Stoichiometry Worksheet #4
... 1. Silver sulfide (Ag2S) is the common tarnish on silver objects. What weight of silver sulfide can be made from 1.23 g of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) obtained from a rotten egg? The reaction of formation of silver sulfide is given below: Ag(s) + H2S(g) + O2(g) Ag2S(s) + H2O(l) (Equation must first be b ...
... 1. Silver sulfide (Ag2S) is the common tarnish on silver objects. What weight of silver sulfide can be made from 1.23 g of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) obtained from a rotten egg? The reaction of formation of silver sulfide is given below: Ag(s) + H2S(g) + O2(g) Ag2S(s) + H2O(l) (Equation must first be b ...
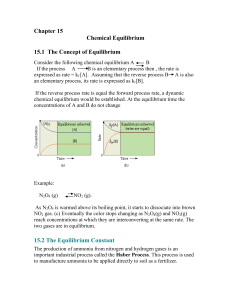
Consider the following chemical equilibrium A B
... As N2O4 is warmed above its boiling point, it starts to dissociate into brown NO2 gas. (c) Eventually the color stops changing as N2O4(g) and NO2(g) reach concentrations at which they are interconverting at the same rate. The two gases are in equilibrium. ...
... As N2O4 is warmed above its boiling point, it starts to dissociate into brown NO2 gas. (c) Eventually the color stops changing as N2O4(g) and NO2(g) reach concentrations at which they are interconverting at the same rate. The two gases are in equilibrium. ...
Final Review 2006
... ____ 30. Which observation does NOT indicate that a chemical reaction has occurred? a. formation of a precipitate c. evolution of heat and light b. production of a gas d. change in total mass of substances ____ 31. A solid produced by a chemical reaction in solution that separates from the solution ...
... ____ 30. Which observation does NOT indicate that a chemical reaction has occurred? a. formation of a precipitate c. evolution of heat and light b. production of a gas d. change in total mass of substances ____ 31. A solid produced by a chemical reaction in solution that separates from the solution ...
111 Exam I Outline
... IV. LIMITING REACTANTS When most reactions are performed, some of the reactants is usually present in excess of the amount needed. If the reaction goes to completion, then some of this excess reactant will be left-over. The limiting reactant is the reactant used-up completely and it "limits" the re ...
... IV. LIMITING REACTANTS When most reactions are performed, some of the reactants is usually present in excess of the amount needed. If the reaction goes to completion, then some of this excess reactant will be left-over. The limiting reactant is the reactant used-up completely and it "limits" the re ...
111 Exam I Outline
... IV. LIMITING REACTANTS When most reactions are performed, some of the reactants is usually present in excess of the amount needed. If the reaction goes to completion, then some of this excess reactant will be left-over. The limiting reactant is the reactant used-up completely and it "limits" the re ...
... IV. LIMITING REACTANTS When most reactions are performed, some of the reactants is usually present in excess of the amount needed. If the reaction goes to completion, then some of this excess reactant will be left-over. The limiting reactant is the reactant used-up completely and it "limits" the re ...
C:\D\Books\Cambridge University Press\CUP Problems\Problems.wpd
... Hint. See data in Table 1.7, assume the density of water is not affected by pressure and use eq 2.78. 20. Consider Figure 1.7. Why are oxides found primarily in the upper regions, and why does iron partition to the inside? 21. Geothermal power. Consider eqs 1.7 and 1.8. About how deep should one dr ...
... Hint. See data in Table 1.7, assume the density of water is not affected by pressure and use eq 2.78. 20. Consider Figure 1.7. Why are oxides found primarily in the upper regions, and why does iron partition to the inside? 21. Geothermal power. Consider eqs 1.7 and 1.8. About how deep should one dr ...
Introduction to Spectroscopic Methods ver.2
... display that has a linear scale extending from 0 to a 100%, operate in such a way that their readings are in percent transmittance, two preliminary adjustments are required. These are the dark current or 0%T adjustment and the 100%T adjustment. The 0%T adjustment is performed with the detector scree ...
... display that has a linear scale extending from 0 to a 100%, operate in such a way that their readings are in percent transmittance, two preliminary adjustments are required. These are the dark current or 0%T adjustment and the 100%T adjustment. The 0%T adjustment is performed with the detector scree ...
pdfInt 2 Homework Unit 2 1 MB
... Scientists have been experimenting to find ways of reducing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. One of these ways involves placing concrete balls on the sea bed. They hope that green plants called algae will grow on the balls and this will help to reduce the carbon dioxide level. Give a reason why the ...
... Scientists have been experimenting to find ways of reducing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. One of these ways involves placing concrete balls on the sea bed. They hope that green plants called algae will grow on the balls and this will help to reduce the carbon dioxide level. Give a reason why the ...
chemistry
... The compound contains two different positive ions. The gram-formula mass of KAl(SO4)2 •12H2O is 474 grams per mole. 66 Identify one positive ion in the hydrated compound. Your response must include both the chemical symbol and charge of the ion. [1] 67 Describe, in terms of composition, one way in w ...
... The compound contains two different positive ions. The gram-formula mass of KAl(SO4)2 •12H2O is 474 grams per mole. 66 Identify one positive ion in the hydrated compound. Your response must include both the chemical symbol and charge of the ion. [1] 67 Describe, in terms of composition, one way in w ...
H - JMap
... If you wish to change an answer, erase your first penciled circle and then circle with pencil the number of the answer you want. After you have completed the examination and you have decided that all of the circled answers represent your best judgment, signal a proctor and turn in all examination ma ...
... If you wish to change an answer, erase your first penciled circle and then circle with pencil the number of the answer you want. After you have completed the examination and you have decided that all of the circled answers represent your best judgment, signal a proctor and turn in all examination ma ...
AP® Chemistry
... 5.. Apply the solubility rules when predicting reaction products. 6. Solve problems involving molarity, molality, percent composition, mole —The course fraction, and normality; to be able to convert between concentration calculations and the designations. (Part of this covered in HC) 7. List the col ...
... 5.. Apply the solubility rules when predicting reaction products. 6. Solve problems involving molarity, molality, percent composition, mole —The course fraction, and normality; to be able to convert between concentration calculations and the designations. (Part of this covered in HC) 7. List the col ...
Chapter 8 Chemical Equations and Reactions
... i) The equation must represent known facts. ii) The equation must contain the correct formulas for the reactants and products. iii) The law of conservation of mass must be satisfied: A coefficient is a small whole number that appears in front of a formula in a chemical equation. ...
... i) The equation must represent known facts. ii) The equation must contain the correct formulas for the reactants and products. iii) The law of conservation of mass must be satisfied: A coefficient is a small whole number that appears in front of a formula in a chemical equation. ...
Chemistry_Stoichiome..
... 80. 100 mL of 10 % NaOH (w/V) is added to 100 mL of 10 % HCl (w/V). The resultant solution becomes: a) alkaline b) strongly alkaline c) acidic d) neutral 81. Calculate the molality of 1 L solution of 80 % H2SO4 (w/V), given that the density of the solution is 1.80 g mL−1 . a) 9.18 b) 8.6 c) 1.02 d) ...
... 80. 100 mL of 10 % NaOH (w/V) is added to 100 mL of 10 % HCl (w/V). The resultant solution becomes: a) alkaline b) strongly alkaline c) acidic d) neutral 81. Calculate the molality of 1 L solution of 80 % H2SO4 (w/V), given that the density of the solution is 1.80 g mL−1 . a) 9.18 b) 8.6 c) 1.02 d) ...
Lecture 13 11-20-02
... Our strategy for sketching a titration curve is simple. We begin by drawing our axes, placing pH on the y-axis and volume of titrant on the x-axis. After calculating the volume of titrant needed to reach the equivalence point, we draw a vertical line that intersects the x-axis at this volume. Next, ...
... Our strategy for sketching a titration curve is simple. We begin by drawing our axes, placing pH on the y-axis and volume of titrant on the x-axis. After calculating the volume of titrant needed to reach the equivalence point, we draw a vertical line that intersects the x-axis at this volume. Next, ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.