Slide 1
... in 1713 gave Nova Scotia, Newfoundland and Hudson Bay to England and limited rights with Spanish America. • The War of Jenkins Ear – War was waged in Caribbean Sea and Georgia, merged with war of Austria succession called King George’s war. • France allied with Spain, but New England colonial troops ...
... in 1713 gave Nova Scotia, Newfoundland and Hudson Bay to England and limited rights with Spanish America. • The War of Jenkins Ear – War was waged in Caribbean Sea and Georgia, merged with war of Austria succession called King George’s war. • France allied with Spain, but New England colonial troops ...
Colonizing North America
... In 1610, Dutch traders began trading with Native Americans in the Hudson River valley. ...
... In 1610, Dutch traders began trading with Native Americans in the Hudson River valley. ...
The Colonies
... (later Charleston) in 1670. The Barbadian immigrants brought their slaves with them, thus establishing African slaves in South Carolina. During the first generation of the colony, Carolina served primarily as an economic colony of Barbados, exporting everything from livestock to timber back to the i ...
... (later Charleston) in 1670. The Barbadian immigrants brought their slaves with them, thus establishing African slaves in South Carolina. During the first generation of the colony, Carolina served primarily as an economic colony of Barbados, exporting everything from livestock to timber back to the i ...
Summary
... left his wife and children and fled south. After trudging through snow for days, he met a group of Indians near Narragansett Bay. The Indians cared for him until spring. When his family and a few followers joined him, Williams bought land from the Indians for a settlement. He called it Providence, a ...
... left his wife and children and fled south. After trudging through snow for days, he met a group of Indians near Narragansett Bay. The Indians cared for him until spring. When his family and a few followers joined him, Williams bought land from the Indians for a settlement. He called it Providence, a ...
Background information
... should turn those raw materials into more expensive finished goods which it, in turn, could export to other countries or back to its colonies. For example, the American colonies were expected to export wood but not furniture, naval stores but not ships, and crops such as tobacco and rice but not the ...
... should turn those raw materials into more expensive finished goods which it, in turn, could export to other countries or back to its colonies. For example, the American colonies were expected to export wood but not furniture, naval stores but not ships, and crops such as tobacco and rice but not the ...
US History Ch 3 PP Notes
... expansion of the colonies? • Why did the Great Awakening both resolve and contribute to religious tensions? ...
... expansion of the colonies? • Why did the Great Awakening both resolve and contribute to religious tensions? ...
The Road to Independence
... The early 1600s saw the beginning of a great tide of emigration from Europe to North America. Spanning more than three centuries, this movement grew from a trickle of a few hundred English colonists to a flood of millions of newcomers. Impelled by powerful and diverse motivations, they built a new c ...
... The early 1600s saw the beginning of a great tide of emigration from Europe to North America. Spanning more than three centuries, this movement grew from a trickle of a few hundred English colonists to a flood of millions of newcomers. Impelled by powerful and diverse motivations, they built a new c ...
Slavery
... Slavery and the British Empire Slave Systems in the English Colonies – Three distinct slave systems were well entrenched in Britain’s mainland colonies • Chesapeake • South Carolina and Georgia • Non- plantation societies of New England and the Middle Colonies – Chesapeake slavery was based on toba ...
... Slavery and the British Empire Slave Systems in the English Colonies – Three distinct slave systems were well entrenched in Britain’s mainland colonies • Chesapeake • South Carolina and Georgia • Non- plantation societies of New England and the Middle Colonies – Chesapeake slavery was based on toba ...
The American Colonies: Introduction This chapter begins with a
... Chesapeake, and one out of eight was black. In 1650, slavery was still a relatively minor institution in Virginia and Maryland but, beginning in the 1670s, tobacco planters began a transition from servant to slave labor that portended slaveryʹs full adoption and institutionalization in the Americ ...
... Chesapeake, and one out of eight was black. In 1650, slavery was still a relatively minor institution in Virginia and Maryland but, beginning in the 1670s, tobacco planters began a transition from servant to slave labor that portended slaveryʹs full adoption and institutionalization in the Americ ...
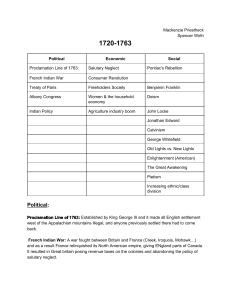
17201763
... Treaty of Paris: Signed on February 10th by Great Britain, France, and Spain. France gave up all of its northern territories and Spain gave the US Florida. ...
... Treaty of Paris: Signed on February 10th by Great Britain, France, and Spain. France gave up all of its northern territories and Spain gave the US Florida. ...
The French and Indian War
... The French and Indian War lasted nearly seven years, and moved forward in three distinct phases. During the first phase (from the debacle at Fort Necessity in 1754, until the expansion of the war to Europe in 1756) it was primarily a local, North American conflict. The English didn’t do very well in ...
... The French and Indian War lasted nearly seven years, and moved forward in three distinct phases. During the first phase (from the debacle at Fort Necessity in 1754, until the expansion of the war to Europe in 1756) it was primarily a local, North American conflict. The English didn’t do very well in ...
Henretta CHP 02 powerpoint.pptx
... mortality rate of more than 40% in the first year." • So why after 1660, were indentured servants increasingly replaced by African slaves?" ...
... mortality rate of more than 40% in the first year." • So why after 1660, were indentured servants increasingly replaced by African slaves?" ...
The Breach Widens: Resistance to the Monarchy
... • The 2nd Continental Congress is called and delegates from all 13 colonies meet in Philadelphia on May 10, 1775 to discuss what should be done in response to the new situations brought about by British aggression. ...
... • The 2nd Continental Congress is called and delegates from all 13 colonies meet in Philadelphia on May 10, 1775 to discuss what should be done in response to the new situations brought about by British aggression. ...
The Colonies Come of Age
... The War lasted until 1763 Treaty of Paris was signed which gave Britain control of all land East of the Mississippi River ...
... The War lasted until 1763 Treaty of Paris was signed which gave Britain control of all land East of the Mississippi River ...
Lesson 3 Middle Colonies
... land belonged to the Native Americans and that settlers should pay for it. He negotiated several treaties with local Native Americans. Penn advertised his colony throughout Europe. By 1683, more than 3,000 English, Welsh, Irish, Dutch, and German settlers had arrived. In 1701, in the Charter of Priv ...
... land belonged to the Native Americans and that settlers should pay for it. He negotiated several treaties with local Native Americans. Penn advertised his colony throughout Europe. By 1683, more than 3,000 English, Welsh, Irish, Dutch, and German settlers had arrived. In 1701, in the Charter of Priv ...
Late Colonial Society
... Vast majority of the population was still east of the Appalachian Mountains, near the coast, but some were beginning to move west, even beyond the mountains to today’s Tennessee and Kentucky Major cities: Philadelphia, New York, Boston and Charleston; still, about 90% lived in rural areas A Mingling ...
... Vast majority of the population was still east of the Appalachian Mountains, near the coast, but some were beginning to move west, even beyond the mountains to today’s Tennessee and Kentucky Major cities: Philadelphia, New York, Boston and Charleston; still, about 90% lived in rural areas A Mingling ...
File - Mr. Harris History
... Took his people and moved to form a colony called Connecticut Fundamental Orders of Connecticut First written constitution in America ...
... Took his people and moved to form a colony called Connecticut Fundamental Orders of Connecticut First written constitution in America ...
Give Me Liberty (New British Policies)
... British officer George Washington was sent to build a fort on the river but was defeated by the French before he could. Native Americans became French allies because it appeared the French would win the war. North American land claims, 1753 ...
... British officer George Washington was sent to build a fort on the river but was defeated by the French before he could. Native Americans became French allies because it appeared the French would win the war. North American land claims, 1753 ...
Exploration Colonization IFD presentation
... voting rights to non-church members helping to bring about representative government. Many people in the area did not like having to live under the strict rules of the Puritans. ...
... voting rights to non-church members helping to bring about representative government. Many people in the area did not like having to live under the strict rules of the Puritans. ...
Notes on Acts
... Declaration of Colonial Rights and Grievances b. stated Parliament lacked power to impose taxes on subjects because colonists were not represented in Parliament and colonists had same rights and liberties as the King’s subjects in England E. British Response to Stamp Act Congress 1. Parliament respo ...
... Declaration of Colonial Rights and Grievances b. stated Parliament lacked power to impose taxes on subjects because colonists were not represented in Parliament and colonists had same rights and liberties as the King’s subjects in England E. British Response to Stamp Act Congress 1. Parliament respo ...
Unit 1: Pre-Columbus Americas through John Adams` Administration
... 1606: The Virginia Company, a joint-stock company, received a charter from the King James I of England for settlement of the New World. o The Virginia Co. was intended to last only a few years, as they hoped to yield a profit, and then liquidate the company. o The charter of the Virginia Co. is si ...
... 1606: The Virginia Company, a joint-stock company, received a charter from the King James I of England for settlement of the New World. o The Virginia Co. was intended to last only a few years, as they hoped to yield a profit, and then liquidate the company. o The charter of the Virginia Co. is si ...
Unit 1: Pre-Columbus Americas through John Adams` Administration
... 1606: The Virginia Company, a joint-stock company, received a charter from the King James I of England for settlement of the New World. o The Virginia Co. was intended to last only a few years, as they hoped to yield a profit, and then liquidate the company. o The charter of the Virginia Co. is si ...
... 1606: The Virginia Company, a joint-stock company, received a charter from the King James I of England for settlement of the New World. o The Virginia Co. was intended to last only a few years, as they hoped to yield a profit, and then liquidate the company. o The charter of the Virginia Co. is si ...
English Colonization in the 19 Century
... Vague boundaries were established and true boundaries weren’t established until the mid 18th Century by the surveyors Charles Mason and Jeremiah Dixon (Mason-Dixon Line) Maryland named in honor of King Charles’ wife Maryland was established as a colony for Catholics, but freedom of religion would ex ...
... Vague boundaries were established and true boundaries weren’t established until the mid 18th Century by the surveyors Charles Mason and Jeremiah Dixon (Mason-Dixon Line) Maryland named in honor of King Charles’ wife Maryland was established as a colony for Catholics, but freedom of religion would ex ...