Gas Stoichiometry
... 1. Upon impact, the bag is inflated by the thermal decomposition of sodium azide (NaN3) to sodium metal and nitrogen gas. 2. Because sodium is toxic and very reactive, it reacts with the potassium nitrate to produce potassium oxide and sodium oxide, and (additional) nitrogen gas. 3. The metal oxides ...
... 1. Upon impact, the bag is inflated by the thermal decomposition of sodium azide (NaN3) to sodium metal and nitrogen gas. 2. Because sodium is toxic and very reactive, it reacts with the potassium nitrate to produce potassium oxide and sodium oxide, and (additional) nitrogen gas. 3. The metal oxides ...
Even-Odd Effect of 35Cl Quadrupole Coupling
... geometrical arrangements in the crystals will be discussed. Since two cations are contained in a unit cell of the rotator phase (space group: P4/nmn, Z = 2), as shown in Fig. 4(a), and since each cation rotates about its long axis along the C4 -axis, we define cation1 and cation2 as located along th ...
... geometrical arrangements in the crystals will be discussed. Since two cations are contained in a unit cell of the rotator phase (space group: P4/nmn, Z = 2), as shown in Fig. 4(a), and since each cation rotates about its long axis along the C4 -axis, we define cation1 and cation2 as located along th ...
Physical chemistry and transition elements 5.1 Rates, equilibrium
... An increase in concentration of NO(g) increases the term on the bottom of the expression for both Kc and Kp. The equilibrium moves to restore Kc or Kp by increasing the top and decreasing the bottom – so the equilibrium moves from left to right. There are more concentration or partial pressure terms ...
... An increase in concentration of NO(g) increases the term on the bottom of the expression for both Kc and Kp. The equilibrium moves to restore Kc or Kp by increasing the top and decreasing the bottom – so the equilibrium moves from left to right. There are more concentration or partial pressure terms ...
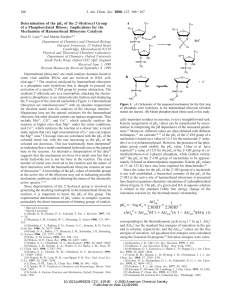
EQUILIBRIUM - SCH4U1-CCVI
... 1. Once a system has reached equilibrium, are the following true or false? a. The reaction is finished, no more products are forming. __________ b. The concentrations of the reactants and the products are equal. ______________ c. The concentrations are no longer changing. ___________ d. The reaction ...
... 1. Once a system has reached equilibrium, are the following true or false? a. The reaction is finished, no more products are forming. __________ b. The concentrations of the reactants and the products are equal. ______________ c. The concentrations are no longer changing. ___________ d. The reaction ...
Soluble - HCC Learning Web
... How does the solubility of silver phosphate in water compare to that of silver phosphate in an acidic solution (made by adding nitric acid to the solution)? Explain. The silver phosphate is more soluble in an acidic solution. Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved ...
... How does the solubility of silver phosphate in water compare to that of silver phosphate in an acidic solution (made by adding nitric acid to the solution)? Explain. The silver phosphate is more soluble in an acidic solution. Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved ...
Chemical Equations
... “yields”; indicates result of a reaction Indicates a reversible reaction A reactant or product in the solid state Alternative to (s); used only for a precipitate (solid) falling out of solution A reactant or product in the liquid state A reactant or product in aqueous solution (dissolved in water) A ...
... “yields”; indicates result of a reaction Indicates a reversible reaction A reactant or product in the solid state Alternative to (s); used only for a precipitate (solid) falling out of solution A reactant or product in the liquid state A reactant or product in aqueous solution (dissolved in water) A ...
Chapter 6.2 Notes
... - because they do not form individual molecules, to write the chemical formulas use the smallest ratio of one ion to another, called the formula unit NaCl 1:1 Na2O 2:1 AlBr3 1:3 - smallest ratio means they will not be divisible by each other and get a whole number - will never have an ionic compound ...
... - because they do not form individual molecules, to write the chemical formulas use the smallest ratio of one ion to another, called the formula unit NaCl 1:1 Na2O 2:1 AlBr3 1:3 - smallest ratio means they will not be divisible by each other and get a whole number - will never have an ionic compound ...
Chemistry - Bourbon County Schools
... I can do the following: Explain how conservation laws form the basis for balancing chemical reactions and know what quantities are conserved in physical, chemical, and nuclear changes ...
... I can do the following: Explain how conservation laws form the basis for balancing chemical reactions and know what quantities are conserved in physical, chemical, and nuclear changes ...
avogadro exam 2001 - University of Waterloo
... The results of Student A are more accurate but less precise. ...
... The results of Student A are more accurate but less precise. ...
chapter 6: chemical reactions: an introduction
... we increase the number of oxygen atoms on the right to 4, which still does not balance the three oxygen atoms on the left. If we change the coefficient in front of 0z to a 3, there will be six oxygen atoms on the right and three on the left. We can ...
... we increase the number of oxygen atoms on the right to 4, which still does not balance the three oxygen atoms on the left. If we change the coefficient in front of 0z to a 3, there will be six oxygen atoms on the right and three on the left. We can ...
February 13, 2008
... A. At equilibrium, the total concentration of products equals the total concentration of reactants B. Equilibrium is the result of the cessation of all chemical change. C. There is only one set of equilibrium concentrations that equals the Kc value. D. The rate constant of the forward reaction is eq ...
... A. At equilibrium, the total concentration of products equals the total concentration of reactants B. Equilibrium is the result of the cessation of all chemical change. C. There is only one set of equilibrium concentrations that equals the Kc value. D. The rate constant of the forward reaction is eq ...
Chapter Five
... Recall that the molar mass relates the mass of a compound (or element) to the number of moles. Therefore, if we know the mass of a given reactant, we can easily determine the number of moles of the reactant, and from there the number of moles of product produced. Remember, you must use the mol ...
... Recall that the molar mass relates the mass of a compound (or element) to the number of moles. Therefore, if we know the mass of a given reactant, we can easily determine the number of moles of the reactant, and from there the number of moles of product produced. Remember, you must use the mol ...
Precipitation and Redox Reactions
... • If one (or more) element(s) in the reaction loses electrons (LEO) and one (or more) element(s) in the reaction gains electrons (GER) then REDOX has occurred. • It is that simple: • Write the equation • Determine the charges on every element • See if LEO-GER has occurred ...
... • If one (or more) element(s) in the reaction loses electrons (LEO) and one (or more) element(s) in the reaction gains electrons (GER) then REDOX has occurred. • It is that simple: • Write the equation • Determine the charges on every element • See if LEO-GER has occurred ...
Chemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds
... Naphthalene is a soft covalent solid that is often used in mothballs. Its molar mass is 128.18 g/mol and it contains 93.75% carbon and 6.25% hydrogen. Determine the molecular formula of napthalene from this ...
... Naphthalene is a soft covalent solid that is often used in mothballs. Its molar mass is 128.18 g/mol and it contains 93.75% carbon and 6.25% hydrogen. Determine the molecular formula of napthalene from this ...
Chapter 15 Fundamentals of Aqueous Corrosion
... Localized corrosion is attack of the metal in penetrations called pits or crevices. The former look like holes dug in the ground, and can often be seen on stainless steel tableware. Crevices, on the other hand, resemble clean cracks. Crevice corrosion most frequently occurs in metals under stress, w ...
... Localized corrosion is attack of the metal in penetrations called pits or crevices. The former look like holes dug in the ground, and can often be seen on stainless steel tableware. Crevices, on the other hand, resemble clean cracks. Crevice corrosion most frequently occurs in metals under stress, w ...
Balancing Oxidation-Reduction Equations
... LO 1.17: The student is able to express the law of conservation of mass quantitatively and qualitatively using symbolic representations and particulate drawings. LO 1.18: The student is able to apply conservation of atoms to the rearrangement of atoms in various processes. LO 3.1: Students can trans ...
... LO 1.17: The student is able to express the law of conservation of mass quantitatively and qualitatively using symbolic representations and particulate drawings. LO 1.18: The student is able to apply conservation of atoms to the rearrangement of atoms in various processes. LO 3.1: Students can trans ...
AP Chemistry
... Percent Yield of CO2 Gas Lab (Wear Goggles) 19. Completely react NaHCO3(s) with 6 M HCl, according to the net ionic equation HCO3- + H+ H2O + CO2(g), measure the volume of CO2 and compare this to the theoretical yield. Mass 0.6 g NaHCO3 and record its mass (m) to the nearest 0.001 g. Add the NaHCO ...
... Percent Yield of CO2 Gas Lab (Wear Goggles) 19. Completely react NaHCO3(s) with 6 M HCl, according to the net ionic equation HCO3- + H+ H2O + CO2(g), measure the volume of CO2 and compare this to the theoretical yield. Mass 0.6 g NaHCO3 and record its mass (m) to the nearest 0.001 g. Add the NaHCO ...
M for Moles - Shop
... involving atoms rearrangement. The total number of atoms at the left is always the same as that on the right. Virtually all simple gas molecules are made of two-atom pairs. They are called diatomics. For example, H2, Cl2, N2 and F2. The exceptions are those belong to Group 0. These are called inert ...
... involving atoms rearrangement. The total number of atoms at the left is always the same as that on the right. Virtually all simple gas molecules are made of two-atom pairs. They are called diatomics. For example, H2, Cl2, N2 and F2. The exceptions are those belong to Group 0. These are called inert ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.