Chem 12 UNIT TWO CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM 7.1 REVERSIBLE
... Entropy can be defined as the measure of the randomness of a chemical system. A large value for entropy means very random. If entropy increases during a chemical reaction, it means the system is becoming more random or disordered. These two variables are related in the Gibb's free energy equation wh ...
... Entropy can be defined as the measure of the randomness of a chemical system. A large value for entropy means very random. If entropy increases during a chemical reaction, it means the system is becoming more random or disordered. These two variables are related in the Gibb's free energy equation wh ...
Redalyc.Chalcopyrite Leaching in Acidic Chloride Solution without
... concentration of 8 ppm. For the tests without dissolved oxygen, an inert gas (nitrogen) was bubbled previously into the solutions to remove the majority of dissolved oxygen and lower its residual concentration to less than 1 ppm. The experimental conditions that varied were dissolved oxygen concentr ...
... concentration of 8 ppm. For the tests without dissolved oxygen, an inert gas (nitrogen) was bubbled previously into the solutions to remove the majority of dissolved oxygen and lower its residual concentration to less than 1 ppm. The experimental conditions that varied were dissolved oxygen concentr ...
MSWord_examle - Magnetic Resonance in Solids
... In paper [7] CEF parameters of Yb3+ ion in KMgF3 crystal have been found (tab. 5). Using the least squares method the experimental values of g-factors (tab. 2) and experimental energy of whole 2F term levels have been taken into account. Obtained CEF parameters satisfy the experimental energy scheme ...
... In paper [7] CEF parameters of Yb3+ ion in KMgF3 crystal have been found (tab. 5). Using the least squares method the experimental values of g-factors (tab. 2) and experimental energy of whole 2F term levels have been taken into account. Obtained CEF parameters satisfy the experimental energy scheme ...
HYDROGEN BONDING AND OTHER MOLECULAR
... Some points to ponder about! • The OH•••∆ interaction is like a typical hydrogen bond as the electron density in CH4 is maximum in that region. • The dispersion energy is responsible for the overall anisotropy of the potential energy surface (in CH4-H2O complex) and obtaining the right global minim ...
... Some points to ponder about! • The OH•••∆ interaction is like a typical hydrogen bond as the electron density in CH4 is maximum in that region. • The dispersion energy is responsible for the overall anisotropy of the potential energy surface (in CH4-H2O complex) and obtaining the right global minim ...
chemistry module p
... In a solid the particles are packed closely together. The particles can vibrate but they cannot move around. Therefore the solid has a fixed shape and volume (when at constant temperature). Because the particles are very close together and in fixed positions, solids are virtually incompressible. A s ...
... In a solid the particles are packed closely together. The particles can vibrate but they cannot move around. Therefore the solid has a fixed shape and volume (when at constant temperature). Because the particles are very close together and in fixed positions, solids are virtually incompressible. A s ...
YU-ISSN 0352-5139
... The protonations of maleic and fumaric acid in an acidic medium (aqueous solutions of sulfuric acid) were followed spectrophotometrically at room temperature. The acid-base equilibria were characterised qualitatively and quantitatively. The pKBH+ values were determined using the Hammett equation, em ...
... The protonations of maleic and fumaric acid in an acidic medium (aqueous solutions of sulfuric acid) were followed spectrophotometrically at room temperature. The acid-base equilibria were characterised qualitatively and quantitatively. The pKBH+ values were determined using the Hammett equation, em ...
- Gondwana University, Gadchiroli
... isothermal & adiabatic conditions for reversible process, carnot’s cycle & its efficiency, thermodynamic scale of temperature. [5L] (C) Thermochemistry: Heat of reaction, standard states, relation between heat of reaction at constant volume & at constant pressure, Hess’s law of constant heat of summ ...
... isothermal & adiabatic conditions for reversible process, carnot’s cycle & its efficiency, thermodynamic scale of temperature. [5L] (C) Thermochemistry: Heat of reaction, standard states, relation between heat of reaction at constant volume & at constant pressure, Hess’s law of constant heat of summ ...
some basic concepts of chemistry
... Total mass of the products (KCl + O2) = 2.96 + 1.92 = 4.88 g Difference between the mass of the reactant and the total mass of the products = 4.90 – 4.88 = 0.02 g. This small difference may be due to experimental error. Thus, law of conservation of mass holds good within experimental errors. Q. Defi ...
... Total mass of the products (KCl + O2) = 2.96 + 1.92 = 4.88 g Difference between the mass of the reactant and the total mass of the products = 4.90 – 4.88 = 0.02 g. This small difference may be due to experimental error. Thus, law of conservation of mass holds good within experimental errors. Q. Defi ...
Solubility and Complex-ion Equilibria
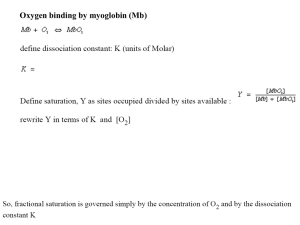
... – The effect is to make calcium oxalate less soluble than it would be in pure water. ...
... – The effect is to make calcium oxalate less soluble than it would be in pure water. ...
reviewTWO
... How many moles of oxygen are needed to react with 0.1 mole of CH4 How many moles of CO2 are produced from 0.1 moles of CH4 How many moles of water are produced from 0.1 moles of CH4 How many moles of carbon dioxide will be produced by 0.1 mole of oxygen gas? How many moles of oxygen gas will react c ...
... How many moles of oxygen are needed to react with 0.1 mole of CH4 How many moles of CO2 are produced from 0.1 moles of CH4 How many moles of water are produced from 0.1 moles of CH4 How many moles of carbon dioxide will be produced by 0.1 mole of oxygen gas? How many moles of oxygen gas will react c ...
Chapter 2
... in a chemical reaction. Elements can only be converted into other elements in nuclear reactions. 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines the chemical behavior of the element. Isotopes of an element differ in the number of neutrons, and thus in mass ...
... in a chemical reaction. Elements can only be converted into other elements in nuclear reactions. 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines the chemical behavior of the element. Isotopes of an element differ in the number of neutrons, and thus in mass ...
File
... (b) Enzymes are particular types of proteins that catalyse chemical reactions. The efficiency of enzymes can be reduced by the presence of other molecules known as inhibitors. Explain how both competitive and non-competitive inhibitors prevent enzymes from ...
... (b) Enzymes are particular types of proteins that catalyse chemical reactions. The efficiency of enzymes can be reduced by the presence of other molecules known as inhibitors. Explain how both competitive and non-competitive inhibitors prevent enzymes from ...
Welcome`to`AP`Chemistry!
... positive)(right))direction)four)places.))[The)decimal)moves)the)number)of)places)equal)to)the)exponent.]))We)then)get)98100) as)our)answer)[move)the)decimal)four)places)right:)9)8)1)0)0].) ...
... positive)(right))direction)four)places.))[The)decimal)moves)the)number)of)places)equal)to)the)exponent.]))We)then)get)98100) as)our)answer)[move)the)decimal)four)places)right:)9)8)1)0)0].) ...
6 theoretical problems 2 practical problems
... are concrete and steel. This problem deals with chemical reactions relating to production and degradation of such materials. Concrete is produced from a mixture of cement, water, sand and small stones. Cement consists primarily of calcium silicates and calcium aluminates formed by heating and grindi ...
... are concrete and steel. This problem deals with chemical reactions relating to production and degradation of such materials. Concrete is produced from a mixture of cement, water, sand and small stones. Cement consists primarily of calcium silicates and calcium aluminates formed by heating and grindi ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.