Intro to Titrimetry
... 1. A Fajans titration of a 0.7908 g sample required 45.32 mL of 0.1046 M AgNO3. What is the %Cl of the sample? 2. The bismuth in 0.7405 g of an alloy was precipitated as BiOCl and separated from the solution by filtration. The washed precipitate was dissolved in nitric acid to convert all chlorine t ...
... 1. A Fajans titration of a 0.7908 g sample required 45.32 mL of 0.1046 M AgNO3. What is the %Cl of the sample? 2. The bismuth in 0.7405 g of an alloy was precipitated as BiOCl and separated from the solution by filtration. The washed precipitate was dissolved in nitric acid to convert all chlorine t ...
SOLUBILITY RULES FOR IONIC COMPOUNDS IN WATER
... 7. A detergent box must bear a warning label if its contents will form a solution of pH greater than 11, because a strong base degrades protein structure. Should a box bear such a label if the H3O+ concentration of a solution of its contents is 2.5 x 10-12 moles per liter? 8. A solution of ammonia h ...
... 7. A detergent box must bear a warning label if its contents will form a solution of pH greater than 11, because a strong base degrades protein structure. Should a box bear such a label if the H3O+ concentration of a solution of its contents is 2.5 x 10-12 moles per liter? 8. A solution of ammonia h ...
Basic Chemical Concepts I
... Determine the empirical formula of an acid which had the following elemental composition by mass: Carbon - 48.64%, Hydrogen - 8.16%, Oxygen !43.19%. The acid in (a) is monobasic (has one ionizable hydrogen) and hence can be given the formula HX. A 8.558 g sample of the acid was dissolved in water to ...
... Determine the empirical formula of an acid which had the following elemental composition by mass: Carbon - 48.64%, Hydrogen - 8.16%, Oxygen !43.19%. The acid in (a) is monobasic (has one ionizable hydrogen) and hence can be given the formula HX. A 8.558 g sample of the acid was dissolved in water to ...
Energy Matters - Perth Grammar
... The number of H+ (aq) ions in the beaker decreased. The pH of the solution decreased. The number of SO42−(aq) ions in the beaker decreased. Water molecules formed during the reaction. A precipitate formed during the reaction. The final solution contained equal numbers of H+(aq) and OH− (aq) ions. ...
... The number of H+ (aq) ions in the beaker decreased. The pH of the solution decreased. The number of SO42−(aq) ions in the beaker decreased. Water molecules formed during the reaction. A precipitate formed during the reaction. The final solution contained equal numbers of H+(aq) and OH− (aq) ions. ...
IB Chemistry Review. Unit I. Topics 2
... 13. 6.0 mol of aluminium reacts with oxygen to form aluminium oxide. What is the amount of oxygen, in mol, needed for complete reaction? 4Al(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Al2O3(s) 14. What is the total number of nitrogen atoms in two mol of NH4NO3? 15. On analysis, a compound with molar mass 60 g mol-1 was found t ...
... 13. 6.0 mol of aluminium reacts with oxygen to form aluminium oxide. What is the amount of oxygen, in mol, needed for complete reaction? 4Al(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Al2O3(s) 14. What is the total number of nitrogen atoms in two mol of NH4NO3? 15. On analysis, a compound with molar mass 60 g mol-1 was found t ...
Topic 1 Review - Capital High School
... 13. 6.0 mol of aluminium reacts with oxygen to form aluminium oxide. What is the amount of oxygen, in mol, needed for complete reaction? 4Al(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Al2O3(s) 14. What is the total number of nitrogen atoms in two mol of NH4NO3? 15. On analysis, a compound with molar mass 60 g mol-1 was found t ...
... 13. 6.0 mol of aluminium reacts with oxygen to form aluminium oxide. What is the amount of oxygen, in mol, needed for complete reaction? 4Al(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Al2O3(s) 14. What is the total number of nitrogen atoms in two mol of NH4NO3? 15. On analysis, a compound with molar mass 60 g mol-1 was found t ...
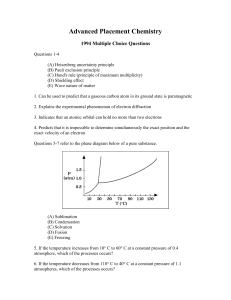
Advanced Placement Chemistry
... 16. Commercial vinegar was titrated with NaOH solution to determine the content of acetic acid, HC2H3O2. For 20.0 milliliters of the vinegar 26.7 milliliters of 0.600-molar NaOH solution was required. What was the concentration of acetic acid in the vinegar if no other acid was present? (A) 1.60 M ( ...
... 16. Commercial vinegar was titrated with NaOH solution to determine the content of acetic acid, HC2H3O2. For 20.0 milliliters of the vinegar 26.7 milliliters of 0.600-molar NaOH solution was required. What was the concentration of acetic acid in the vinegar if no other acid was present? (A) 1.60 M ( ...
GCE Chemistry Question Paper Unit 04 - Kinetics, Equilibria
... Use the data from Experiment 1 to calculate a value for the rate constant (k) at this temperature. Deduce the units of k. Calculation ......................................................................................................................... ...
... Use the data from Experiment 1 to calculate a value for the rate constant (k) at this temperature. Deduce the units of k. Calculation ......................................................................................................................... ...
Physics - Check Your Accuracy
... 5. On completion of the test, the candidate must handover the answer sheet to the invigilator in the room/ Hall. The candidates are allowed to take away this text booklet with them. 6. Make sure that the CODE printed on side – 2 of the answer sheet is the same as that on this booklet, In case of dis ...
... 5. On completion of the test, the candidate must handover the answer sheet to the invigilator in the room/ Hall. The candidates are allowed to take away this text booklet with them. 6. Make sure that the CODE printed on side – 2 of the answer sheet is the same as that on this booklet, In case of dis ...
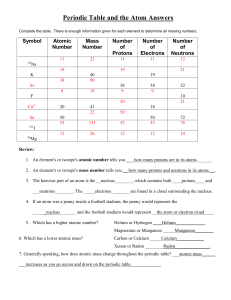
Periodic Table and the Atom Answers
... b) Arrange the pH in increasing order of hydrogen ion comcentration. 2) Define the term "pH"; what does" pH" stand for? Answer: The term "pH" is defined as the negative logarithm of H+ ion concentration of a given solution; the concentration being expressed as moles per litre. Mathematically pH = - ...
... b) Arrange the pH in increasing order of hydrogen ion comcentration. 2) Define the term "pH"; what does" pH" stand for? Answer: The term "pH" is defined as the negative logarithm of H+ ion concentration of a given solution; the concentration being expressed as moles per litre. Mathematically pH = - ...
Chemistry Reference Table Review
... 84. Based on Table G, a solution of NaNO3 that contains 120 grams of solute dissolved in 100 grams of H2O at 50°C is best described as (1) saturated and dilute (2) saturated and concentrated (3) supersaturated and dilute (4) supersaturated and concentrated 85. A student calculated the percent by mas ...
... 84. Based on Table G, a solution of NaNO3 that contains 120 grams of solute dissolved in 100 grams of H2O at 50°C is best described as (1) saturated and dilute (2) saturated and concentrated (3) supersaturated and dilute (4) supersaturated and concentrated 85. A student calculated the percent by mas ...
Document
... (determine the charge or oxidation number using your periodic table) Write the symbol for the negative ion second (determine the charge or oxidation number using your periodic table). An oxidation number (or charge) indicates how many electrons are lost, gained or shared when bonding occurs. ...
... (determine the charge or oxidation number using your periodic table) Write the symbol for the negative ion second (determine the charge or oxidation number using your periodic table). An oxidation number (or charge) indicates how many electrons are lost, gained or shared when bonding occurs. ...
Unit D: Quantitative Relationships in Chemical Change
... For each of the following questions, write a balanced chemical equation and then use the mole ratio to answer the question. 1. A student mixes together a solution of silver nitrate with a solution of sodium chromate and a precipitate forms. What amount of precipitate will form if the student has rea ...
... For each of the following questions, write a balanced chemical equation and then use the mole ratio to answer the question. 1. A student mixes together a solution of silver nitrate with a solution of sodium chromate and a precipitate forms. What amount of precipitate will form if the student has rea ...
Ionic Bonding
... noble gas core, they are not found in ionic compounds with a noble gas core (thus they may have color). Some examples which can form a noble gas core (and be colorless): Ag: [Kr]5s14d10 Ag+ [Kr]4d10 Compound: AgCl Cd: [Kr]5s24d10 Cd2+ [Kr]4d10 Compound: CdS The valence electrons do not adhere to the ...
... noble gas core, they are not found in ionic compounds with a noble gas core (thus they may have color). Some examples which can form a noble gas core (and be colorless): Ag: [Kr]5s14d10 Ag+ [Kr]4d10 Compound: AgCl Cd: [Kr]5s24d10 Cd2+ [Kr]4d10 Compound: CdS The valence electrons do not adhere to the ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.