RMTF - The Greeks - Society of Actuaries
... The concept of using partial derivatives in pricing and hedging options and other financial instruments is well known and mathematically correct. It is necessary to evaluate some of these derivatives to understand the risk in a portfolio. However, the partial derivatives of option prices depend on t ...
... The concept of using partial derivatives in pricing and hedging options and other financial instruments is well known and mathematically correct. It is necessary to evaluate some of these derivatives to understand the risk in a portfolio. However, the partial derivatives of option prices depend on t ...
Title goes here This is a sample subtitle
... • Allows for “stochastic” (nondeterministic) analysis using multiple variables and randomly generated “real world” trials ...
... • Allows for “stochastic” (nondeterministic) analysis using multiple variables and randomly generated “real world” trials ...
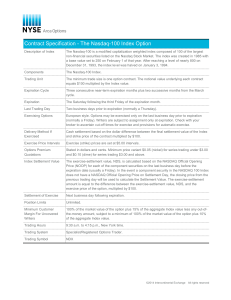
Options Contract Mechanics, Canola Futures
... Part of an option contract’s value is tied to volatility in the underlying futures market. The wider futures prices swing from day to day, the higher the likelihood of an option moving into-the-money before the contract expires. An option’s volatility value is measured by its ‘delta’, which is calc ...
... Part of an option contract’s value is tied to volatility in the underlying futures market. The wider futures prices swing from day to day, the higher the likelihood of an option moving into-the-money before the contract expires. An option’s volatility value is measured by its ‘delta’, which is calc ...
Valuing Stock Options: The Black
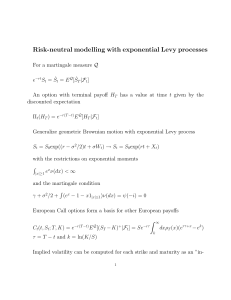
... • The implied volatility of an option is the volatility for which the Black-Scholes price equals the market price • The is a one-to-one correspondence between prices and implied volatilities • Traders and brokers often quote implied volatilities rather than dollar prices ...
... • The implied volatility of an option is the volatility for which the Black-Scholes price equals the market price • The is a one-to-one correspondence between prices and implied volatilities • Traders and brokers often quote implied volatilities rather than dollar prices ...