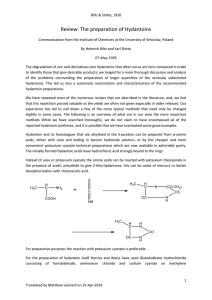
Experimental Section Materials Instrumentation Synthesis
... second microwave activation (10 x 1’, 300 W, 75 °C) and cooling to room temperature, the mixture was poured into distilled water (300 mL) and the precipitate was filtered off and washed with hot distilled water (300 mL) and hot EtOH (150 mL). The product was dried at 50 °C under vacuum (1.50 g, mass ...
... second microwave activation (10 x 1’, 300 W, 75 °C) and cooling to room temperature, the mixture was poured into distilled water (300 mL) and the precipitate was filtered off and washed with hot distilled water (300 mL) and hot EtOH (150 mL). The product was dried at 50 °C under vacuum (1.50 g, mass ...
Eötvös Loránd Science University Faculty of Sciences Department of
... Equilibrium reactions, parallel and consecutive reactions. Methods to solve coupled differential equations. The steady-state approximation of a set of differential equations. Chain reactions, explosions and their kinetic description. Catalysts and inhibitors. Acidbase catalysis. Experimental methods ...
... Equilibrium reactions, parallel and consecutive reactions. Methods to solve coupled differential equations. The steady-state approximation of a set of differential equations. Chain reactions, explosions and their kinetic description. Catalysts and inhibitors. Acidbase catalysis. Experimental methods ...
Cooperative Hydration of Pyruvic Acid in Ice
... 2.32, and 4.64 M, respectively. Although these solutions freeze without discontinuities in QH, the slope: ∂QH/∂T ) ∂(K1 × anw)/∂T, reverses its sign at Tf for the more dilute 0.1 M PA solution. Ultimately, all QH’s asymptotically merge into a common QH ) 4.2 ( 0.3 value below ∼250 K (Figure 4). Ther ...
... 2.32, and 4.64 M, respectively. Although these solutions freeze without discontinuities in QH, the slope: ∂QH/∂T ) ∂(K1 × anw)/∂T, reverses its sign at Tf for the more dilute 0.1 M PA solution. Ultimately, all QH’s asymptotically merge into a common QH ) 4.2 ( 0.3 value below ∼250 K (Figure 4). Ther ...
The applicability of activities in kinetic expressions Haubrock, J.
... the reactor was monitored by a pressure transducer (Dresser), with a maximum absolute deviation of 0.15 mbar under the experimental conditions applied. Furthermore, the temperatures in the reactor and the gas supply vessel were measured by means of PT 100 elements. Pressures and temperatures were di ...
... the reactor was monitored by a pressure transducer (Dresser), with a maximum absolute deviation of 0.15 mbar under the experimental conditions applied. Furthermore, the temperatures in the reactor and the gas supply vessel were measured by means of PT 100 elements. Pressures and temperatures were di ...
ExamView - 1984 AP Chemistry Exam.tst
... Web or Mass distribution prohibited. (2) AP® is a registered trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Entrance Examination Board was not involved in the production of and does not endorse this product. Permission is granted for individual classroom teachers to reproduce the a ...
... Web or Mass distribution prohibited. (2) AP® is a registered trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Entrance Examination Board was not involved in the production of and does not endorse this product. Permission is granted for individual classroom teachers to reproduce the a ...
vce chemistry trial exam 1
... 13C and 1H spectra. A is incorrect because neither UV-visible spectroscopy nor NMR spectroscopy allow the separation of compounds. B is incorrect because thin-layer chromatography is not precise enough to reliably separate esters for collection. IR spectroscopy will enable the identification of func ...
... 13C and 1H spectra. A is incorrect because neither UV-visible spectroscopy nor NMR spectroscopy allow the separation of compounds. B is incorrect because thin-layer chromatography is not precise enough to reliably separate esters for collection. IR spectroscopy will enable the identification of func ...
Ionic and Covalent Bonding - Fall River Public Schools
... Trick to remember: “ca+ion” Non-metals form negative ions called anions Ionic bonds are formed by a transfer of electrons ...
... Trick to remember: “ca+ion” Non-metals form negative ions called anions Ionic bonds are formed by a transfer of electrons ...
Chapter 4: Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Weak Electrolytes • Produce relatively few ions in aqueous solution • The most common weak electrolytes are weak acids and weak bases. • Acetic acid is a typical weak acid: HC2H3O2(aq) ...
... Weak Electrolytes • Produce relatively few ions in aqueous solution • The most common weak electrolytes are weak acids and weak bases. • Acetic acid is a typical weak acid: HC2H3O2(aq) ...
Strumenti tutor LIM
... A chemical transformation takes place when....................(atoms in the reactants are rearranged to form new substabces)(old bonds are broken and new bonds are formed)( at least one new substance is formed) We can realize that a chemical reaction is taking place when...........( there is a chang ...
... A chemical transformation takes place when....................(atoms in the reactants are rearranged to form new substabces)(old bonds are broken and new bonds are formed)( at least one new substance is formed) We can realize that a chemical reaction is taking place when...........( there is a chang ...
June Exam Review Material World
... A) When a strong acid is used with indicator 1, the solution turns blue. B) A neutral solution will be colourless when indicator 2 is used. C) When a strong base is used with indicator 3, the solution turns red. D) When the solution is a weak acid and indicator 4 is used, the solution turns red. ...
... A) When a strong acid is used with indicator 1, the solution turns blue. B) A neutral solution will be colourless when indicator 2 is used. C) When a strong base is used with indicator 3, the solution turns red. D) When the solution is a weak acid and indicator 4 is used, the solution turns red. ...
- sartep.com
... 18. __________A method of separation where a mobile phase is passed through a stationary phase is called: (A) distillation (B) decanting (C) using a magnet (D) chromatography 19. __________Which of the following experimental procedures is used to separate two substances by taking advantage of their ...
... 18. __________A method of separation where a mobile phase is passed through a stationary phase is called: (A) distillation (B) decanting (C) using a magnet (D) chromatography 19. __________Which of the following experimental procedures is used to separate two substances by taking advantage of their ...
Summer Work
... 6. How many kilojoules of heat energy are required to heat all the aluminum (C of Al =0.902J/g•°C) in a roll of aluminum foil (500.0 g) from room temperature (25.0 °C) to the temperature of a hot oven (250.0 °C)? ...
... 6. How many kilojoules of heat energy are required to heat all the aluminum (C of Al =0.902J/g•°C) in a roll of aluminum foil (500.0 g) from room temperature (25.0 °C) to the temperature of a hot oven (250.0 °C)? ...
I Physical characterization of a-Si thin films deposited by thermal I
... HECVD systems using silane precursors, which fail to provide hydrogen incorporation during deposition [l]. For those systems hydrogenation is accomplished in a second step after film deposition using hydrogen plasma [ l l ] or H' ion implantation [12]. The absence of any detectable hydrogen incorpor ...
... HECVD systems using silane precursors, which fail to provide hydrogen incorporation during deposition [l]. For those systems hydrogenation is accomplished in a second step after film deposition using hydrogen plasma [ l l ] or H' ion implantation [12]. The absence of any detectable hydrogen incorpor ...
CHEM1001 2012-J-2 June 2012 22/01(a) • Complete the following
... 1800 °C and 1.00 atm? Assume all gases behave as ideal gases. Show all working. Using the ideal gas equation, PV = nRT, the total number of moles of gas produced is: n = PV / RT = (1.00 atm × 720 L) / (0.08206 atm L K-1 mol-1 × (1800 + 273) K) = 4.23 mol From the chemical equation, detonation of 4 m ...
... 1800 °C and 1.00 atm? Assume all gases behave as ideal gases. Show all working. Using the ideal gas equation, PV = nRT, the total number of moles of gas produced is: n = PV / RT = (1.00 atm × 720 L) / (0.08206 atm L K-1 mol-1 × (1800 + 273) K) = 4.23 mol From the chemical equation, detonation of 4 m ...
17.2 The Avogadro Number
... The large number in front of H2 tells how many molecules of H2 are required for the reaction to proceed. The large number in front of H2O tells how many molecules of water are formed by the reaction. These numbers are called coefficients. Using coefficients, we can balance chemical equations so that ...
... The large number in front of H2 tells how many molecules of H2 are required for the reaction to proceed. The large number in front of H2O tells how many molecules of water are formed by the reaction. These numbers are called coefficients. Using coefficients, we can balance chemical equations so that ...
PowerPoint - Science Geek
... Stoichiometry “In solving a problem of this sort, the grand thing is to be able to reason backward. This is a very useful accomplishment, and a very easy one, but people do not practice it much.” Sherlock Holmes, in Sir Arthur Conan Doyle’s A Study in Scarlet ...
... Stoichiometry “In solving a problem of this sort, the grand thing is to be able to reason backward. This is a very useful accomplishment, and a very easy one, but people do not practice it much.” Sherlock Holmes, in Sir Arthur Conan Doyle’s A Study in Scarlet ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.















![Hydrogen bond strength and [beta]-sheet propensities: The role of a](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001016933_1-f0906f8b94f5874649a4b4bfebaa6ef4-300x300.png)