L1 L2 THE CRITICAL PERIOD HYPOTHESIS
... • Most items are acquired by meaningful learning, by anchoring and relating new items & experiences to knowledge that exists in the cognitive framework. • Children’s learning is not rote but meaningful with activities that is contextualized and purposeful. ...
... • Most items are acquired by meaningful learning, by anchoring and relating new items & experiences to knowledge that exists in the cognitive framework. • Children’s learning is not rote but meaningful with activities that is contextualized and purposeful. ...
Learning Objectives Acknowledgements Device Abandonment
... in whatever modes and as effectively and efficiently as their specific abilities will allow. ...
... in whatever modes and as effectively and efficiently as their specific abilities will allow. ...
Chapter 5. The Sensual and Perceptual Theories of Visual
... A sign is simply anything that stands for something else What is not a sign? Almost any action, object, or image will mean something to someone somewhere For something to be sign, the viewer must understand its meaning ...
... A sign is simply anything that stands for something else What is not a sign? Almost any action, object, or image will mean something to someone somewhere For something to be sign, the viewer must understand its meaning ...
PsychSim: Learning - Socialscientist.us
... How would you interpret these graphs? Did your subject show evidence of stimulus generalization, or stimulus discrimination, or both? Extinction Trials How would you interpret these results? Has the conditioned response been extinguished in your subject? What would happen if we continued immedia ...
... How would you interpret these graphs? Did your subject show evidence of stimulus generalization, or stimulus discrimination, or both? Extinction Trials How would you interpret these results? Has the conditioned response been extinguished in your subject? What would happen if we continued immedia ...
Cognitive Processes in Animal Behavior
... – Donald R. Griffin (see below) gives it an important role – Heyes thinks it should be ignored • "It is perhaps at this moment that the cognitive ethologist decides to hang up his field glasses, become a cognitive psychologist, and have nothing further to do with talk about consciousness or intentio ...
... – Donald R. Griffin (see below) gives it an important role – Heyes thinks it should be ignored • "It is perhaps at this moment that the cognitive ethologist decides to hang up his field glasses, become a cognitive psychologist, and have nothing further to do with talk about consciousness or intentio ...
Frances Celine J. Tan How do descriptive (empirical) claims and
... 14.) What is the veil of ignorance in the original position in Rawl’s social contact theory? The veil of ignorance in the original position in Rawl’s social contact theory, that the “rights” is hypothesized to explain and justify the obligations that human beings have to one another. Also he recogni ...
... 14.) What is the veil of ignorance in the original position in Rawl’s social contact theory? The veil of ignorance in the original position in Rawl’s social contact theory, that the “rights” is hypothesized to explain and justify the obligations that human beings have to one another. Also he recogni ...
Study Guide – Exam #1
... -accommodation and assimilation Know the difference between genotype and phenotype Understand relationship between dominant and recessive genes Know the three stages of labor Reflexes – what are they and what are the 2 types Understand the different developments in language Understand the purpose an ...
... -accommodation and assimilation Know the difference between genotype and phenotype Understand relationship between dominant and recessive genes Know the three stages of labor Reflexes – what are they and what are the 2 types Understand the different developments in language Understand the purpose an ...
Notification of Child Death
... prior condition that might be expected to cause the death at that time, and the child dies either immediately or subsequently from the consequences of the precipitating event or collapse. ...
... prior condition that might be expected to cause the death at that time, and the child dies either immediately or subsequently from the consequences of the precipitating event or collapse. ...
AAAI Proceedings Template - Computer Science Division
... and behaviorist psychology – explained children’s attachment to their parents in terms of secondary drives (Cassidy 1999). Children, so the theory went, have a primary drive to get food. Parents provide food, therefore the children learn their attachment to their parents out of a self-interested nee ...
... and behaviorist psychology – explained children’s attachment to their parents in terms of secondary drives (Cassidy 1999). Children, so the theory went, have a primary drive to get food. Parents provide food, therefore the children learn their attachment to their parents out of a self-interested nee ...
human development
... 2. Culture is the total pattern of a group’s customs, beliefs, art, and technology passed along through language. Upp 3. A biological perspective is also offered in this text, especially in terms of how biology interacts with cultural and social influences. 4. In the past, culture was largely ignore ...
... 2. Culture is the total pattern of a group’s customs, beliefs, art, and technology passed along through language. Upp 3. A biological perspective is also offered in this text, especially in terms of how biology interacts with cultural and social influences. 4. In the past, culture was largely ignore ...
File - SSHS AP Psychology
... 1) Theory of Value: what knowledge and skills are worth learning? (varies--past experiences and prior knowledge important to create new ideas--language, culture and social interactions important) 2) Theory of Knowledge: how is knowledge different from belief? (intellectual abilities are specific to ...
... 1) Theory of Value: what knowledge and skills are worth learning? (varies--past experiences and prior knowledge important to create new ideas--language, culture and social interactions important) 2) Theory of Knowledge: how is knowledge different from belief? (intellectual abilities are specific to ...
Agenda 3.4 Balance Theory P-O-X Theory (or Balance theory
... • General attitudes (“I like old people”) are poor predictors of specific behaviors (“Will I help my elderly neighbor carry his groceries today?”) • 2. Aggregated (summed) Attitudes When we can view attitudes and subsequent behavior over time, we can better predict future behavior • 3. Attitudes com ...
... • General attitudes (“I like old people”) are poor predictors of specific behaviors (“Will I help my elderly neighbor carry his groceries today?”) • 2. Aggregated (summed) Attitudes When we can view attitudes and subsequent behavior over time, we can better predict future behavior • 3. Attitudes com ...
Review for final exam
... heart rated during exercise is still going to be lower than it was in his/her 20s ...
... heart rated during exercise is still going to be lower than it was in his/her 20s ...
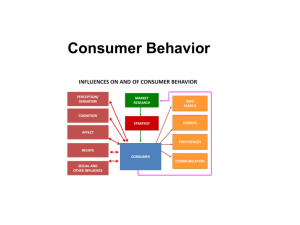
CB Lecture
... Consumer behavior: consists of the actions a person takes in purchasing and using products and services, including the mental and social processes that come before and after these actions. ...
... Consumer behavior: consists of the actions a person takes in purchasing and using products and services, including the mental and social processes that come before and after these actions. ...
PsychSim5: Maze Learning 1 PsychSim 5: MAZE LEARNING Name
... Results for Maze B Compare the number of moves and the path you took in the first run with your performance in the second run. Did you get better with practice? Did you use the same strategy that you used on the Maze A, or did you try a different approach? ...
... Results for Maze B Compare the number of moves and the path you took in the first run with your performance in the second run. Did you get better with practice? Did you use the same strategy that you used on the Maze A, or did you try a different approach? ...
Brittney Carroll
... fixed time period, such as checking to see if something you are cooking is done. The final type is variable interval schedules, which reinforces after varying time intervals, such as receiving mail or an email. Observational learning is where we observe and imitate others. Albert Bandure was involve ...
... fixed time period, such as checking to see if something you are cooking is done. The final type is variable interval schedules, which reinforces after varying time intervals, such as receiving mail or an email. Observational learning is where we observe and imitate others. Albert Bandure was involve ...
distance learning system «Web
... information technologies in areas of mental activity, what are most difficult to understanding, when the difficulty of training is depended on much work. • On the basis of Laboratory of the integrated environments for learning of Scientific and research institute of informational technology of ...
... information technologies in areas of mental activity, what are most difficult to understanding, when the difficulty of training is depended on much work. • On the basis of Laboratory of the integrated environments for learning of Scientific and research institute of informational technology of ...
Cognitive Psychology
... • Zhang, X., Li, T., & Zhou, X. (2008). Brain responses to facial expressions by adults with different attachmentorientations. Neuroreport, 19, 437-441. • Wei, P., Müller, H., Lü, J., & Zhou, X. (2008). Searching for two feature singletons in the visual scene: The localized attentional interference ...
... • Zhang, X., Li, T., & Zhou, X. (2008). Brain responses to facial expressions by adults with different attachmentorientations. Neuroreport, 19, 437-441. • Wei, P., Müller, H., Lü, J., & Zhou, X. (2008). Searching for two feature singletons in the visual scene: The localized attentional interference ...
Operant Conditioning Powerpoint
... • Biological Predispositions of Operant Conditioning • It is easier to reinforce behaviors normally associated with their natural behaviors – Example – can use a food reinforcer to get a hamster to rear up, more difficult to use a food reinforcer to get a hamster to wash its face ...
... • Biological Predispositions of Operant Conditioning • It is easier to reinforce behaviors normally associated with their natural behaviors – Example – can use a food reinforcer to get a hamster to rear up, more difficult to use a food reinforcer to get a hamster to wash its face ...
Alfred Adler - Twinsburg City Schools
... Along with John Palmer showed people a filmed automobile accident, asked how fast cars were going when they smashed or bumped or contacted, asked if they had seen broken glass in the film (there was none) to study the tendency of people to construct memories based on how they are questioned Abraham ...
... Along with John Palmer showed people a filmed automobile accident, asked how fast cars were going when they smashed or bumped or contacted, asked if they had seen broken glass in the film (there was none) to study the tendency of people to construct memories based on how they are questioned Abraham ...
Computational Theory of Mind
... Original Goal A. To formally describe the meanings humans make of their worlds & then hypothesize what meaning-making processes might be involved Key Feature 2. Faith that central to any understanding of the human mind is the computer ...
... Original Goal A. To formally describe the meanings humans make of their worlds & then hypothesize what meaning-making processes might be involved Key Feature 2. Faith that central to any understanding of the human mind is the computer ...
Chapter 7 Learning Goals File
... 6. What did John Watson teach little Albert? What conclusions did Watson draw from these experiments with little Albert? 7. What did Mary Cover Jones discover? 8. What is the difference between classical and operant conditioning? 9. According to B.F. Skinner, why do we perform certain behaviors? 10. ...
... 6. What did John Watson teach little Albert? What conclusions did Watson draw from these experiments with little Albert? 7. What did Mary Cover Jones discover? 8. What is the difference between classical and operant conditioning? 9. According to B.F. Skinner, why do we perform certain behaviors? 10. ...
Chapter 5 - West Ada
... A) They took longer to respond as the details asked for became smaller B) They took the same amount of time to respond regardless of how large or small the detail asked for was C) It took them longer to rotate objects in space D) It took them no longer to respond regardless of whether or not they ha ...
... A) They took longer to respond as the details asked for became smaller B) They took the same amount of time to respond regardless of how large or small the detail asked for was C) It took them longer to rotate objects in space D) It took them no longer to respond regardless of whether or not they ha ...
Lecture05
... unrelated words. Then they had to recall all lists a second time cued by the first word of each list. Narrative subjects were to make a story incorporating the words in the list. Control subjects were told just to study each of the list and were given the same amount of time. Results Immediate recal ...
... unrelated words. Then they had to recall all lists a second time cued by the first word of each list. Narrative subjects were to make a story incorporating the words in the list. Control subjects were told just to study each of the list and were given the same amount of time. Results Immediate recal ...