experiment 10 - Faculty Web Pages
... Consider this generalized reaction between two ionic compounds: AB + CD AD + CB where A, B, C, and D all exist as ions in solution. Will a reaction happen, and if so, what will be the products? Each of the positive ions could combine with the negative ion of the other compound, i.e. A+ and D¯ and C+ ...
... Consider this generalized reaction between two ionic compounds: AB + CD AD + CB where A, B, C, and D all exist as ions in solution. Will a reaction happen, and if so, what will be the products? Each of the positive ions could combine with the negative ion of the other compound, i.e. A+ and D¯ and C+ ...
Chapter 1
... *Notes-A ______Subscript_________ is a number written below and to the right of a chemical symbol. C6H12O6 The 6, 12, and 6 are all subscripts. *To find the number of atoms in a compound you should __add____ the subscripts. *Notes-If there is no subscript, only __1_____ atom of that element is prese ...
... *Notes-A ______Subscript_________ is a number written below and to the right of a chemical symbol. C6H12O6 The 6, 12, and 6 are all subscripts. *To find the number of atoms in a compound you should __add____ the subscripts. *Notes-If there is no subscript, only __1_____ atom of that element is prese ...
Chapter 18 Review 18.1 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation
... - a battery will normally run out of energy, but it can be recharged by using the method of electrolysis - this reverses the redox reaction happening in the battery - electrolysis is also used in the production of metals from their ores - when the redox reaction is reversed, it’s called an electrol ...
... - a battery will normally run out of energy, but it can be recharged by using the method of electrolysis - this reverses the redox reaction happening in the battery - electrolysis is also used in the production of metals from their ores - when the redox reaction is reversed, it’s called an electrol ...
1 Types of Chemical Reactions
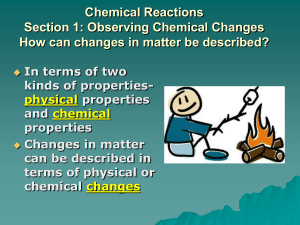
... During chemical changes new substances with different physical and chemical properties are formed. Chemical reactions can be grouped into categories depending on the nature of the chemical reaction. ...
... During chemical changes new substances with different physical and chemical properties are formed. Chemical reactions can be grouped into categories depending on the nature of the chemical reaction. ...
Spontaniety
... Using ΔG°f values from Appendix 1, calculate the standard free energy change at 25°C for the reaction CaSO4 (s) Ca2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq) Using ΔG°f values from Appendix 1, calculate the standard free energy change at 25°C for the dissolution of 1 mole of calcium chloride. ...
... Using ΔG°f values from Appendix 1, calculate the standard free energy change at 25°C for the reaction CaSO4 (s) Ca2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq) Using ΔG°f values from Appendix 1, calculate the standard free energy change at 25°C for the dissolution of 1 mole of calcium chloride. ...
Final
... Perform molarity calculations and conversions Be able to develop a precipitation and acid/base neutralization reaction given the names of the starting materials Determine whether a material is soluble or insoluble Determine whether a precipitation and acid/base neutralization reaction occurs Write c ...
... Perform molarity calculations and conversions Be able to develop a precipitation and acid/base neutralization reaction given the names of the starting materials Determine whether a material is soluble or insoluble Determine whether a precipitation and acid/base neutralization reaction occurs Write c ...
Chemistry
... its use in the determination of the relative molecular mass of a gas or vapour (calculations limited to simple examples). Use of gas syringe for the determination of relative molecular mass. ...
... its use in the determination of the relative molecular mass of a gas or vapour (calculations limited to simple examples). Use of gas syringe for the determination of relative molecular mass. ...
Equilibrium
... E=Electron Pair ● When molecules exhibit resonance, any structures can be used to predict molecular structure using VSEPR model ● VSEPR works in most cases for non-ionic compounds Sigma and pi bonds ● Sigma Bonds: Bond in which the electron pair is shared in an area centered on a line running betwee ...
... E=Electron Pair ● When molecules exhibit resonance, any structures can be used to predict molecular structure using VSEPR model ● VSEPR works in most cases for non-ionic compounds Sigma and pi bonds ● Sigma Bonds: Bond in which the electron pair is shared in an area centered on a line running betwee ...
Chapter 14 Chemical Reactions
... A balanced chemical equation has the same number of each type of atom on the product side and the reactant side. To balance the equation, we add another water molecule to the product side and add another oxygen molecule to the reactant side. We can practice balancing equations using CPO period ...
... A balanced chemical equation has the same number of each type of atom on the product side and the reactant side. To balance the equation, we add another water molecule to the product side and add another oxygen molecule to the reactant side. We can practice balancing equations using CPO period ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... (s) after the formula –solid Cu(s) (g) after the formula –gas H2 (g) (l) after the formula -liquid H2O(l) (aq) after the formula - dissolved in water, an aqueous solution. CaCl2 (aq) used after a product indicates a gas (same as (g)) O2 used after a product indicates a solid (same as (s)) ...
... (s) after the formula –solid Cu(s) (g) after the formula –gas H2 (g) (l) after the formula -liquid H2O(l) (aq) after the formula - dissolved in water, an aqueous solution. CaCl2 (aq) used after a product indicates a gas (same as (g)) O2 used after a product indicates a solid (same as (s)) ...
Chemistry Final Study Guide
... glucose into carbon dioxide, water, and usable energy. In a __________ reaction, simple reactants combine to form a more complex product. In a __________ reaction, a complex reactant is broken down into simpler products. In a __________ reaction, oxygen is always a reactant and energy is always prod ...
... glucose into carbon dioxide, water, and usable energy. In a __________ reaction, simple reactants combine to form a more complex product. In a __________ reaction, a complex reactant is broken down into simpler products. In a __________ reaction, oxygen is always a reactant and energy is always prod ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS 1
... its use in the determination of the relative molecular mass of a gas or vapour (calculations limited to simple examples). Use of gas syringe for the determination of relative molecular mass. ...
... its use in the determination of the relative molecular mass of a gas or vapour (calculations limited to simple examples). Use of gas syringe for the determination of relative molecular mass. ...
Answers to Final Exam Review
... covalent, and if ionic, write the formula for the predicted compound. a. Na and Fionic c. K and Brionic e. H and Ncovalent b. C and Ocovalent d. Ca and Fionic f. Mg and Oionic 33. Which statement describes the compound formed between sodium and oxygen? a. It is NaO2, which is ionic. c. It is Na2O, w ...
... covalent, and if ionic, write the formula for the predicted compound. a. Na and Fionic c. K and Brionic e. H and Ncovalent b. C and Ocovalent d. Ca and Fionic f. Mg and Oionic 33. Which statement describes the compound formed between sodium and oxygen? a. It is NaO2, which is ionic. c. It is Na2O, w ...
chemical reaction - Peoria Public Schools
... A word equation is an equation in which the reactants and products in a chemical reaction are represented with words methane + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water ...
... A word equation is an equation in which the reactants and products in a chemical reaction are represented with words methane + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water ...
Part II - American Chemical Society
... d. The most stable allotrope of sulfur is the cyclic S8 molecule while S2 is a highly unstable gas. In contrast, O2 is the most stable allotrope of oxygen and O8 is unknown. Account for these differences in the relative stability of the allotropes of these two elements. 8. (12%) There are four struc ...
... d. The most stable allotrope of sulfur is the cyclic S8 molecule while S2 is a highly unstable gas. In contrast, O2 is the most stable allotrope of oxygen and O8 is unknown. Account for these differences in the relative stability of the allotropes of these two elements. 8. (12%) There are four struc ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... steroid based e.g. testosterone, progesterone C. Proteins – structural building blocks of the body 1. composed of amino acid monomers 2. Chemical composition CHON 3. Enzymes are protein catalysts a. Substrate – material enzyme is working on b. Binding site (active site) – place where substrate bonds ...
... steroid based e.g. testosterone, progesterone C. Proteins – structural building blocks of the body 1. composed of amino acid monomers 2. Chemical composition CHON 3. Enzymes are protein catalysts a. Substrate – material enzyme is working on b. Binding site (active site) – place where substrate bonds ...
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER-II Chemistry (Theory) Class-XII
... Neetu and Asha look organic compound synthesis as their chemistry project. They prepare benzene diazonium chloride and stored it at room temperature. Due to holiday, they start preparing azodye but it cannot be prepared. Then their friend Reena told them to prepare benzene diazonium chloride again a ...
... Neetu and Asha look organic compound synthesis as their chemistry project. They prepare benzene diazonium chloride and stored it at room temperature. Due to holiday, they start preparing azodye but it cannot be prepared. Then their friend Reena told them to prepare benzene diazonium chloride again a ...
2011
... hexane has more surface area for interacting with neighbouring hexane molecules. C) hexane has hydrogen bonding. D) hexane has less surface area for interacting with neighbouring hexane molecules. ...
... hexane has more surface area for interacting with neighbouring hexane molecules. C) hexane has hydrogen bonding. D) hexane has less surface area for interacting with neighbouring hexane molecules. ...
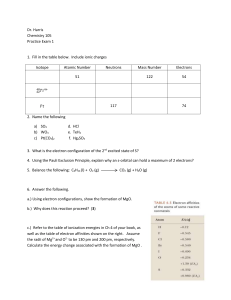
Dr. Harris Chemistry 105 Practice Exam 1 Isotope Atomic Number
... Why do atoms exhibit discontinuous (line) spectra when they emit light? Why can’t an atom emit any wavelength of light? ...
... Why do atoms exhibit discontinuous (line) spectra when they emit light? Why can’t an atom emit any wavelength of light? ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.