls down. The motivation is gravity. It would take more energy to make the ball go up than down, so the ball falls. In order to get the ball to go up, energy has to be added. This motivation is called a driving force. R ...
... will be the ones that happen. After all, when you let go of a bowling ball, it falls down. The motivation is gravity. It would take more energy to make the ball go up than down, so the ball falls. In order to get the ball to go up, energy has to be added. This motivation is called a driving force. R ...
Energetics - chemistryatdulwich
... Lattice enthalpy is the ionic equivalent to bond enthalpies. Bond enthalpies in molecular substances indicate the strength of covalent bonds. Lattice enthalpy is an indicator of the strength of an ionic bond within an ionic lattice. Lattice enthalpy = is the enthalpy change when one mole of a solid ...
... Lattice enthalpy is the ionic equivalent to bond enthalpies. Bond enthalpies in molecular substances indicate the strength of covalent bonds. Lattice enthalpy is an indicator of the strength of an ionic bond within an ionic lattice. Lattice enthalpy = is the enthalpy change when one mole of a solid ...
AP CHEMISTRY MRS. SPENCER CHAPTER 4 TEST: SOLUTION
... Page Ref: Sec. 4.4 7) What is the concentration (M) of NaBr in a solution made by mixing 35.0 mL of 0.250 M NaBr with 65.0 mL of 0.250 M NaBr? A) 0.100 B) 0.0500 C) 0.0333 D) 0.2500 E) 125 Answer: D Analysis: Both solutions are the same concentration of the same compound. If you combine them, you s ...
... Page Ref: Sec. 4.4 7) What is the concentration (M) of NaBr in a solution made by mixing 35.0 mL of 0.250 M NaBr with 65.0 mL of 0.250 M NaBr? A) 0.100 B) 0.0500 C) 0.0333 D) 0.2500 E) 125 Answer: D Analysis: Both solutions are the same concentration of the same compound. If you combine them, you s ...
Avogadro`s Law is relation between
... 4- Identify the elements in each chemical formula and tell how many atoms of each are present. a. K2Cr2O7 b. C5H8NNaO4 (MSG, fl avor enhancer) c. C10H16N2O3S (vitamin B7) 5- Identify the element that fi ts each description. a. an alkali metal in period 6 b. a transition metal in period 5, group 8 c ...
... 4- Identify the elements in each chemical formula and tell how many atoms of each are present. a. K2Cr2O7 b. C5H8NNaO4 (MSG, fl avor enhancer) c. C10H16N2O3S (vitamin B7) 5- Identify the element that fi ts each description. a. an alkali metal in period 6 b. a transition metal in period 5, group 8 c ...
H - Deans Community High School
... Reactions happen at different rates. Industry needs to control reaction rates to increase production and get a good return for the investment ...
... Reactions happen at different rates. Industry needs to control reaction rates to increase production and get a good return for the investment ...
Strumenti tutor LIM
... A chemical transformation takes place when....................(atoms in the reactants are rearranged to form new substabces)(old bonds are broken and new bonds are formed)( at least one new substance is formed) We can realize that a chemical reaction is taking place when...........( there is a chang ...
... A chemical transformation takes place when....................(atoms in the reactants are rearranged to form new substabces)(old bonds are broken and new bonds are formed)( at least one new substance is formed) We can realize that a chemical reaction is taking place when...........( there is a chang ...
1.8 M - Thierry Karsenti
... fundamental concepts and principles associated with chemical reactions notably their rates of reaction,how they are investigated and in paticular, the factors including energy considerations that affect the different rates of reactions.. The module will look at the physical properties of solutions, ...
... fundamental concepts and principles associated with chemical reactions notably their rates of reaction,how they are investigated and in paticular, the factors including energy considerations that affect the different rates of reactions.. The module will look at the physical properties of solutions, ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.