Invitation to the Life Span by Kathleen Stassen Berger
... • An extension of behaviorism that emphasizes the influence that other people have over a person’s behavior. • Modeling- people learn by observing other people and then copying them. • Self-efficacy- how effective people think they are when it comes to changing themselves or altering their social co ...
... • An extension of behaviorism that emphasizes the influence that other people have over a person’s behavior. • Modeling- people learn by observing other people and then copying them. • Self-efficacy- how effective people think they are when it comes to changing themselves or altering their social co ...
PSYC200 Chapter 2
... • An extension of behaviorism that emphasizes the influence that other people have over a person’s behavior. • Modeling- people learn by observing other people and then copying them. • Self-efficacy- how effective people think they are when it comes to changing themselves or altering their social co ...
... • An extension of behaviorism that emphasizes the influence that other people have over a person’s behavior. • Modeling- people learn by observing other people and then copying them. • Self-efficacy- how effective people think they are when it comes to changing themselves or altering their social co ...
comstock_daniel auditory_oddball_task
... Lobe during the experiment using a 64 sensor electrode net. ...
... Lobe during the experiment using a 64 sensor electrode net. ...
History and Approaches History Hippocrates
... • these were observations, ruminations and detailed information on physical and psychological development • stimulated study into individual differences in seeing, hearing and problem solving ...
... • these were observations, ruminations and detailed information on physical and psychological development • stimulated study into individual differences in seeing, hearing and problem solving ...
ALH 1002 Chapter 2
... • An extension of behaviorism that emphasizes the influence that other people have over a person’s behavior. • Modeling- people learn by observing other people and then copying them. • Self-efficacy- how effective people think they are when it comes to changing themselves or altering their social co ...
... • An extension of behaviorism that emphasizes the influence that other people have over a person’s behavior. • Modeling- people learn by observing other people and then copying them. • Self-efficacy- how effective people think they are when it comes to changing themselves or altering their social co ...
Chapter 2
... • An extension of behaviorism that emphasizes the influence that other people have over a person’s behavior. • Modeling- people learn by observing other people and then copying them. • Self-efficacy- how effective people think they are when it comes to changing themselves or altering their social co ...
... • An extension of behaviorism that emphasizes the influence that other people have over a person’s behavior. • Modeling- people learn by observing other people and then copying them. • Self-efficacy- how effective people think they are when it comes to changing themselves or altering their social co ...
Ch02LifeSpanPPT
... • An extension of behaviorism that emphasizes the influence that other people have over a person’s behavior. • Modeling- people learn by observing other people and then copying them. • Self-efficacy- how effective people think they are when it comes to changing themselves or altering their social co ...
... • An extension of behaviorism that emphasizes the influence that other people have over a person’s behavior. • Modeling- people learn by observing other people and then copying them. • Self-efficacy- how effective people think they are when it comes to changing themselves or altering their social co ...
Introduction to Psychology
... • William Wundt = “father of psychology”; first lab 1879 – first formal school of psychology – emphasis on analyzing the basic elements or structure of conscious mental experience through the use of introspection (looking inward) • Example: report sensations, feelings, etc. when looking at a photogr ...
... • William Wundt = “father of psychology”; first lab 1879 – first formal school of psychology – emphasis on analyzing the basic elements or structure of conscious mental experience through the use of introspection (looking inward) • Example: report sensations, feelings, etc. when looking at a photogr ...
PSYC 2314 Chapter 6
... • Which particular affordance an individual perceives and acts on depends on that person’s: ...
... • Which particular affordance an individual perceives and acts on depends on that person’s: ...
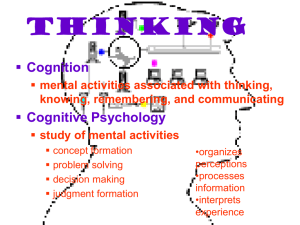
Thinking Cognition mental activities associated with thinking
... judgments that are quick but often in error Means–end analysis - heuristic in which difference between starting situation and goal is determined then steps taken to ...
... judgments that are quick but often in error Means–end analysis - heuristic in which difference between starting situation and goal is determined then steps taken to ...
Theories of Development
... stages in our cognitive development • Each stage is associated with a particular age although there is some individual variation • Piaget proposed that each stage must be progressed through in order- an individual cannot skip stages • Each stage describes the thinking capable by an individual stage ...
... stages in our cognitive development • Each stage is associated with a particular age although there is some individual variation • Piaget proposed that each stage must be progressed through in order- an individual cannot skip stages • Each stage describes the thinking capable by an individual stage ...
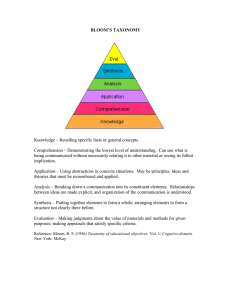
BLOOM`S TAXONOMY Knowledge – Recalling specific facts or
... Knowledge – Recalling specific facts or general concepts. Comprehension – Demonstrating the lowest level of understanding. Can use what is being communicated without necessarily relating it to other material or seeing its fullest implication. Application – Using abstractions in concrete situations. ...
... Knowledge – Recalling specific facts or general concepts. Comprehension – Demonstrating the lowest level of understanding. Can use what is being communicated without necessarily relating it to other material or seeing its fullest implication. Application – Using abstractions in concrete situations. ...
Chapter 1
... Cognitive Psychology – Experimental research on mental processes or cognition Modern Perspective and the Eclectic Approach ...
... Cognitive Psychology – Experimental research on mental processes or cognition Modern Perspective and the Eclectic Approach ...
Jean Piaget (1896
... 1. Children will offer different explanations of reality at different stages of cognitive development 2. Cognitive development is made possible by providing activities or situations that connect learners and require adaptation (i.e. assimilation and accommodation). 3. Learning materials and ac ...
... 1. Children will offer different explanations of reality at different stages of cognitive development 2. Cognitive development is made possible by providing activities or situations that connect learners and require adaptation (i.e. assimilation and accommodation). 3. Learning materials and ac ...
ltheories
... animal and human learning that only focuses on objectively observable behaviors and discounts mental activities. ...
... animal and human learning that only focuses on objectively observable behaviors and discounts mental activities. ...
PROCESSING APPROACHES
... Autonomous and active learners Processes take time The mind is a limited-capacity processor Learn a second language is to learn a skill Learning is a cognitive process ...
... Autonomous and active learners Processes take time The mind is a limited-capacity processor Learn a second language is to learn a skill Learning is a cognitive process ...
Chapter 4 Developmental
... Adolescence—Biological dev and puberty, Identity, peers and parents Adulthood—physical development; Erikson stage Summary of current views on Nature/Nurture, Continuity versus stages and Stability versus change in lifelong development. Chapter 7: Learning Define learning, Classical conditioning, be ...
... Adolescence—Biological dev and puberty, Identity, peers and parents Adulthood—physical development; Erikson stage Summary of current views on Nature/Nurture, Continuity versus stages and Stability versus change in lifelong development. Chapter 7: Learning Define learning, Classical conditioning, be ...
cogscience.
... how is the nature of the human mind? “… seeks to understand perceiving, thinking, remembering, understanding language, learning, and other mental phenomena.” ...
... how is the nature of the human mind? “… seeks to understand perceiving, thinking, remembering, understanding language, learning, and other mental phenomena.” ...
Talk title: Creative Cognitive Systems Ana
... Computational creativity focuses on implementing and evaluating artificial creative systems, while human creative cognition approaches center on working to understand the processes and types of representations humans use when being creative or creatively problem solving. An interdisciplinary cogniti ...
... Computational creativity focuses on implementing and evaluating artificial creative systems, while human creative cognition approaches center on working to understand the processes and types of representations humans use when being creative or creatively problem solving. An interdisciplinary cogniti ...
Cognitive Revolution - University of Guelph
... Social development reflects a person’s set of learned responses to the environment How does a person become aggressive? “Aggressive behavior” is a conditioned response. ...
... Social development reflects a person’s set of learned responses to the environment How does a person become aggressive? “Aggressive behavior” is a conditioned response. ...
Developmental Psychology
... probability that we will produce such behaviors. Added benefit: We don’t have to be punished to learn “what-not-to-do.” ...
... probability that we will produce such behaviors. Added benefit: We don’t have to be punished to learn “what-not-to-do.” ...
Chapter 14
... programmed development. Empiricists argue that virtually all knowledge comes from experience with the environment. Implications for the potential to change. ...
... programmed development. Empiricists argue that virtually all knowledge comes from experience with the environment. Implications for the potential to change. ...
Kye Paradise EDU 511 Summer 2014 GLOSSARY OF TERMS
... Modeling in reinforcement, punishment, environment: (p. 113) The environment can occasionally reinforce or punish modeling in the following ways: The observer is reinforced by the model, The observer is reinforced by a third person, The imitated behavior itself leads to reinforcing consequenc ...
... Modeling in reinforcement, punishment, environment: (p. 113) The environment can occasionally reinforce or punish modeling in the following ways: The observer is reinforced by the model, The observer is reinforced by a third person, The imitated behavior itself leads to reinforcing consequenc ...
File
... comprehension input promotes acquisition. Therefore, it could be deduced that adjustment promotes acquisition. A---B B---C ...
... comprehension input promotes acquisition. Therefore, it could be deduced that adjustment promotes acquisition. A---B B---C ...
Cognitive Processes PSY 334
... time in sequence, stopping when they get the answer. People look at the numbers one at a time in sequence but continue until the end before giving a response. People look at all three of the numbers at once, responding when they recognize the target number in the set. ...
... time in sequence, stopping when they get the answer. People look at the numbers one at a time in sequence but continue until the end before giving a response. People look at all three of the numbers at once, responding when they recognize the target number in the set. ...