Effects of composition on the properties of phospholipid bilayers
... The lipid makeup of biological membranes is such that fluidity is maintained at the temperatures encountered1. For instance, neural cells in carp adapt to low temperatures by modifying the composition of their cell membranes, increasing the number of short chain unsaturated phospholipids that have h ...
... The lipid makeup of biological membranes is such that fluidity is maintained at the temperatures encountered1. For instance, neural cells in carp adapt to low temperatures by modifying the composition of their cell membranes, increasing the number of short chain unsaturated phospholipids that have h ...
Solutions - ChemConnections
... Magnesium is an alkaline earth metal; Mg will oxidize to Mg2+. The oxidation state of hydrogen in HCl is +1. To be reduced, the oxidation state of H must decrease. The obvious choice for the hydrogen product is H2(g), where hydrogen has a zero oxidation state. The balanced reaction is Mg(s) + 2HCl(a ...
... Magnesium is an alkaline earth metal; Mg will oxidize to Mg2+. The oxidation state of hydrogen in HCl is +1. To be reduced, the oxidation state of H must decrease. The obvious choice for the hydrogen product is H2(g), where hydrogen has a zero oxidation state. The balanced reaction is Mg(s) + 2HCl(a ...
Effects of Electrolyte Concentration and pH on
... therefore, explained with their effect on the surface forces, e.g., by modifying the electrical potential of drop surface12,22 and the van der Waals interactions,36,37 and by creating a steric barrier to drop-drop coalescence.22,31,35 In other words, it is assumed in these studies that the main role ...
... therefore, explained with their effect on the surface forces, e.g., by modifying the electrical potential of drop surface12,22 and the van der Waals interactions,36,37 and by creating a steric barrier to drop-drop coalescence.22,31,35 In other words, it is assumed in these studies that the main role ...
College Chemistry
... measurement were exact to the nearest 0.01 cm, it would have been recorded as 15.70 cm. We say that the first measurement is accurate to 3 significant figures and the second to 4. A recorded volume of 2.8 L represents two significant figures. If this same volume were written 0.028 m3, it would still ...
... measurement were exact to the nearest 0.01 cm, it would have been recorded as 15.70 cm. We say that the first measurement is accurate to 3 significant figures and the second to 4. A recorded volume of 2.8 L represents two significant figures. If this same volume were written 0.028 m3, it would still ...
Chemistry 211
... •How much product is formed from some given amount of reactant? (Theoretical Yield) •How much of one reactant is required to bring a reaction to completion given some amount of another reactant? (Limiting Reagent) ...
... •How much product is formed from some given amount of reactant? (Theoretical Yield) •How much of one reactant is required to bring a reaction to completion given some amount of another reactant? (Limiting Reagent) ...
Chapter 9
... • Phosphoric acid (H3PO4) is one of the most widely produced industrial chemicals in the world. • Most of the world’s phosphoric acid is produced by the wet process which involves the reaction of phosphate rock, Ca5(PO4)3F, with sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Ca5(PO4)3F(s) + 5H2SO4 3H3PO4 + HF + 5CaSO ...
... • Phosphoric acid (H3PO4) is one of the most widely produced industrial chemicals in the world. • Most of the world’s phosphoric acid is produced by the wet process which involves the reaction of phosphate rock, Ca5(PO4)3F, with sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Ca5(PO4)3F(s) + 5H2SO4 3H3PO4 + HF + 5CaSO ...
B.Sc. (Hons.) Chemistry
... Strong, moderate and weak electrolytes, degree of ionization, factors affecting degree of ionization, ionization constant and ionic product of water. Ionization of weak acids and bases, pH scale, common ion effect; dissociation constants of mono-, di-and triprotic acids (exact treatment). Salt hydro ...
... Strong, moderate and weak electrolytes, degree of ionization, factors affecting degree of ionization, ionization constant and ionic product of water. Ionization of weak acids and bases, pH scale, common ion effect; dissociation constants of mono-, di-and triprotic acids (exact treatment). Salt hydro ...
TOPIC 9. CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS III
... and mass of O2 produced = molar mass of O2 × moles O2 = 32.00 × 0.0368 = 1.18 g In the above, for convenience the term “molecules” was applied to ionic species such as NaOH which do not actually exist as molecules. Strictly the more cumbersome term such as “formula units” would be more correct. Also ...
... and mass of O2 produced = molar mass of O2 × moles O2 = 32.00 × 0.0368 = 1.18 g In the above, for convenience the term “molecules” was applied to ionic species such as NaOH which do not actually exist as molecules. Strictly the more cumbersome term such as “formula units” would be more correct. Also ...
questions based on high order thinking skill - Entrance
... Ans. Ethyl alcohol and water (95.4% ethyl alcohol and 4.6% water) form constant boiling mixture (azeotrope) boiling at 351.1 °K. Hence, further water cannot be separated completely from ethyl alcohol by fractional distillation. Q. 5. Why a person suffering from high blood pressure is advised to take ...
... Ans. Ethyl alcohol and water (95.4% ethyl alcohol and 4.6% water) form constant boiling mixture (azeotrope) boiling at 351.1 °K. Hence, further water cannot be separated completely from ethyl alcohol by fractional distillation. Q. 5. Why a person suffering from high blood pressure is advised to take ...
questions based on high order thinking skill
... Ans. Ethyl alcohol and water (95.4% ethyl alcohol and 4.6% water) form constant boiling mixture (azeotrope) boiling at 351.1 °K. Hence, further water cannot be separated completely from ethyl alcohol by fractional distillation. Q. 5. Why a person suffering from high blood pressure is advised to take ...
... Ans. Ethyl alcohol and water (95.4% ethyl alcohol and 4.6% water) form constant boiling mixture (azeotrope) boiling at 351.1 °K. Hence, further water cannot be separated completely from ethyl alcohol by fractional distillation. Q. 5. Why a person suffering from high blood pressure is advised to take ...
Support Material
... Q.41. An element crystallizes in FCC structure; 200 g of this element has 4.12 1024 atoms. If the density of A is 7.2 g cm-3, calculate the edge length of unit cell. Q.42. Niobium crystallizes in bcc structure. If its density is 8.55 cm -3, calculate its atomic radius. (Atomic mass of Niobium = 92 ...
... Q.41. An element crystallizes in FCC structure; 200 g of this element has 4.12 1024 atoms. If the density of A is 7.2 g cm-3, calculate the edge length of unit cell. Q.42. Niobium crystallizes in bcc structure. If its density is 8.55 cm -3, calculate its atomic radius. (Atomic mass of Niobium = 92 ...
2 - OnCourse
... Must multiply subscripts of the derived formula, C1H1.33O1, by some factor to convert the fractional atom into a whole number. This is done by trial and error, but the multiples are usually small, whole numbers. x 2 = C2H2.66O2 ...
... Must multiply subscripts of the derived formula, C1H1.33O1, by some factor to convert the fractional atom into a whole number. This is done by trial and error, but the multiples are usually small, whole numbers. x 2 = C2H2.66O2 ...
Chem Agenda+ETDsHWK to End of Year 102714 Update
... Too small to see, so how do we know what they look like or that they exist. (old dot on board with 100s of billions of atoms) Super Models: Dalton to Rutherford sheet: Part I (took 20 mins) studs use internet, book to do Part I Democritus Thomson (then stop and review Dalton’s Atomic Theory (5 rul ...
... Too small to see, so how do we know what they look like or that they exist. (old dot on board with 100s of billions of atoms) Super Models: Dalton to Rutherford sheet: Part I (took 20 mins) studs use internet, book to do Part I Democritus Thomson (then stop and review Dalton’s Atomic Theory (5 rul ...
Homogeneous Catalysis
... Chemical Kinetics is the study of reaction rates; that is, how fast a given reaction does proceeds. It is a measure of the change of the concentration of reactants (or products) as a function of time. Reaction rates provide information regarding how fast a chemical process occurs as well as the mech ...
... Chemical Kinetics is the study of reaction rates; that is, how fast a given reaction does proceeds. It is a measure of the change of the concentration of reactants (or products) as a function of time. Reaction rates provide information regarding how fast a chemical process occurs as well as the mech ...
Vibrational signatures of Hydrogen bonding in the protonated
... Strong hydrogen bonds, characterized by large bond energies of up to 30 kcal/mol and low barriers for proton transfer, play an important role in ion solvation, proton conductivity, and proton transfer across biomembranes.1 They are intriguing from a spectroscopic perspective, because the potential e ...
... Strong hydrogen bonds, characterized by large bond energies of up to 30 kcal/mol and low barriers for proton transfer, play an important role in ion solvation, proton conductivity, and proton transfer across biomembranes.1 They are intriguing from a spectroscopic perspective, because the potential e ...
Fulltext: english,
... If this effect is observed,60,61 other processes besides complexation are taking place in solution. As a result, the data should be referred to as ‘apparent’ data where ions and ion pairs are present in solution. To fulfil the fundamental issue of electroneutrality, a neutral receptor complexing eit ...
... If this effect is observed,60,61 other processes besides complexation are taking place in solution. As a result, the data should be referred to as ‘apparent’ data where ions and ion pairs are present in solution. To fulfil the fundamental issue of electroneutrality, a neutral receptor complexing eit ...
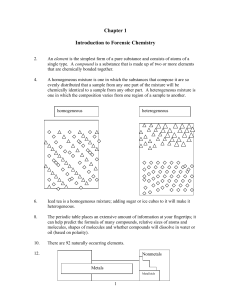
Chapter 1 Introduction to Forensic Chemistry
... Proust did his experimental work very carefully so that he was able to obtain both accurate and precise work. ...
... Proust did his experimental work very carefully so that he was able to obtain both accurate and precise work. ...
Calculations and the Chemical Equation
... The chemical equation enables the determination of the quantity of reactants needed to produce a certain quantity of products, and expresses these quantities in terms of moles. The number of moles of each product and reactant is indicated by placing a whole-number coefficient before the formula of e ...
... The chemical equation enables the determination of the quantity of reactants needed to produce a certain quantity of products, and expresses these quantities in terms of moles. The number of moles of each product and reactant is indicated by placing a whole-number coefficient before the formula of e ...
HW 19
... Strategy: The standard emf (E°) can be calculated using the standard reduction potentials in Table 19.1 of the text. Because the reactions are not run under standard-state conditions (concentrations are not 1 M), we need Nernst's equation [Equation (19.8) of the text] to calculate the emf (E) of a h ...
... Strategy: The standard emf (E°) can be calculated using the standard reduction potentials in Table 19.1 of the text. Because the reactions are not run under standard-state conditions (concentrations are not 1 M), we need Nernst's equation [Equation (19.8) of the text] to calculate the emf (E) of a h ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... Law of Conservation of Mass “We may lay it down as an incontestable axiom that, in all the operations of art and nature, nothing is created; an equal amount of matter exists both before and after the experiment. Upon this principle, the whole art of performing chemical ...
... Law of Conservation of Mass “We may lay it down as an incontestable axiom that, in all the operations of art and nature, nothing is created; an equal amount of matter exists both before and after the experiment. Upon this principle, the whole art of performing chemical ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.