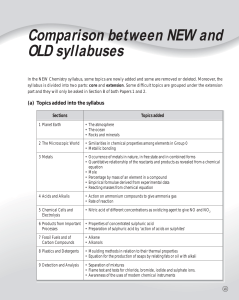
Unit 2 Summary - A
... 10 g of propan-1-ol was oxidised under reflux and 8.5 g of propanoic acid was made. What was the percentage yield in this reaction? ...
... 10 g of propan-1-ol was oxidised under reflux and 8.5 g of propanoic acid was made. What was the percentage yield in this reaction? ...
View
... Develop a model to illustrate that the release or absorption of energy from a chemical reaction system depends upon the changes in total bond energy. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on the idea that a chemical reaction is a system that affects the energy change. Examples of models could includ ...
... Develop a model to illustrate that the release or absorption of energy from a chemical reaction system depends upon the changes in total bond energy. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on the idea that a chemical reaction is a system that affects the energy change. Examples of models could includ ...
Determination of the Molar Volume of H2(g) and of O2(g)
... For an atomic compound such as He or K or Fe, 1.00 mol contains 6.02 x 1023 ___________________________________. For a molecular compound such as H2O, 1.00 mol H2O contains 6.02 x 1023 ______________________________ . For an ionic compound such as NaCl, 1.00 mol NaCl contains 6.02 x 1023 ___________ ...
... For an atomic compound such as He or K or Fe, 1.00 mol contains 6.02 x 1023 ___________________________________. For a molecular compound such as H2O, 1.00 mol H2O contains 6.02 x 1023 ______________________________ . For an ionic compound such as NaCl, 1.00 mol NaCl contains 6.02 x 1023 ___________ ...
Chapter 5
... have a slightly distorted square-planar geometry, in which the allyl ligand coordinates in a π manner and occupies two coordination sites. We postulate that 1 and 2 might be the π-allyl complexes formed at an early stage of the reaction. The energy required to obtain these complexes is not low, but ...
... have a slightly distorted square-planar geometry, in which the allyl ligand coordinates in a π manner and occupies two coordination sites. We postulate that 1 and 2 might be the π-allyl complexes formed at an early stage of the reaction. The energy required to obtain these complexes is not low, but ...
Carefully detach the last page. It is the Data Sheet.
... Which of the following statements accounts for the water of hydration. The remaining solid weighed observation that the molar volume of C2H6(g) is smaller ...
... Which of the following statements accounts for the water of hydration. The remaining solid weighed observation that the molar volume of C2H6(g) is smaller ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... Heat is added to a 200.-gram sample of H2O(s) to melt the sample at 0°C. Then the resulting H2O(ℓ) is heated to a final temperature of 65°C. 59 Determine the total amount of heat required to completely melt the sample. [1] 60 In the space in your answer booklet, show a numerical setup for calculatin ...
... Heat is added to a 200.-gram sample of H2O(s) to melt the sample at 0°C. Then the resulting H2O(ℓ) is heated to a final temperature of 65°C. 59 Determine the total amount of heat required to completely melt the sample. [1] 60 In the space in your answer booklet, show a numerical setup for calculatin ...
3 - Rates
... reaction as fast or slow. H2(g) + O2(g) ----> H2O (g) fast Fe + 1/2O2 + H2O ---> Fe(OH)2 slow Quantitatively rates are expressed by observing the rate at which a reactant disappears or a product appears. ...
... reaction as fast or slow. H2(g) + O2(g) ----> H2O (g) fast Fe + 1/2O2 + H2O ---> Fe(OH)2 slow Quantitatively rates are expressed by observing the rate at which a reactant disappears or a product appears. ...
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY LECTURE NOTES
... Is concerned with the determination of amounts of different constituents present in a system.(usually the given material is first analysed qualitatively and this is followed by quantitative analysis). Quantitative analysis methods: 1. Gravimetric methods determine the mass of the analyte. 2. Volumet ...
... Is concerned with the determination of amounts of different constituents present in a system.(usually the given material is first analysed qualitatively and this is followed by quantitative analysis). Quantitative analysis methods: 1. Gravimetric methods determine the mass of the analyte. 2. Volumet ...
01.CN_Other pages/p1-9
... – Conclusions are made that water and air (oxygen) are both essential conditions for the formation of rust. And that rusting is a slow chemical reaction. ...
... – Conclusions are made that water and air (oxygen) are both essential conditions for the formation of rust. And that rusting is a slow chemical reaction. ...
homework assignment 2 - the Petersen Home Page
... 1. A 15.40-g sample of a finely-divided mixture of only Fe2S3 and FeS was reacted with excess H2 at elevated temperatures. If the weight percent of Fe2S3 in this mixture is 57.4%, then calculate the total mass in grams of Fe that can be produced. Assume the only other product of these reactions is H ...
... 1. A 15.40-g sample of a finely-divided mixture of only Fe2S3 and FeS was reacted with excess H2 at elevated temperatures. If the weight percent of Fe2S3 in this mixture is 57.4%, then calculate the total mass in grams of Fe that can be produced. Assume the only other product of these reactions is H ...
Balancing Chemical Equations
... • Describe a chemical reaction by using a word equation and a formula equation. • Relate the conservation of mass to the rearrangement of atoms in a chemical reaction • Write and interpret a balanced chemical equation for a reaction, and relate conservation of mass to the balanced equation ...
... • Describe a chemical reaction by using a word equation and a formula equation. • Relate the conservation of mass to the rearrangement of atoms in a chemical reaction • Write and interpret a balanced chemical equation for a reaction, and relate conservation of mass to the balanced equation ...
Oregon State University, Summer 2009 Chemistry 121 Midterm
... This exam consists of 20 multiple-choice questions. Each multiple-choice question has 5 points associated with it. Select the best answer by filling in the corresponding circle on the rear page of the answer sheet. If you have any questions before the exam, please ask. If you have any questions duri ...
... This exam consists of 20 multiple-choice questions. Each multiple-choice question has 5 points associated with it. Select the best answer by filling in the corresponding circle on the rear page of the answer sheet. If you have any questions before the exam, please ask. If you have any questions duri ...
9791/02 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL
... Using the molecular orbital diagram or otherwise, give the bond order in these species. Bond order in P22+ = .......... ...
... Using the molecular orbital diagram or otherwise, give the bond order in these species. Bond order in P22+ = .......... ...
Every reaction is reversible: A chemical reaction is in equilibrium
... This particular equilibrium constant, K, is known as the Partition Coefficient. It depends on the two immiscible liquids involved, the solute and the temperature. Iodine is much more soluble in Methylbenzene than in Water. The value of the partition coefficient is quite high. Solvent extraction is a ...
... This particular equilibrium constant, K, is known as the Partition Coefficient. It depends on the two immiscible liquids involved, the solute and the temperature. Iodine is much more soluble in Methylbenzene than in Water. The value of the partition coefficient is quite high. Solvent extraction is a ...
Grade 11 Unit 6 - Amazon Web Services
... of the other three. Every chemical reaction involves energy in some form, because all chemical reactions involve either the breaking of old bonds or the forming of new bonds or both. We know that every chemical bond contains energy or it would not exist. This result means that every chemical Do this ...
... of the other three. Every chemical reaction involves energy in some form, because all chemical reactions involve either the breaking of old bonds or the forming of new bonds or both. We know that every chemical bond contains energy or it would not exist. This result means that every chemical Do this ...
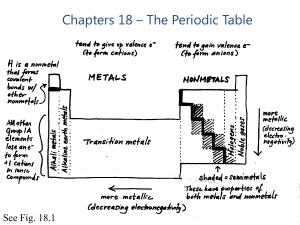
Chapters 18 – The Periodic Table
... H2 (g); H2 molecules dissociate at the metal surface and H atoms occupy holes in the crystal structure (potential use as a portable fuel) ...
... H2 (g); H2 molecules dissociate at the metal surface and H atoms occupy holes in the crystal structure (potential use as a portable fuel) ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... step 1 is the slowest overall step 2 is the slowest overall step 3 is the slowest overall ...
... step 1 is the slowest overall step 2 is the slowest overall step 3 is the slowest overall ...
CHAP 1 - NCERT books
... equal. This equation is now balanced. This method of balancing chemical equations is called hit-and-trial method as we make trials to balance the equation by using the smallest whole number coefficient. Step VII: Writing Symbols of Physical States Carefully examine the above balanced Eq. (1.9). Does ...
... equal. This equation is now balanced. This method of balancing chemical equations is called hit-and-trial method as we make trials to balance the equation by using the smallest whole number coefficient. Step VII: Writing Symbols of Physical States Carefully examine the above balanced Eq. (1.9). Does ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.