Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... Never change a subscript to balance an equation (You can only change coefficients) – If you change the subscript (formula) you are describing a different chemical. – H2O is a different compound than H2O2 Never put a coefficient in the middle of a formula; they must go only in the front ...
... Never change a subscript to balance an equation (You can only change coefficients) – If you change the subscript (formula) you are describing a different chemical. – H2O is a different compound than H2O2 Never put a coefficient in the middle of a formula; they must go only in the front ...
What You Need to Know to Pass the Chemistry
... Polar substances are dissolved only by another polar substance. Non-polar substances are dissolved only by other non-polar substances, “like dissolves like”. 4. Chemical bonds are formed when valence electrons are: Transferred from one atom to another – ionic. Shared between atoms – covalent. ...
... Polar substances are dissolved only by another polar substance. Non-polar substances are dissolved only by other non-polar substances, “like dissolves like”. 4. Chemical bonds are formed when valence electrons are: Transferred from one atom to another – ionic. Shared between atoms – covalent. ...
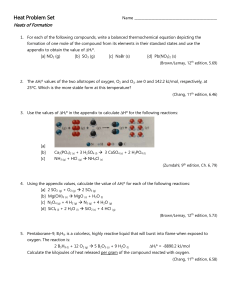
Heats of Formation WS
... Heats of Formation 1. For each of the following compounds, write a balanced thermochemical equation depicting the formation of one mole of the compound from its elements in their standard states and use the appendix to obtain the value of ∆Hfº. [a] NO2 (g) ...
... Heats of Formation 1. For each of the following compounds, write a balanced thermochemical equation depicting the formation of one mole of the compound from its elements in their standard states and use the appendix to obtain the value of ∆Hfº. [a] NO2 (g) ...
Chapter 3
... – how much reactant is consumed and how much product is formed – coefficients must be consistent with the Law of Conservation of Mass; atoms are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. – i.e. chemical equation must be balanced ...
... – how much reactant is consumed and how much product is formed – coefficients must be consistent with the Law of Conservation of Mass; atoms are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. – i.e. chemical equation must be balanced ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... Never change a subscript to balance an equation (You can only change coefficients) – If you change the subscript (formula) you are describing a different chemical. – H2O is a different compound than H2O2 Never put a coefficient in the middle of a formula; they must go only in the front ...
... Never change a subscript to balance an equation (You can only change coefficients) – If you change the subscript (formula) you are describing a different chemical. – H2O is a different compound than H2O2 Never put a coefficient in the middle of a formula; they must go only in the front ...
AP Chemistry Chapter 16
... 16.7 The Dependence of Free Energy on Pressure -summary of affects: entropy large volume > entropy of small volume entropy low pressure > entropy high pressure -this section deals with free energy at non-standard conditions -entropy affected by pressure -more positions are possible at lower pressure ...
... 16.7 The Dependence of Free Energy on Pressure -summary of affects: entropy large volume > entropy of small volume entropy low pressure > entropy high pressure -this section deals with free energy at non-standard conditions -entropy affected by pressure -more positions are possible at lower pressure ...
Hydrothermal Reactions from Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate to Phenol
... that the yield of phenol dramatically increases. This experiment confirms our mechanisms and may also provide industrial possibilities. Our study on the hydrothermal reactions from sodium hydrogen carbonate to phenol makes it possible to form prebiotic organic molecules based on carbonate under mild ...
... that the yield of phenol dramatically increases. This experiment confirms our mechanisms and may also provide industrial possibilities. Our study on the hydrothermal reactions from sodium hydrogen carbonate to phenol makes it possible to form prebiotic organic molecules based on carbonate under mild ...
Chapter 6
... • If the reaction is performed in a rigid container, there may be a change in pressure, but if there is no change in volume, the atmosphere outside the container didn’t “move” and without movement, no work is done by or on the system. • If there is no change in volume (V= 0), then no work is done by ...
... • If the reaction is performed in a rigid container, there may be a change in pressure, but if there is no change in volume, the atmosphere outside the container didn’t “move” and without movement, no work is done by or on the system. • If there is no change in volume (V= 0), then no work is done by ...
A) 0% B) 20% C) 50% D) 80% E) 100% 1. Naturally occurring boron
... 62. Hydrogen gas is collected over water at 29 oC. The total pressure of the system is 773 torr. If the vapor pressure of water at 29 oC is 30 torr, what is the partial pressure 67. Under which conditions does a real gas most closely of the hydrogen gas? approximate an ideal gas? A) 803 torr C) 74 ...
... 62. Hydrogen gas is collected over water at 29 oC. The total pressure of the system is 773 torr. If the vapor pressure of water at 29 oC is 30 torr, what is the partial pressure 67. Under which conditions does a real gas most closely of the hydrogen gas? approximate an ideal gas? A) 803 torr C) 74 ...
Using mass to calculate molecular formula
... on the positive ions (cations) as there are on the negative ions (anions) and this determines the formula for that compound. Example: Sodium chloride, NaCl, 'table salt' ...
... on the positive ions (cations) as there are on the negative ions (anions) and this determines the formula for that compound. Example: Sodium chloride, NaCl, 'table salt' ...
Chapter 3: Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... colligative property, freezing point depression, boiling point elevation Essential Questions and Content: Describe the colligative properties of a solution. Calculate the freezing point depression or boiling point elevation of a solution. ...
... colligative property, freezing point depression, boiling point elevation Essential Questions and Content: Describe the colligative properties of a solution. Calculate the freezing point depression or boiling point elevation of a solution. ...
Energy and Chemical Reactions
... exhaust of our cars. Which has higher energy, (1) a NO2 molecule moving at 439 m/s or (2) the same NO2 molecule moving at 399 m/s. (These are the average velocities of NO2 molecules at 80 °C and 20 °C.) c. Which has higher energy, (1) a nitrogen monoxide molecule, NO, moving out your car’s tailpipe ...
... exhaust of our cars. Which has higher energy, (1) a NO2 molecule moving at 439 m/s or (2) the same NO2 molecule moving at 399 m/s. (These are the average velocities of NO2 molecules at 80 °C and 20 °C.) c. Which has higher energy, (1) a nitrogen monoxide molecule, NO, moving out your car’s tailpipe ...
HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY MINI-MOCK UNIT 2
... Electrolysis can be used to remove unwanted hair from the skin. The hair is first coated with a layer of gel containing ions in solution. The positive electrode is connected by a patch to the skin.The negative electrode is connected to the hair. Electricity flows through the gel and causes electroly ...
... Electrolysis can be used to remove unwanted hair from the skin. The hair is first coated with a layer of gel containing ions in solution. The positive electrode is connected by a patch to the skin.The negative electrode is connected to the hair. Electricity flows through the gel and causes electroly ...
g - Valencia College
... a negative sign (loss of energy). (-DE or - DH) • Energy flow from the surroundings to the system has ...
... a negative sign (loss of energy). (-DE or - DH) • Energy flow from the surroundings to the system has ...
ppt - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Direction of Change in Reactions: Reaction Quotient (Q) ...
... Direction of Change in Reactions: Reaction Quotient (Q) ...
Fall 2012
... 45. (6 pts each) Draw the Lewis structures, including any resonance structures, for: C2F2Cl2 and SiO3 -2 46. (1 pt each blank) Fill in the blanks for each Lewis structure. F ...
... 45. (6 pts each) Draw the Lewis structures, including any resonance structures, for: C2F2Cl2 and SiO3 -2 46. (1 pt each blank) Fill in the blanks for each Lewis structure. F ...
Honors Chemistry I
... m. The combustion of ethanol (C2H5OH) in the presence of oxygen gas forms carbon dioxide and water vapor. n. Solid zinc metal reacts with aqueous hydrogen chloride to form aqueous zinc chloride and hydrogen gas. o. Aqueous strontium hydroxide reacts with aqueous hydrogen bromide (aka “hydrobromic ac ...
... m. The combustion of ethanol (C2H5OH) in the presence of oxygen gas forms carbon dioxide and water vapor. n. Solid zinc metal reacts with aqueous hydrogen chloride to form aqueous zinc chloride and hydrogen gas. o. Aqueous strontium hydroxide reacts with aqueous hydrogen bromide (aka “hydrobromic ac ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... questions on this separate answer sheet. Record your answers for the questions in Part B–2 and Part C in your separate answer booklet. Be sure to fill in the heading on the front of your answer booklet. All answers in your answer booklet should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, whic ...
... questions on this separate answer sheet. Record your answers for the questions in Part B–2 and Part C in your separate answer booklet. Be sure to fill in the heading on the front of your answer booklet. All answers in your answer booklet should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, whic ...
Notes for Matter Packet- Balancing equations (PDF
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.