CLASS X carbon and its compound
... Ethanol reacts with sodium and potassium to form their respective ethoxides and hydrogen gas. Ethanol gets dehydrated to ethene when heated with conc. sulphuric acid at 443 K (170°C). Methylated spirit is ethanol in which a small amount of methanol is mixed. This makes it unfit for drinking purposes ...
... Ethanol reacts with sodium and potassium to form their respective ethoxides and hydrogen gas. Ethanol gets dehydrated to ethene when heated with conc. sulphuric acid at 443 K (170°C). Methylated spirit is ethanol in which a small amount of methanol is mixed. This makes it unfit for drinking purposes ...
Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions
... System being developed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) to replace the retired Space Shuttle fleet (Figure 4.1). The engines of these rockets rely on carefully prepared solid mixtures of chemicals combined in precisely measured amounts. Igniting the mixture initiates a vig ...
... System being developed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) to replace the retired Space Shuttle fleet (Figure 4.1). The engines of these rockets rely on carefully prepared solid mixtures of chemicals combined in precisely measured amounts. Igniting the mixture initiates a vig ...
Final Review 2
... a) They have similar sizes b) They have similar electronegativities c) Nonmetals prefer to share electrons rather than transfer them d) None of the above 78) Why do covalent compounds usually have lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds? a) No bonds need to be broken to melt a covalent ...
... a) They have similar sizes b) They have similar electronegativities c) Nonmetals prefer to share electrons rather than transfer them d) None of the above 78) Why do covalent compounds usually have lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds? a) No bonds need to be broken to melt a covalent ...
Smith Reaction- HW PSI Chemistry
... 53) The type of reaction that takes place when one metal reacts with a metal compound to form a new compound and a different metal is a _____. A) combination reaction B) decomposition reaction C) single-replacement reaction D) double-replacement reaction E) combustion reaction 54) In a double-replac ...
... 53) The type of reaction that takes place when one metal reacts with a metal compound to form a new compound and a different metal is a _____. A) combination reaction B) decomposition reaction C) single-replacement reaction D) double-replacement reaction E) combustion reaction 54) In a double-replac ...
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com Downloaded from www
... Due to more reduction electrode potential value of Cu+, it undergoes oxidation reaction quite feasibly. Hence, Copper (I) ion is not known in aqueous solution. The actinoids show a larger number of oxidation states because of very small energy gap between the 5f, 6d and 7s sub-shells. Hence all thei ...
... Due to more reduction electrode potential value of Cu+, it undergoes oxidation reaction quite feasibly. Hence, Copper (I) ion is not known in aqueous solution. The actinoids show a larger number of oxidation states because of very small energy gap between the 5f, 6d and 7s sub-shells. Hence all thei ...
Chemistry for Changing Times 11th Edition Hill and Kolb
... Reactants → Products The arrow (→) means “yield(s)” or “react(s) to produce”. © 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. ...
... Reactants → Products The arrow (→) means “yield(s)” or “react(s) to produce”. © 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. ...
Downloaded - University of San Diego
... profile throughout the presheath in an Ar – Xe plasma with comparable Ar and Xe densities are shown in Fig. 1. These data show the difference in flow speeds throughout the presheath is small and that the difference in rms drift velocity never exceeds 175 6 50 m/s. The heavy ion (Xe) velocity is fast ...
... profile throughout the presheath in an Ar – Xe plasma with comparable Ar and Xe densities are shown in Fig. 1. These data show the difference in flow speeds throughout the presheath is small and that the difference in rms drift velocity never exceeds 175 6 50 m/s. The heavy ion (Xe) velocity is fast ...
Practice Test Stoichiometry
... 17.) A hydrocarbon (a compound consisting solely of carbon and hydrogen) is found to be 85.6% carbon by mass. What is the empirical formula for this compound? A) CH B) CH2 C) C2H D) C3H E) CH4 18.) The empirical formula of a group of compounds is CHCl. Lindane, a powerful insecticide, is a member o ...
... 17.) A hydrocarbon (a compound consisting solely of carbon and hydrogen) is found to be 85.6% carbon by mass. What is the empirical formula for this compound? A) CH B) CH2 C) C2H D) C3H E) CH4 18.) The empirical formula of a group of compounds is CHCl. Lindane, a powerful insecticide, is a member o ...
(General Equilibrium) Part 1
... 2. water- molar concentration is constant in aqueous solutions. (55.6M) (This is not true in gas phase reactions that produce water.) 3. Concentrations of pure solids or pure liquids are _________ (their activity is set to “1”.) when writing the equilibrium equation for any heterogeneous equilibriu ...
... 2. water- molar concentration is constant in aqueous solutions. (55.6M) (This is not true in gas phase reactions that produce water.) 3. Concentrations of pure solids or pure liquids are _________ (their activity is set to “1”.) when writing the equilibrium equation for any heterogeneous equilibriu ...
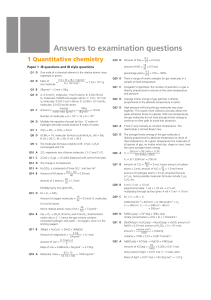
Answers to examination questions
... has two lone pairs around the central atom, compared with one for ammonia and none for methane. Lone pair repulsion is greater than bonding pair repulsion. ...
... has two lone pairs around the central atom, compared with one for ammonia and none for methane. Lone pair repulsion is greater than bonding pair repulsion. ...
Sample Exercise 20.1 Identifying Oxidizing and Reducing Agents
... Now we can use the summary in Figure 20.6 to help us describe the voltaic cell. The first half-reaction is the reduction process (electrons on the reactant side of the equation). By definition, the reduction process occurs at the cathode. The second half-reaction is the oxidation process (electrons ...
... Now we can use the summary in Figure 20.6 to help us describe the voltaic cell. The first half-reaction is the reduction process (electrons on the reactant side of the equation). By definition, the reduction process occurs at the cathode. The second half-reaction is the oxidation process (electrons ...
Multivalent Ionic Compounds
... 12. Draw Lewis Diagrams for the atoms and ions of the first 18 elements in the Periodic Table. If the element does not form an ion simply state “no ion”. The first two are done for you as an example. Hint: Ions are usually formed by losing all electrons in the Lewis diagram or gaining enough to crea ...
... 12. Draw Lewis Diagrams for the atoms and ions of the first 18 elements in the Periodic Table. If the element does not form an ion simply state “no ion”. The first two are done for you as an example. Hint: Ions are usually formed by losing all electrons in the Lewis diagram or gaining enough to crea ...
Chapter 23 The Chemistry of Amines
... product A can form an ethyl ether, its —OH group is not affected in the first reaction. Consequently, compound A is p-acetamidophenol and compound B is its ethyl ether. This is reasonable because, so long as the hydroxy group is not ionized, the amino group is the most basic group in the molecule, a ...
... product A can form an ethyl ether, its —OH group is not affected in the first reaction. Consequently, compound A is p-acetamidophenol and compound B is its ethyl ether. This is reasonable because, so long as the hydroxy group is not ionized, the amino group is the most basic group in the molecule, a ...
Honors Chemistry Unit 4 Student Packet: Honors Chemistry Problem
... The volume occupied by one mole of a gas is dependent on the Molar mass of the gas. The volume of a gas at STP can be calculated from the number of molecules of the gas. It is necessary to know the formula of a compound in order to calculate its percent composition. If the percent by mass of carbon ...
... The volume occupied by one mole of a gas is dependent on the Molar mass of the gas. The volume of a gas at STP can be calculated from the number of molecules of the gas. It is necessary to know the formula of a compound in order to calculate its percent composition. If the percent by mass of carbon ...
C - Thierry Karsenti
... Solutions are important in that many chemical reactions occur in solutions. In order for a chemical reaction to occur, molecules must come into contact. Solutions allow intimate contact of molecules of different types thereby facilitating chemical reactions. The study of solutions is important as mo ...
... Solutions are important in that many chemical reactions occur in solutions. In order for a chemical reaction to occur, molecules must come into contact. Solutions allow intimate contact of molecules of different types thereby facilitating chemical reactions. The study of solutions is important as mo ...
Chem 11 Notes Booklet (pdf version)
... Remember that the unit for energy is the Joule (J). b) Physical State - Chemical reactions often depend on the physical state of the chemicals involved. This information can be included in an equation by using these symbols: (s) = solid (l) = liquid (g) = gas (a) = aqueous (dissolved in water) For e ...
... Remember that the unit for energy is the Joule (J). b) Physical State - Chemical reactions often depend on the physical state of the chemicals involved. This information can be included in an equation by using these symbols: (s) = solid (l) = liquid (g) = gas (a) = aqueous (dissolved in water) For e ...
Worked out problems
... Now we can use the summary in Figure 20.6 to help us describe the voltaic cell. The first half-reaction is the reduction process (electrons on the reactant side of the equation). By definition, the reduction process occurs at the cathode. The second half-reaction is the oxidation process (electrons ...
... Now we can use the summary in Figure 20.6 to help us describe the voltaic cell. The first half-reaction is the reduction process (electrons on the reactant side of the equation). By definition, the reduction process occurs at the cathode. The second half-reaction is the oxidation process (electrons ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.