The Sun and Planets Homework 2.
... is increasing. In the past there were more days per year and in the future there will be fewer days per year. However, the length of the year is not changing perceptibly. Instead, it is the rotation of the Earth that is changing; the rotation is slowing down which causes longer days. Likewise, the r ...
... is increasing. In the past there were more days per year and in the future there will be fewer days per year. However, the length of the year is not changing perceptibly. Instead, it is the rotation of the Earth that is changing; the rotation is slowing down which causes longer days. Likewise, the r ...
Chapter 11
... Now considered Dwarf Planet – a celestial body orbiting the Sun that is generally smaller than a planet but massive enough for its own gravity to give it a round shape. However they are not strong enough to clear their orbit of debris There are many other “dwarf planets” some are bigger and some lik ...
... Now considered Dwarf Planet – a celestial body orbiting the Sun that is generally smaller than a planet but massive enough for its own gravity to give it a round shape. However they are not strong enough to clear their orbit of debris There are many other “dwarf planets” some are bigger and some lik ...
A. Objects in the Universe
... simultaneously. The distance from the Sun varies due to Earth’s elliptical orbit. (MS) ...
... simultaneously. The distance from the Sun varies due to Earth’s elliptical orbit. (MS) ...
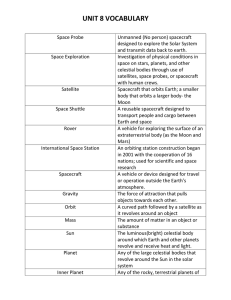
unit 8 vocabulary
... A natural chunk of rock or dust existing outside Earth’s atmosphere. Remains of meteoroids that strike the surface of Earth or the Moon Piece of rock or metal made up of material similar to that which formed the planets that orbit the sun The region of interplanetary space between the inner and oute ...
... A natural chunk of rock or dust existing outside Earth’s atmosphere. Remains of meteoroids that strike the surface of Earth or the Moon Piece of rock or metal made up of material similar to that which formed the planets that orbit the sun The region of interplanetary space between the inner and oute ...
webquest – solar system - Teach
... 1. You are going on a mission to space. Sit in pairs. Write down five words you can think of which are related to the Solar System. ...
... 1. You are going on a mission to space. Sit in pairs. Write down five words you can think of which are related to the Solar System. ...
Astronomy Unit – Part 3: The Planets Terrestrial Planet – the four
... Terrestrial Planet – the four small, dense, rocky planets that orbit closest to the sun Astronomical Unit (AU) – the average distance between the sun and the Earth, or 150 million km. Prograde Rotation – counterclockwise spin of a planet. Retrograde Rotation – the clockwise spin of a planet. (Venus) ...
... Terrestrial Planet – the four small, dense, rocky planets that orbit closest to the sun Astronomical Unit (AU) – the average distance between the sun and the Earth, or 150 million km. Prograde Rotation – counterclockwise spin of a planet. Retrograde Rotation – the clockwise spin of a planet. (Venus) ...
Station 1: Planet Earth * Size, Distance and Location
... from the Sun to Earth? • The Sun is at an average distance of about 93,000,000 miles (150 million kilometers) away from Earth. It is so far away that light from the Sun, traveling at a speed of 186,000 miles (300,000 kilometers) per second, takes about 8 minutes to reach us. ...
... from the Sun to Earth? • The Sun is at an average distance of about 93,000,000 miles (150 million kilometers) away from Earth. It is so far away that light from the Sun, traveling at a speed of 186,000 miles (300,000 kilometers) per second, takes about 8 minutes to reach us. ...
day 1 lesson plan - University of Chicago
... different weights on the other planets? If so, on which planet do you think you weigh the least? the most? Go over opener (5min) Introduce todayʼs topics: Universal Gravitation (10 mins) Universal Gravitation: Law of universal gravitation: Fgravity ...
... different weights on the other planets? If so, on which planet do you think you weigh the least? the most? Go over opener (5min) Introduce todayʼs topics: Universal Gravitation (10 mins) Universal Gravitation: Law of universal gravitation: Fgravity ...
SC Astronauts - Knowitall.org
... 8.E.4A.2 Construct and analyze scientific arguments to support claims that the universe began with a period of extreme and rapid expansion using evidence from the composition of stars and gases and the motion of galaxies in the universe. Standard 8.E.4 The student will demonstrate an understanding o ...
... 8.E.4A.2 Construct and analyze scientific arguments to support claims that the universe began with a period of extreme and rapid expansion using evidence from the composition of stars and gases and the motion of galaxies in the universe. Standard 8.E.4 The student will demonstrate an understanding o ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... b) Smaller circular motions on the larger orbit c) Explained retrograde motion ...
... b) Smaller circular motions on the larger orbit c) Explained retrograde motion ...
3-4 Astronomy Review 2
... 4. What is a galaxy? What are the three different categories of galaxies? How are these types of galaxies different from one another? How are many galaxies held together? ...
... 4. What is a galaxy? What are the three different categories of galaxies? How are these types of galaxies different from one another? How are many galaxies held together? ...
Slide 1
... the equator) from some point in the Northern Hemisphere will be deflected to its right (west). Effects such as these that come about because we live on a rotating frame of reference are referred to as Coriolis ...
... the equator) from some point in the Northern Hemisphere will be deflected to its right (west). Effects such as these that come about because we live on a rotating frame of reference are referred to as Coriolis ...
Ch. 28.3 Formation of the Solar System
... Formation of the Sun • Solar nebula—the cloud of dust and gas that developed into our solar system. • A shock wave hitting the nebula caused it to start contracting 4 or 5 billion years ago. • The sun formed in its center. • 99% of the nebula’s matter became the sun. ...
... Formation of the Sun • Solar nebula—the cloud of dust and gas that developed into our solar system. • A shock wave hitting the nebula caused it to start contracting 4 or 5 billion years ago. • The sun formed in its center. • 99% of the nebula’s matter became the sun. ...
Friday 25th October 2013 4.00 p.m. Professor Linda T. Elkins
... impact on Earth, had been thought to dry their target materials through heat and fragmentation. New mission data from Mars, the Moon, and Mercury, however, all indicate that these bodies have water in their interiors that originated with accretion, and so accretionary processes do not dry rocky plan ...
... impact on Earth, had been thought to dry their target materials through heat and fragmentation. New mission data from Mars, the Moon, and Mercury, however, all indicate that these bodies have water in their interiors that originated with accretion, and so accretionary processes do not dry rocky plan ...
Chapter 28.3
... Formation of the Sun • Solar nebula—the cloud of dust and gas that developed into our solar system. • A shock wave hitting the nebula caused it to start contracting 4 or 5 billion years ago. • The sun formed in its center. • 99% of the nebula’s matter became the sun. ...
... Formation of the Sun • Solar nebula—the cloud of dust and gas that developed into our solar system. • A shock wave hitting the nebula caused it to start contracting 4 or 5 billion years ago. • The sun formed in its center. • 99% of the nebula’s matter became the sun. ...
The Solar System Ch. 28
... of the solar system that states that the sun is the center of the solar system and the planets revolve around it ...
... of the solar system that states that the sun is the center of the solar system and the planets revolve around it ...
The Change in the Mass of the Sun and the Expansion of the Solar
... mass/year, corresponding to an increase in the radius of Earth’s orbit of 1.5 cm/yr. But the Earth’s orbital velocity also decreases and since angular momentum remains conserved, the velocity is further reduced. There is also the possibility that G changes although neither a change in G or M have ac ...
... mass/year, corresponding to an increase in the radius of Earth’s orbit of 1.5 cm/yr. But the Earth’s orbital velocity also decreases and since angular momentum remains conserved, the velocity is further reduced. There is also the possibility that G changes although neither a change in G or M have ac ...
The Solar System, Planets and Small Celestial Bodies
... Big Bang Theory • Scientific theory of the origin of the universe • 10-15 billion years ago all matter came together to one point • Due to density and high temperature a huge explosion (big bang) occurred • Since the beginning universe has been expanding • Galaxies moving away from each other ...
... Big Bang Theory • Scientific theory of the origin of the universe • 10-15 billion years ago all matter came together to one point • Due to density and high temperature a huge explosion (big bang) occurred • Since the beginning universe has been expanding • Galaxies moving away from each other ...
Name Date ______ Go to the Planet 10 Web Site: http://www
... 9. Two types of solar objects are Asteroids and Comets. Click the information button for each one on the left and read about them. There are 3 pages of information to read about comets and 2 pages to read about asteroids. What did you learn? ...
... 9. Two types of solar objects are Asteroids and Comets. Click the information button for each one on the left and read about them. There are 3 pages of information to read about comets and 2 pages to read about asteroids. What did you learn? ...
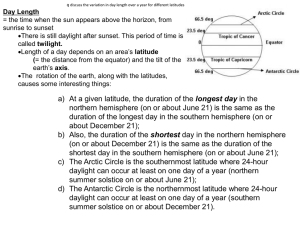
Earth's rotation

Earth's rotation is the rotation of the planet Earth around its own axis. The Earth rotates from the west towards east. As viewed from North Star or polestar Polaris, the Earth turns counter-clockwise.The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. This point is distinct from the Earth's North Magnetic Pole. The South Pole is the other point where the Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface, in Antarctica.The Earth rotates once in about 24 hours with respect to the sun and once every 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds with respect to the stars (see below). Earth's rotation is slowing slightly with time; thus, a day was shorter in the past. This is due to the tidal effects the Moon has on Earth's rotation. Atomic clocks show that a modern-day is longer by about 1.7 milliseconds than a century ago, slowly increasing the rate at which UTC is adjusted by leap seconds.