Alkenes Group
... • Because they have a double bond, they are called unsaturated. (Alkanes have no double bonds, so are saturated) • They are much more reactive than alkanes C2H4 + H2 ---C3H6 The hydrogen just add on, so this is called an addition reaction • Alkenes also do an addition reaction with steam, to form c ...
... • Because they have a double bond, they are called unsaturated. (Alkanes have no double bonds, so are saturated) • They are much more reactive than alkanes C2H4 + H2 ---C3H6 The hydrogen just add on, so this is called an addition reaction • Alkenes also do an addition reaction with steam, to form c ...
IR Lecture
... n = wavenumbers. Larger n = higher energy Excitation depends on atomic mass and how tightly they are bound a) Hooke’s Law for 2 masses connected by a spring ...
... n = wavenumbers. Larger n = higher energy Excitation depends on atomic mass and how tightly they are bound a) Hooke’s Law for 2 masses connected by a spring ...
Chapter 11 - Geobiology
... Volcanoes release hydrogen sulfide gas. Tectonic processes uplift rocks, and weathering breaks down sulfurbearing minerals. ...
... Volcanoes release hydrogen sulfide gas. Tectonic processes uplift rocks, and weathering breaks down sulfurbearing minerals. ...
5.2 REACTIONS OF THE CARBONYL GROUPv2
... CN¯ acts as a nucleophile and attacks the slightly positive C One of the C=O bonds breaks; a pair of electrons goes onto the O ...
... CN¯ acts as a nucleophile and attacks the slightly positive C One of the C=O bonds breaks; a pair of electrons goes onto the O ...
Topic 3 – Chemical Structure and Bonding
... The rules for naming organic compounds were devised by IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry). They are as follows. 1) The functional group gives the ending of the name e.g. –ol for an alcohol 2) The number of carbons gives the first part of the name e.g. prop- or propan- for 3 ca ...
... The rules for naming organic compounds were devised by IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry). They are as follows. 1) The functional group gives the ending of the name e.g. –ol for an alcohol 2) The number of carbons gives the first part of the name e.g. prop- or propan- for 3 ca ...
ch15 lecture 7e
... • An addition reaction results in more atoms bonded to C. • An elimination reaction results in fewer atoms bonded to C. • If there are the same number of atoms bonded to C, the reaction is a substitution. ...
... • An addition reaction results in more atoms bonded to C. • An elimination reaction results in fewer atoms bonded to C. • If there are the same number of atoms bonded to C, the reaction is a substitution. ...
Naming Ethers Naming Ethers
... • Thiols are known for their unpleasant odor. • Skunks use thiols as a defense mechanism: (E)-2butene-1-thiol, 3-methyl-1-butanethiol, and 2quinolinemethanethiol, and acetate thioesters of these. • Methanethiol is added to natural gas (methane) so that gas leaks can be detected. • The hydrosulfi ...
... • Thiols are known for their unpleasant odor. • Skunks use thiols as a defense mechanism: (E)-2butene-1-thiol, 3-methyl-1-butanethiol, and 2quinolinemethanethiol, and acetate thioesters of these. • Methanethiol is added to natural gas (methane) so that gas leaks can be detected. • The hydrosulfi ...
chap 4 org chem
... Carbon Will readily bond with itself (C) with – or = bonds (single, double or even triple) Also bonds with H – O = N, P, & S Forms long chains or backbones of organic molecules Carbon will always have four lines connecting to other atoms. ...
... Carbon Will readily bond with itself (C) with – or = bonds (single, double or even triple) Also bonds with H – O = N, P, & S Forms long chains or backbones of organic molecules Carbon will always have four lines connecting to other atoms. ...
The carbonyl group
... causes the B.P of aldehydes and ketones to be higher than similar molecular weight alkanes and others but lower than alcohols which are held together by H-bonds. Aldehyde < Alcohols > Alkane ...
... causes the B.P of aldehydes and ketones to be higher than similar molecular weight alkanes and others but lower than alcohols which are held together by H-bonds. Aldehyde < Alcohols > Alkane ...
OCR Chemistry A Basic concepts of organic chemistry Specification
... Can you explain the term structural isomers (compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulae) and determine possible structural formulae of an organic molecule, given its molecular formula? ...
... Can you explain the term structural isomers (compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulae) and determine possible structural formulae of an organic molecule, given its molecular formula? ...
Chapter 9
... • The _______ main fossil fuel, also formed from the remains of marine organisms. • Often known as _____oil, is pumped from deep beneath Earth’s ________. • It must be separated into simpler mixtures, or fractions, such as _______ and heating ______. ...
... • The _______ main fossil fuel, also formed from the remains of marine organisms. • Often known as _____oil, is pumped from deep beneath Earth’s ________. • It must be separated into simpler mixtures, or fractions, such as _______ and heating ______. ...
Fall Exam 4 - Chemistry - University of Kentucky
... When gaseous ethane (C2H6) is reacted with gaseous oxygen to form carbon monoxide gas and water vapor in the reaction below, what is the coefficient on CO when the reaction is properly balanced? C2H6 (g) + O2 (g) → CO (g) + H2O (g) ...
... When gaseous ethane (C2H6) is reacted with gaseous oxygen to form carbon monoxide gas and water vapor in the reaction below, what is the coefficient on CO when the reaction is properly balanced? C2H6 (g) + O2 (g) → CO (g) + H2O (g) ...
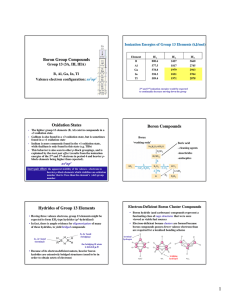
Boron Group Compounds Oxidation States Boron
... • How does this trend agree with electronegativities of X? • In the trigonal planar BX3 structure, π-bonding exists, most X X important for smaller elements B Rem: correct Lewis F F B structure shows all bonds and electrons F ...
... • How does this trend agree with electronegativities of X? • In the trigonal planar BX3 structure, π-bonding exists, most X X important for smaller elements B Rem: correct Lewis F F B structure shows all bonds and electrons F ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Notes Sheet
... In an alkyl halide, one of the hydrogen atoms in an alkane has been replaced by a halogen. – What are halogens again? Alkyl halides are easy to name; – name of the alkane is preceded by the number of the carbon on which the halogen is substituted and the name of the halogen, – modified so that -ine ...
... In an alkyl halide, one of the hydrogen atoms in an alkane has been replaced by a halogen. – What are halogens again? Alkyl halides are easy to name; – name of the alkane is preceded by the number of the carbon on which the halogen is substituted and the name of the halogen, – modified so that -ine ...
Organic Lab
... the ring. Benzene exhibits the phenomenon of resonance; that is, the structure of benzene shown, as well as any other structure that might be drawn on paper, does not really represent the true electronic structure of benzene. The electrons of the “double bonds” of the benzene are, in fact, delocaliz ...
... the ring. Benzene exhibits the phenomenon of resonance; that is, the structure of benzene shown, as well as any other structure that might be drawn on paper, does not really represent the true electronic structure of benzene. The electrons of the “double bonds” of the benzene are, in fact, delocaliz ...
Unit 2
... b) When liquid phosphorus trichloride is added to water it reacts to form phosphous acid (sometimes called phosphorous acid) and hydrochloric acid. ...
... b) When liquid phosphorus trichloride is added to water it reacts to form phosphous acid (sometimes called phosphorous acid) and hydrochloric acid. ...
Unit 2
... b) When liquid phosphorus trichloride is added to water it reacts to form phosphous acid (sometimes called phosphorous acid) and hydrochloric acid. ...
... b) When liquid phosphorus trichloride is added to water it reacts to form phosphous acid (sometimes called phosphorous acid) and hydrochloric acid. ...
Chemical Bonds
... same rate that is it coming out of solution. You know the solution is a. An electrolyte b. A nonelectrolyte c. A buffered solution d. A saturated solution 20. As the temperature of water decreases, the solubility of CO2 in water a. Increases b. Decreases c. Remains the same d. Increases then decreas ...
... same rate that is it coming out of solution. You know the solution is a. An electrolyte b. A nonelectrolyte c. A buffered solution d. A saturated solution 20. As the temperature of water decreases, the solubility of CO2 in water a. Increases b. Decreases c. Remains the same d. Increases then decreas ...
Lesson 1 - Working With Chemicals
... - Consist of two or more different atoms (covalently bonded) containing an overall charge. e.g. NO3- Found in the box at the top of the table. - All are negatively charged, except ammonium ion, and most names end in ‘ate’ - All act as non-metals except ammonium ion, NH4+, which acts as a metal in co ...
... - Consist of two or more different atoms (covalently bonded) containing an overall charge. e.g. NO3- Found in the box at the top of the table. - All are negatively charged, except ammonium ion, and most names end in ‘ate’ - All act as non-metals except ammonium ion, NH4+, which acts as a metal in co ...
N-METAL COMPOUNDS
... metals with the cyclopentadienyl anion. Other metals that form sandwichtype structures similar to ferrocene include nickel, titanium, cobalt, ruthenium, zirconium, and osmium. The stability of metallocenes varies greatly with the metal and its oxidation state; ferrocene, ruthenocene, and osmocene ar ...
... metals with the cyclopentadienyl anion. Other metals that form sandwichtype structures similar to ferrocene include nickel, titanium, cobalt, ruthenium, zirconium, and osmium. The stability of metallocenes varies greatly with the metal and its oxidation state; ferrocene, ruthenocene, and osmocene ar ...
Organosulfur compounds

Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin (pictured below) and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium and carbon–tellurium compounds, which is true to some extent.A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur compounds is the Carius halogen method.