Chemistry Olympiad Support Booklet
... Drawing the structure of tartaric acid clearly might suggest that there are four stereoisomers (since there are two asymmetric carbon atoms present which can each have ‘left’ and ‘right’ handed orientation), but since the chiral centres are identical there are in fact only three. These are shown bel ...
... Drawing the structure of tartaric acid clearly might suggest that there are four stereoisomers (since there are two asymmetric carbon atoms present which can each have ‘left’ and ‘right’ handed orientation), but since the chiral centres are identical there are in fact only three. These are shown bel ...
This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy
... an easy phase separation. In the subsequent step, Section 3 including reactions (9) and (10), the separation of HI from L − 2, the heavier iodine/iodide–water phase, is the most critical scenario of the cycle [4] and believed to be the most expensive and energy-consuming step [5]. After establishing ...
... an easy phase separation. In the subsequent step, Section 3 including reactions (9) and (10), the separation of HI from L − 2, the heavier iodine/iodide–water phase, is the most critical scenario of the cycle [4] and believed to be the most expensive and energy-consuming step [5]. After establishing ...
A STUDY OF THE RATE OF THE REACTION OF CHLORINE
... tell us the order of the reaction with respect to blue dye (i.e. if “n” = 1 or 2) and the value of kobs. You will now have a unique value of kobs for each trial and the value of “n”. Since we complete two different trials, each with the same [blue dye] but with a different, but known, [bleach], we w ...
... tell us the order of the reaction with respect to blue dye (i.e. if “n” = 1 or 2) and the value of kobs. You will now have a unique value of kobs for each trial and the value of “n”. Since we complete two different trials, each with the same [blue dye] but with a different, but known, [bleach], we w ...
LESSON 16: Crystal Art
... The opposite change is freezing. Freezing is a change in state from a liquid to a solid. A change in state from a liquid to a gas is known as vaporization, while a change in state from a gas to a liquid is known as condensation. Changes that occur directly between the solid and gaseous states, witho ...
... The opposite change is freezing. Freezing is a change in state from a liquid to a solid. A change in state from a liquid to a gas is known as vaporization, while a change in state from a gas to a liquid is known as condensation. Changes that occur directly between the solid and gaseous states, witho ...
Chapter 15 Notes - Mr. Julien`s Homepage
... a. The components of the oxidation half-cell (anode) are written on the left side in this shorthand notation. b. The components of the reduction half-cell (cathode) are written on the right side in this shorthand notation. c. A single vertical line separates the solid zinc anode from the zinc(II) io ...
... a. The components of the oxidation half-cell (anode) are written on the left side in this shorthand notation. b. The components of the reduction half-cell (cathode) are written on the right side in this shorthand notation. c. A single vertical line separates the solid zinc anode from the zinc(II) io ...
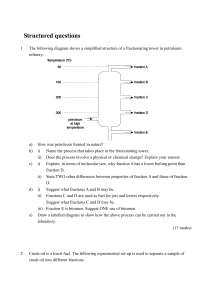
Structured questions
... ii) Explain why this pollutant can be found in exhaust of motor vehicles. iii) State ONE harmful effect of this pollutant. iv) Suggest a method to reduce the amount of this pollutant. Emission from power stations contains a large amount of particulates. i) State ONE health problem associated with pa ...
... ii) Explain why this pollutant can be found in exhaust of motor vehicles. iii) State ONE harmful effect of this pollutant. iv) Suggest a method to reduce the amount of this pollutant. Emission from power stations contains a large amount of particulates. i) State ONE health problem associated with pa ...
pulsed laser atom probe characterization of silicon carbide
... at a mass-to-charge ratio of 12 amu was assigned exclusively to the C + ion and not the doubly charged C, species. This assignment could result in a slight underestimate of the carbon level. The measured compositions under these conditions were consistent with each other within the statistical scatt ...
... at a mass-to-charge ratio of 12 amu was assigned exclusively to the C + ion and not the doubly charged C, species. This assignment could result in a slight underestimate of the carbon level. The measured compositions under these conditions were consistent with each other within the statistical scatt ...
10/18/11 - Note: Once it is downloaded, click SET
... What’s involved? Periodic table, electron, atomic number Electrons are arranged in orbitals around the nucleus Things to know: -Hund’s Rule, Aufbau Principle, Pauli’s Exclusion Principle -Electron Dot- shows how many valence electrons it has. -SPDF (orbitals) S- 1- up to 2 electrons P- 3- up to 6 el ...
... What’s involved? Periodic table, electron, atomic number Electrons are arranged in orbitals around the nucleus Things to know: -Hund’s Rule, Aufbau Principle, Pauli’s Exclusion Principle -Electron Dot- shows how many valence electrons it has. -SPDF (orbitals) S- 1- up to 2 electrons P- 3- up to 6 el ...
Class-XII, Summer assignment
... i) Silica gel placed in the atmosphere saturated with water. ii) Anhydrous CaCl2 placed in the atmosphere saturated with water. (b) How does BF3 act as a catalyst in industrial process? (c) Give an example of shape-selective catalysis. 15. What are micelles? How do they differ from ordinary colloida ...
... i) Silica gel placed in the atmosphere saturated with water. ii) Anhydrous CaCl2 placed in the atmosphere saturated with water. (b) How does BF3 act as a catalyst in industrial process? (c) Give an example of shape-selective catalysis. 15. What are micelles? How do they differ from ordinary colloida ...
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
... Define the properties of acids and bases. Compare and contrast acids and bases as defined by the theories of Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry, and Lewis. 5. Hydrogen Ions and Acidity Describe how [H+] and [OH-] are related in an aqueous solution. Classify a solution as neutral, acidic, or basic giv ...
... Define the properties of acids and bases. Compare and contrast acids and bases as defined by the theories of Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry, and Lewis. 5. Hydrogen Ions and Acidity Describe how [H+] and [OH-] are related in an aqueous solution. Classify a solution as neutral, acidic, or basic giv ...
s-BLOCK ELEMENTS - einstein classes
... alkali metal ions in decreasing order is Li+ > Na+ > K+ > Rb+ > Cs+. Potassium is lighter than sodium. The alkali metals do not occur free in nature. This is because they have very low ionization enthalpy and form electropositive ions. Sodium is less reactive than potassium this is because the ioniz ...
... alkali metal ions in decreasing order is Li+ > Na+ > K+ > Rb+ > Cs+. Potassium is lighter than sodium. The alkali metals do not occur free in nature. This is because they have very low ionization enthalpy and form electropositive ions. Sodium is less reactive than potassium this is because the ioniz ...
chemistry
... question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You may use scrap paper to work out the answers to the questions, but be sure to ...
... question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You may use scrap paper to work out the answers to the questions, but be sure to ...
Building the sense of math in physics activities
... B.1 Write an equation for the Reynolds number for this example, simplifying the equation as much as possible (e.g., cancelling factors that are both in the numerator and denominator). B.2 If the viscosity of air is about 10-3 kg/m-s, find the value of the Reynolds number for the coffee filter fallin ...
... B.1 Write an equation for the Reynolds number for this example, simplifying the equation as much as possible (e.g., cancelling factors that are both in the numerator and denominator). B.2 If the viscosity of air is about 10-3 kg/m-s, find the value of the Reynolds number for the coffee filter fallin ...
2015 chemistry
... Explain why the percentage of oil converted in an enzyme-catalysed reaction is very low at high temperatures. _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Explain why the percentage of oil converted in an enzyme-catalysed reaction is very low at high temperatures. _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ...
225 Unit 7, Lab 1 - Pope John Paul II High School
... In the example seen above, 3O2 had to be added to the right side of the equation to balance it and show that the excess oxygen is not consumed during the reaction. In this example, methane is called the limiting reactant. Although we have discussed balancing equations in terms of numbers of atoms an ...
... In the example seen above, 3O2 had to be added to the right side of the equation to balance it and show that the excess oxygen is not consumed during the reaction. In this example, methane is called the limiting reactant. Although we have discussed balancing equations in terms of numbers of atoms an ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.