Subject Materials for Chemistry
... Glycerol decreases the rate of reaction. So glycerol is –ve catalyst. No, Catalyst doesn’t undergo any change chemically. A Catalyst may be recovered in mass and composition at the end of the chemical reaction. 6. What is the effect of temperature on the following? i) Dissociation of an electrolyte ...
... Glycerol decreases the rate of reaction. So glycerol is –ve catalyst. No, Catalyst doesn’t undergo any change chemically. A Catalyst may be recovered in mass and composition at the end of the chemical reaction. 6. What is the effect of temperature on the following? i) Dissociation of an electrolyte ...
2003 AP Chemistry Form B Scoring Guidelines - AP Central
... (iii) How many moles of Fe(s) are formed in the reaction? 2 mol Fe ö nFe = 0.0964 mol Fe2O3 æç ÷ = 0.193 mol Fe produced è1 mol Fe2O3ø If 0.626 mol CO is used as the limiting reactant, then the number of moles of Fe formed is: 2 mol Fe ö nFe = 0.626 mol CO æ = 0.417 mol Fe è3 mol COø ...
... (iii) How many moles of Fe(s) are formed in the reaction? 2 mol Fe ö nFe = 0.0964 mol Fe2O3 æç ÷ = 0.193 mol Fe produced è1 mol Fe2O3ø If 0.626 mol CO is used as the limiting reactant, then the number of moles of Fe formed is: 2 mol Fe ö nFe = 0.626 mol CO æ = 0.417 mol Fe è3 mol COø ...
2014 VCE Chemistry written examination report
... The selection of alternative A by most students suggests that they focused on the fact that Hg was balanced on both sides but did not consider that the equation must be balanced for all elements present. The most effective way to balance the equation for a redox reaction is to consider the relevant ...
... The selection of alternative A by most students suggests that they focused on the fact that Hg was balanced on both sides but did not consider that the equation must be balanced for all elements present. The most effective way to balance the equation for a redox reaction is to consider the relevant ...
What is a mole? - Chemical Paradigms
... aqueous solution. An aqueous solution is formed when a solid compound is dissolved in water. For example sodium chloride solution is formed by taking a known amount of solid sodium chloride and dissolving it in a known volume of water. More about this later. In a chemical reaction substances need to ...
... aqueous solution. An aqueous solution is formed when a solid compound is dissolved in water. For example sodium chloride solution is formed by taking a known amount of solid sodium chloride and dissolving it in a known volume of water. More about this later. In a chemical reaction substances need to ...
Coagulation Kinetics of Humic Aggregates in Mono- and Di
... combination of other analytical tools. For monovalent electrolyte sodium chloride (NaCl) solution, at its low concentrations the average hydrodynamic radius () of aggregates kept nearly constant. However, at high NaCl
concentrations, could be scaled to the time t as ∝ ta, suggesting a
...
... combination of other analytical tools. For monovalent electrolyte sodium chloride (NaCl) solution, at its low concentrations the average hydrodynamic radius (
CHEMISTRY
... units. I use dimensional analysis to do metric-metric conversions, stressing that many different types of calculations can be done using dimensional analysis. I will also intentionally set up a problem incorrectly and show the students that the units do not cancel, demonstrating the importance of ch ...
... units. I use dimensional analysis to do metric-metric conversions, stressing that many different types of calculations can be done using dimensional analysis. I will also intentionally set up a problem incorrectly and show the students that the units do not cancel, demonstrating the importance of ch ...
AP CHEMISTRY COURSE SYLLABUS
... 3. Oxidation-reduction reactions a. Oxidation number b. The role of the electron in oxidationreduction ...
... 3. Oxidation-reduction reactions a. Oxidation number b. The role of the electron in oxidationreduction ...
Chemistry 6
... included. This section must be word-processed. Identify the calculation, such as, volume of HCl used. ...
... included. This section must be word-processed. Identify the calculation, such as, volume of HCl used. ...
picture_as_pdf Released Materials 2013 (16551
... A hand-warmer packet contains a mixture of powdered iron, carbon, sodium chloride, sawdust, and zeolite, all moistened by a little water. The packet is activated by removing the plastic cover, which exposes the materials in the packet to air. The reaction that occurs is represented by the following ...
... A hand-warmer packet contains a mixture of powdered iron, carbon, sodium chloride, sawdust, and zeolite, all moistened by a little water. The packet is activated by removing the plastic cover, which exposes the materials in the packet to air. The reaction that occurs is represented by the following ...
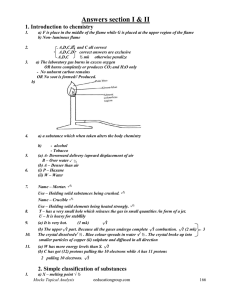
OXIDATION NUMBERS
... • electronegativity increases across a period and decreases down a group • O is further to the right in the periodic table so it has the negative value (-2) • C is to the left so it has the positive value (+4) • one needs two O’s at -2 each to balance one C at +4 ...
... • electronegativity increases across a period and decreases down a group • O is further to the right in the periodic table so it has the negative value (-2) • C is to the left so it has the positive value (+4) • one needs two O’s at -2 each to balance one C at +4 ...
A Level Chemistry transition task
... we need to know how heavy each atom is. From the periodic table: Mg = 24.3 and S = 32.1 If I weigh out exactly 24.3g of magnesium this will be 1 mole of magnesium, if we counted how many atoms were present in this mass it would be a huge number (6.02 x 1023!!!!), if I weigh out 32.1g of sulfur then ...
... we need to know how heavy each atom is. From the periodic table: Mg = 24.3 and S = 32.1 If I weigh out exactly 24.3g of magnesium this will be 1 mole of magnesium, if we counted how many atoms were present in this mass it would be a huge number (6.02 x 1023!!!!), if I weigh out 32.1g of sulfur then ...
Revisiting the role of Calcium and Gypsum for Sodic
... the Exchangeable Sodium Percentage (ESP) via replacement of monovalent Sodium ions at soil exchange sites – increasing the potential for sodium leaching from the soil profile.. However, restoring soil quality and improving soil stability of sodic soils is much more complex. Multi-component biogeoche ...
... the Exchangeable Sodium Percentage (ESP) via replacement of monovalent Sodium ions at soil exchange sites – increasing the potential for sodium leaching from the soil profile.. However, restoring soil quality and improving soil stability of sodic soils is much more complex. Multi-component biogeoche ...
template - Communications in Inorganic Synthesis
... MnCl2·4H2O (0.30 g, 1.5 mmol) were dissolved in 5 mL of water. 2,2-oxydiacetic acid (0.40 g, 3.0 mmol) were dissolved in another 5 mL of water, and the pH value was adjusted to 8.0 with ammonium hydroxide. Both solutions were mixed, and a clear solution was obtained. The solution was allowed to evap ...
... MnCl2·4H2O (0.30 g, 1.5 mmol) were dissolved in 5 mL of water. 2,2-oxydiacetic acid (0.40 g, 3.0 mmol) were dissolved in another 5 mL of water, and the pH value was adjusted to 8.0 with ammonium hydroxide. Both solutions were mixed, and a clear solution was obtained. The solution was allowed to evap ...
stoichiometry
... 9) You have 100 bolts, 150 nuts and 150 washers. You assemble a nut/bolt/washer set using the following recipe or equation: 2 washers + 1 bolt + 1 nut = 1 set a. How many sets can you make from your supply? b. Which is the limiting component? ...
... 9) You have 100 bolts, 150 nuts and 150 washers. You assemble a nut/bolt/washer set using the following recipe or equation: 2 washers + 1 bolt + 1 nut = 1 set a. How many sets can you make from your supply? b. Which is the limiting component? ...
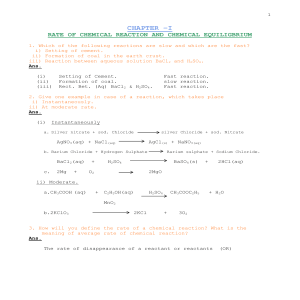
CHEMICAL REACTIONS - World Colleges Information
... CHEMICAL REACTIONS Double decomposition reaction is Oxidation: A chemical reaction which involves any reaction in which exchange of ions between two reactants occur, leading to addition of oxygen or removal of the formation of two different products. hydrogen or loss of electron(s) is called as oxi ...
... CHEMICAL REACTIONS Double decomposition reaction is Oxidation: A chemical reaction which involves any reaction in which exchange of ions between two reactants occur, leading to addition of oxygen or removal of the formation of two different products. hydrogen or loss of electron(s) is called as oxi ...
H2 Chemistry Syllabus (9729)
... laws, and theories); it is a way of knowing and doing. It includes an understanding of the nature of scientific knowledge and how this knowledge is generated, established and communicated. Scientists rely on a set of established procedures and practices associated with scientific inquiry to gather e ...
... laws, and theories); it is a way of knowing and doing. It includes an understanding of the nature of scientific knowledge and how this knowledge is generated, established and communicated. Scientists rely on a set of established procedures and practices associated with scientific inquiry to gather e ...
Chemical Reactions and Equations - 2012 Book Archive
... 1. From the statement “nitrogen and hydrogen react to produce ammonia,” identify the reactants and the products. 2. From the statement “sodium metal reacts with water to produce sodium hydroxide and hydrogen,” identify the reactants and the products. 3. From the statement “magnesium hydroxide reacts ...
... 1. From the statement “nitrogen and hydrogen react to produce ammonia,” identify the reactants and the products. 2. From the statement “sodium metal reacts with water to produce sodium hydroxide and hydrogen,” identify the reactants and the products. 3. From the statement “magnesium hydroxide reacts ...
Topic 15 Energetics - slider-dpchemistry-11
... i.e. a temperature of 298 K and a pressure of one atmosphere. These conditions are designated by °, e.g. ΔH°. Standard state is the stable state of an element or compound, under standard conditions, e.g. the standard state of CO2 is a gas, while water a liquid. No they are not the same. Conditions d ...
... i.e. a temperature of 298 K and a pressure of one atmosphere. These conditions are designated by °, e.g. ΔH°. Standard state is the stable state of an element or compound, under standard conditions, e.g. the standard state of CO2 is a gas, while water a liquid. No they are not the same. Conditions d ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.