AP Chemistry Summer Assignment Summer 2015 Ms. Osquist
... • Determine if an element is a metal or nonmetal and the charge of its most common ion (for A-group elements) using the periodic table. • Write the formula of an ionic compound given its name (including polyatomic ions). • Explain how a cation or anion would form from a neutral atom. • Identify the ...
... • Determine if an element is a metal or nonmetal and the charge of its most common ion (for A-group elements) using the periodic table. • Write the formula of an ionic compound given its name (including polyatomic ions). • Explain how a cation or anion would form from a neutral atom. • Identify the ...
avogadro exam 2012 - University of Waterloo
... 25 A 1.0 L sample of N2(g) has a pressure of exactly 100 kPa. A 2.0 L sample of O2(g) has a pressure of 50 kPa at the same temperature. The samples are mixed and forced into a 1.0 L container. Assuming that no reaction occurs and that the temperature remains constant, what is the final pressure of t ...
... 25 A 1.0 L sample of N2(g) has a pressure of exactly 100 kPa. A 2.0 L sample of O2(g) has a pressure of 50 kPa at the same temperature. The samples are mixed and forced into a 1.0 L container. Assuming that no reaction occurs and that the temperature remains constant, what is the final pressure of t ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... summer packet during the first week of school. You can expect a quiz in naming compounds, identifying ions the first day of school. Based on prior knowledge I can tell you that kids are not coming prepared with the material even though the assignment is completed. Make sure just completing assignmen ...
... summer packet during the first week of school. You can expect a quiz in naming compounds, identifying ions the first day of school. Based on prior knowledge I can tell you that kids are not coming prepared with the material even though the assignment is completed. Make sure just completing assignmen ...
5.1 questions - DrBravoChemistry
... Calculate the standard enthalpy change and the standard entropy change for this reaction. Standard enthalpy change ........................................................................... ...
... Calculate the standard enthalpy change and the standard entropy change for this reaction. Standard enthalpy change ........................................................................... ...
ANSWER KEY Chemistry CPA Final Exam Study Guide Final Exam
... 38. What is the kinetic molecular theory? Gas particles are always in constant, random motion. The higher the temperature, the higher the kinetic energy. Gas particles collide with one another in perfectly elastic collisions. As temp and KE increase, so do collisions, which raises the pressure withi ...
... 38. What is the kinetic molecular theory? Gas particles are always in constant, random motion. The higher the temperature, the higher the kinetic energy. Gas particles collide with one another in perfectly elastic collisions. As temp and KE increase, so do collisions, which raises the pressure withi ...
Dr David`s Chemistry Revision Themes
... (f) would you expect the first ionisation energy of rubidium to be greater than or less than that of potassium. Explain. Less than. The atomic radius of Rb is larger than that of K. The outer electron of Rb is further from the nucleus. It is held less strongly and therefore easier to remove. ...
... (f) would you expect the first ionisation energy of rubidium to be greater than or less than that of potassium. Explain. Less than. The atomic radius of Rb is larger than that of K. The outer electron of Rb is further from the nucleus. It is held less strongly and therefore easier to remove. ...
Unit 2 Chemical Reactions
... Acetylene gas is a fuel used in welding torches, and it combines with oxygen to produce a very hot flame. Because it is an organic compound, it contains carbon. When it burns in pure oxygen, it should produce carbon dioxide. This gas is the product of complete combustion. If there is not enough oxyg ...
... Acetylene gas is a fuel used in welding torches, and it combines with oxygen to produce a very hot flame. Because it is an organic compound, it contains carbon. When it burns in pure oxygen, it should produce carbon dioxide. This gas is the product of complete combustion. If there is not enough oxyg ...
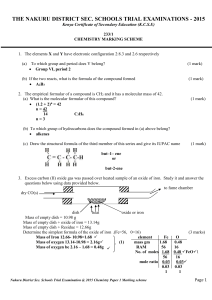
the nakuru district sec. schools trial examinations - 2015
... With reasons, select a substance (a) With an eletrodent bond C 1 has high m.p and B.P and only conducts electricity in molten state. 1 ...
... With reasons, select a substance (a) With an eletrodent bond C 1 has high m.p and B.P and only conducts electricity in molten state. 1 ...
green chemistry - Catalysis Eprints database
... the molecular scale and is an extremely important area of Chemistry due to the importance of Chemistry in our world today and the implications it can show on our environment. • The Green Chemistry program supports the invention of more environmentally friendly chemical processes which reduce or even ...
... the molecular scale and is an extremely important area of Chemistry due to the importance of Chemistry in our world today and the implications it can show on our environment. • The Green Chemistry program supports the invention of more environmentally friendly chemical processes which reduce or even ...
PART 2 – CHEMISTRY
... where the atom has more than one shell, then the atom is said to be stable. This means that the atom does not react with any other kind of atom and thus remains isolated and inert. For example, this is so in the case of the rare gases, argon, neon, helium etc. meaning that they cannot form compounds ...
... where the atom has more than one shell, then the atom is said to be stable. This means that the atom does not react with any other kind of atom and thus remains isolated and inert. For example, this is so in the case of the rare gases, argon, neon, helium etc. meaning that they cannot form compounds ...
chapter 21 chemistry of the main-group elements i
... bond them together. To bond these four atoms into a chain requires three electron pairs. Since each electron pair in a bridging bond replaces two “normal” bonds, there must be at least two bridging bonds in the B4 H10 molecules. By analogy with B2 H 6 , we might write the structure below left. But t ...
... bond them together. To bond these four atoms into a chain requires three electron pairs. Since each electron pair in a bridging bond replaces two “normal” bonds, there must be at least two bridging bonds in the B4 H10 molecules. By analogy with B2 H 6 , we might write the structure below left. But t ...
Ionic Equations
... Small Intro to Redox (MUCH more on this later!) • A reaction in which electrons are transferred from one atom to another is called an ____________________ reaction. ...
... Small Intro to Redox (MUCH more on this later!) • A reaction in which electrons are transferred from one atom to another is called an ____________________ reaction. ...
Reaction of amino acids with exo-3,6-epoxy-1,2,3,6
... When an aqueous solution of glycine and the anhydride 2 was heated and subsequently evaporated by azeotropic distillation of toluene as described by Ondruš et al., we obtained material which corresponded with that reported by them.6 However, upon attempted crystallization from chloroform, as previou ...
... When an aqueous solution of glycine and the anhydride 2 was heated and subsequently evaporated by azeotropic distillation of toluene as described by Ondruš et al., we obtained material which corresponded with that reported by them.6 However, upon attempted crystallization from chloroform, as previou ...
thermodynamics
... 27. Given that ∆H = 0 for mixing of two gases. Explain whether the diffusion of these gases into each other in a closed container is a spontaneous process or not? 28. Heat has randomising influence on a system and temperature is the measure of average chaotic motion of particles in the system. Write ...
... 27. Given that ∆H = 0 for mixing of two gases. Explain whether the diffusion of these gases into each other in a closed container is a spontaneous process or not? 28. Heat has randomising influence on a system and temperature is the measure of average chaotic motion of particles in the system. Write ...
Electrochemistry
... Review: What’s the oxidizing agent? the reducing agent? What’s E° for the reverse reaction? ...
... Review: What’s the oxidizing agent? the reducing agent? What’s E° for the reverse reaction? ...
Table of contents
... ▪ As you move down a group, atomic radius increases. This is because the number of energy levels increase as you move down a group. Each subsequent energy level is further from the nucleus than the last. ▪ As you move across a period, atomic radius decreases. As you go across a period, electrons are ...
... ▪ As you move down a group, atomic radius increases. This is because the number of energy levels increase as you move down a group. Each subsequent energy level is further from the nucleus than the last. ▪ As you move across a period, atomic radius decreases. As you go across a period, electrons are ...
1 [Turn Over Section A For each question there are four possible
... When iron filings are added to nitric acid, a yellow solution and nitrogen dioxide gas are formed. On the addition of ammonium thiocyanate to the resultant solution, a bloodred colouration due to an iron (III) complex is formed. Which statements are correct? ...
... When iron filings are added to nitric acid, a yellow solution and nitrogen dioxide gas are formed. On the addition of ammonium thiocyanate to the resultant solution, a bloodred colouration due to an iron (III) complex is formed. Which statements are correct? ...
Progression of Learning in Secondary School Chemistry Secondary
... Associates a characteristic property of a substance or material with its use (e.g. metal is used to make pots because it is a good conductor of heat) Physical Changes Recognizes different physical changes Molecule Describes a molecule using Dalton's atomic model (combination of atoms linked by chemi ...
... Associates a characteristic property of a substance or material with its use (e.g. metal is used to make pots because it is a good conductor of heat) Physical Changes Recognizes different physical changes Molecule Describes a molecule using Dalton's atomic model (combination of atoms linked by chemi ...
Various Types of RXNS
... NOTE: Not all of the following chemical reactions are balanced. They have been intentionally left unbalanced for your practice. ...
... NOTE: Not all of the following chemical reactions are balanced. They have been intentionally left unbalanced for your practice. ...
Stoichiometry - VernonScienceLSA
... In these types of calculations, the reactant that it present in lesser amount is called the LIMITING REACTANT. Since the limiting reactant gets completely used up first, it sets the limit on the amount of product that can be formed and the amount of the excess reactant used in the reaction. LIMITING ...
... In these types of calculations, the reactant that it present in lesser amount is called the LIMITING REACTANT. Since the limiting reactant gets completely used up first, it sets the limit on the amount of product that can be formed and the amount of the excess reactant used in the reaction. LIMITING ...
Summary of 5.4
... 5.4.1d Practicals with electrophilic substitution 5.4.1d carry out the reactions in 5.4.1b where appropriate (using methylbenzene or methoxybenzene) 5.4.1e Reactions of phenol carry out the reaction of phenol with bromine water and dilute nitric acid and use these results to illustrate the activatio ...
... 5.4.1d Practicals with electrophilic substitution 5.4.1d carry out the reactions in 5.4.1b where appropriate (using methylbenzene or methoxybenzene) 5.4.1e Reactions of phenol carry out the reaction of phenol with bromine water and dilute nitric acid and use these results to illustrate the activatio ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.