Answers - logo Pre-U Chemistry Textbook
... Different molecules have different bond strengths for a particular type of bond that depend on its precise environment. For example, the O–H in water (H2O) is different from the O–H in methanol (CH3OH). Bond enthalpy data are averages for many molecules rather than the exact value for an individual ...
... Different molecules have different bond strengths for a particular type of bond that depend on its precise environment. For example, the O–H in water (H2O) is different from the O–H in methanol (CH3OH). Bond enthalpy data are averages for many molecules rather than the exact value for an individual ...
x - SharpSchool
... In a 500 mL stainless steel reaction vessel at 900C, carbon monoxide and water vapour react to produce carbon dioxide and hydrogen. Evidence indicates that this reaction establishes an equilibrium with only partial conversion of reactants to products. Initially, 2.00 mol of each reactant is placed ...
... In a 500 mL stainless steel reaction vessel at 900C, carbon monoxide and water vapour react to produce carbon dioxide and hydrogen. Evidence indicates that this reaction establishes an equilibrium with only partial conversion of reactants to products. Initially, 2.00 mol of each reactant is placed ...
Amines By
... The Amines are the organic chemistry relatives of ammonia However in amines one or more of the hydrogen atoms on the ammonia molecule are replaced by alkyl chains Amines with one alkyl group are primary amines, with two they are secondary, and with three they are tertiary amines. Like ammoni ...
... The Amines are the organic chemistry relatives of ammonia However in amines one or more of the hydrogen atoms on the ammonia molecule are replaced by alkyl chains Amines with one alkyl group are primary amines, with two they are secondary, and with three they are tertiary amines. Like ammoni ...
BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY
... For acids and the bases f = 1 / m (where m is the basidity of an acid or acidity of a base). For oxides and salts f = 1 / n x V (where n is the number of metallic atoms in the compound, and V is the valency of the metal). Number of equivalents: n = m / МE (for any substance); n = V / VE (for gaseous ...
... For acids and the bases f = 1 / m (where m is the basidity of an acid or acidity of a base). For oxides and salts f = 1 / n x V (where n is the number of metallic atoms in the compound, and V is the valency of the metal). Number of equivalents: n = m / МE (for any substance); n = V / VE (for gaseous ...
Chapter 14 Solutions
... • Remove the elements of H and OH from two adjacent C’s, and draw a double bond between these C’s in the product. • When two different alkenes are formed, the major product has more C’s bonded to the C=C. ...
... • Remove the elements of H and OH from two adjacent C’s, and draw a double bond between these C’s in the product. • When two different alkenes are formed, the major product has more C’s bonded to the C=C. ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and
... compound reacts with oxygen in the air to produce carbon dioxide & water. ...
... compound reacts with oxygen in the air to produce carbon dioxide & water. ...
REASONING QUESTIONS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. Explain. Ans: Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. This is due to more extensive association of carboxylic acid molecules through intermolecular hydrogen bonding. The hydrog ...
... even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. Explain. Ans: Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. This is due to more extensive association of carboxylic acid molecules through intermolecular hydrogen bonding. The hydrog ...
REASONING QUESTIONS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY TEXT
... even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. Explain. Ans: Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. This is due to more extensive association of carboxylic acid molecules through intermolecular hydrogen bonding. The hydrog ...
... even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. Explain. Ans: Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. This is due to more extensive association of carboxylic acid molecules through intermolecular hydrogen bonding. The hydrog ...
$doc.title
... Alcohols contain an OH group connected to a saturated C (sp3) They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to a carbon in a benzene ring Methanol, CH3OH ...
... Alcohols contain an OH group connected to a saturated C (sp3) They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to a carbon in a benzene ring Methanol, CH3OH ...
1 1411_chapter 6 exercises with answers CHEM 1411, chapter 6
... 29. Glycine, C2H5O2N, is important for biological energy. The combustion reaction of glycine is given by the equation 4C2H5O2N(s) + 9O2(g) 8CO2(g) + 10H2O(l) + 2N2(g) H°rxn = –3857 kJ/mol Given that H°f[CO2(g)] = –393.5 kJ/mol and H°f[H2O(l)] = –285.8 kJ/mol, calculate the enthalpy of formation ...
... 29. Glycine, C2H5O2N, is important for biological energy. The combustion reaction of glycine is given by the equation 4C2H5O2N(s) + 9O2(g) 8CO2(g) + 10H2O(l) + 2N2(g) H°rxn = –3857 kJ/mol Given that H°f[CO2(g)] = –393.5 kJ/mol and H°f[H2O(l)] = –285.8 kJ/mol, calculate the enthalpy of formation ...
PDF - mockies – Mockiesgateacademy
... order to the chemical world, and from then on chemists have never looked back. Modern society looks to chemists to produce, amongst many things, healing drugs, pesticides and fertilisers to ensure better crops and chemicals for the many synthetic materials produced in the twenty-first century. It al ...
... order to the chemical world, and from then on chemists have never looked back. Modern society looks to chemists to produce, amongst many things, healing drugs, pesticides and fertilisers to ensure better crops and chemicals for the many synthetic materials produced in the twenty-first century. It al ...
Alcohols
... Can be more or less acidic than phenol itself. Remember, the acidity of any alcohol is determined by the stability of the alkoxide or phenoxide anion produced. The more stable the anion produced the more acidic the alcohol An electron-withdrawing substituent makes a phenol more acidic by delocalizin ...
... Can be more or less acidic than phenol itself. Remember, the acidity of any alcohol is determined by the stability of the alkoxide or phenoxide anion produced. The more stable the anion produced the more acidic the alcohol An electron-withdrawing substituent makes a phenol more acidic by delocalizin ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... • One mole of atoms, ions, or molecules contains Avogadro’s number of those particles • One mole of molecules or formula units contains Avogadro’s number times the number of atoms or ions of each element in the compound Stoichiometry ...
... • One mole of atoms, ions, or molecules contains Avogadro’s number of those particles • One mole of molecules or formula units contains Avogadro’s number times the number of atoms or ions of each element in the compound Stoichiometry ...
Alcohols, Phenols , Phenols and Ethers Alcohols
... think of life without paper; no note-books, books, newspapers, currency notes, cheques, certificates, etc. The magazines carrying beautiful photographs and interesting stories would disappear from our life. It would have been really a different world. An alcohol contains one or more hydroxyl (OH) gr ...
... think of life without paper; no note-books, books, newspapers, currency notes, cheques, certificates, etc. The magazines carrying beautiful photographs and interesting stories would disappear from our life. It would have been really a different world. An alcohol contains one or more hydroxyl (OH) gr ...
CSEC Chemistry Revision Guide Answers.indd
... Chlorine is above bromine in group VII so it has a smaller atomic radius and the attractive pull of the positive nucleus on the electron to be gained is stronger in chlorine. As a result, chlorine has a greater strength of oxidising power and readily takes electrons from the Br– ions causing them to ...
... Chlorine is above bromine in group VII so it has a smaller atomic radius and the attractive pull of the positive nucleus on the electron to be gained is stronger in chlorine. As a result, chlorine has a greater strength of oxidising power and readily takes electrons from the Br– ions causing them to ...
Chemistry booklet
... What about the following PHOSPHO-GLYCERIDE molecule containing both hydrophilic ( water-loving) and hydro-phobic ( water-hating ) regions ( termed an amphi-philic molecule) ? ...
... What about the following PHOSPHO-GLYCERIDE molecule containing both hydrophilic ( water-loving) and hydro-phobic ( water-hating ) regions ( termed an amphi-philic molecule) ? ...
TOPIC 11 Further equilibrium 11.1 Chemical equilibrium
... Acidic. NH4NO3 is a salt of a strong acid (HNO3) and a weak base (NH3). Alkaline. CH3CH2COOK is a salt of a weak acid (CH3CH2COOH) and a strong base (KOH). Neutral. NaNO3 is a salt of a strong acid (HNO3) and a strong base (NaOH). ...
... Acidic. NH4NO3 is a salt of a strong acid (HNO3) and a weak base (NH3). Alkaline. CH3CH2COOK is a salt of a weak acid (CH3CH2COOH) and a strong base (KOH). Neutral. NaNO3 is a salt of a strong acid (HNO3) and a strong base (NaOH). ...
lab 15: hydrocarbons
... have partially negative or partially positive atoms there is minimal attraction between hydrocarbon molecules. Thus, hydrocarbons require less energy to evaporate or vaporize than do polar compounds. Small hydrocarbons require less energy to vaporize than large ones. They are highly volatile. ...
... have partially negative or partially positive atoms there is minimal attraction between hydrocarbon molecules. Thus, hydrocarbons require less energy to evaporate or vaporize than do polar compounds. Small hydrocarbons require less energy to vaporize than large ones. They are highly volatile. ...
Alcohols and Phenols
... alcohols (pKa ~ 16) due to resonance stabilization of the phenoxide ion Phenols react with NaOH solutions (but alcohols do not), forming soluble salts that are soluble in dilute aqueous A phenolic component can be separated from an organic solution by extraction into basic aqueous solution and i ...
... alcohols (pKa ~ 16) due to resonance stabilization of the phenoxide ion Phenols react with NaOH solutions (but alcohols do not), forming soluble salts that are soluble in dilute aqueous A phenolic component can be separated from an organic solution by extraction into basic aqueous solution and i ...
Module 5 Reactions with Miscellaneous Reagents
... Sons, Inc., L. A. Paquette, Ed., New York, 1995, 2, 1512. Major sources for the preparation of diazomethane are the basic hydrolysis of Nmethyl-N-nitrosocompounds (Scheme 1-3). ...
... Sons, Inc., L. A. Paquette, Ed., New York, 1995, 2, 1512. Major sources for the preparation of diazomethane are the basic hydrolysis of Nmethyl-N-nitrosocompounds (Scheme 1-3). ...
phenol
... for organic compounds, they are used frequently for organic reactions such as SN2 displacement reactions. The ОН group of alcohols can participate in the hydrogen bond network of water. The lower alcohols are completely soluble in water. As the hydrocarbon chain gets larger, the compound begins to l ...
... for organic compounds, they are used frequently for organic reactions such as SN2 displacement reactions. The ОН group of alcohols can participate in the hydrogen bond network of water. The lower alcohols are completely soluble in water. As the hydrocarbon chain gets larger, the compound begins to l ...
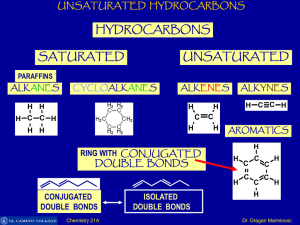
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
... Benzene is resistant to addition reactions. Adding something new to the ring would need you to use some of the delocalized electrons to form bonds with whatever you are adding. That results in a major loss of stability as the delocalization is broken. Instead, benzene mainly undergoes substitution r ...
... Benzene is resistant to addition reactions. Adding something new to the ring would need you to use some of the delocalized electrons to form bonds with whatever you are adding. That results in a major loss of stability as the delocalization is broken. Instead, benzene mainly undergoes substitution r ...
5. Homework 5-Answers
... 7. An exothermic reaction causes the surroundings to A) warm up. D) decrease its temperature. B) become acidic. E) release CO2. C) expand. Ans: A 8. Copper metal has a specific heat of 0.385 J/g·°C. Calculate the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 22.8 g of Cu from 20.0°C to 875°C. ...
... 7. An exothermic reaction causes the surroundings to A) warm up. D) decrease its temperature. B) become acidic. E) release CO2. C) expand. Ans: A 8. Copper metal has a specific heat of 0.385 J/g·°C. Calculate the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 22.8 g of Cu from 20.0°C to 875°C. ...
Chapter 3 HWsolutions (from Handout)
... molar masses of these elements as conversion factors to convert to moles. nC 35.51 g C 1 mol C 2.9567 mol C 12.01 g C nH 4.77 g H 1 mol H 4.732 mol H 1.008 g H nO 37.85 g O nN 8.29 g N 1 mol O 2.3656 mol O 16.00 g O 1 mol N 0.5917 mol N 14.01 g N nNa 13.60 g Na 1 mol Na ...
... molar masses of these elements as conversion factors to convert to moles. nC 35.51 g C 1 mol C 2.9567 mol C 12.01 g C nH 4.77 g H 1 mol H 4.732 mol H 1.008 g H nO 37.85 g O nN 8.29 g N 1 mol O 2.3656 mol O 16.00 g O 1 mol N 0.5917 mol N 14.01 g N nNa 13.60 g Na 1 mol Na ...
Ch 10 Practice Problems 1. Consider the process A(l) A(s). Which
... For the reaction A + B C + D, H° = +40 kJ and S° = +50 J/K. Therefore, the reaction under standard conditions is A) spontaneous at temperatures less than 10 K. B) spontaneous at temperatures greater than 800 K. C) spontaneous only at temperatures between 10 K and 800 K. D) spontaneous at all tem ...
... For the reaction A + B C + D, H° = +40 kJ and S° = +50 J/K. Therefore, the reaction under standard conditions is A) spontaneous at temperatures less than 10 K. B) spontaneous at temperatures greater than 800 K. C) spontaneous only at temperatures between 10 K and 800 K. D) spontaneous at all tem ...
Organosulfur compounds

Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin (pictured below) and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium and carbon–tellurium compounds, which is true to some extent.A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur compounds is the Carius halogen method.