Astrophysics - Student Reference Packet
... Astronomers have attempted to develop a uniform standard of classification for the variety of astronomical objects that have been, and continue to be, discovered. The International Astronomical Union (IAU), founded in 1919 and composed of professional astronomers from around the world, serves as the ...
... Astronomers have attempted to develop a uniform standard of classification for the variety of astronomical objects that have been, and continue to be, discovered. The International Astronomical Union (IAU), founded in 1919 and composed of professional astronomers from around the world, serves as the ...
Properties of the Planets & Formation of the Solar
... In this chapter you will discover… how moons formed throughout the solar system the “debris” in the solar system that disks of gas and dust, as well as planets, have been observed around a growing number of stars that newly forming stars & planetary systems are being observed ...
... In this chapter you will discover… how moons formed throughout the solar system the “debris” in the solar system that disks of gas and dust, as well as planets, have been observed around a growing number of stars that newly forming stars & planetary systems are being observed ...
Explain. How is Copernicus`s description of the system of planets
... and gravity—combine to keep the planets in orbit. • Inertia-the tendency of a moving object to continue in a straight line or a stationary object to remain in place. • Gravity- attracts all objects toward one another. The strength of gravity depends on the masses of the objects and the distance betw ...
... and gravity—combine to keep the planets in orbit. • Inertia-the tendency of a moving object to continue in a straight line or a stationary object to remain in place. • Gravity- attracts all objects toward one another. The strength of gravity depends on the masses of the objects and the distance betw ...
Introductory Physics I (54
... c) away from the Sun and disappears at perihelion. d) away from the Sun and becomes longest and brightest at perihelion. e) in the direction of the comet's motion. 15) The Trojan asteroids are found a) orbiting around the Kuiper Belt body Hector. b) with the others, between Mars and Jupiter; their r ...
... c) away from the Sun and disappears at perihelion. d) away from the Sun and becomes longest and brightest at perihelion. e) in the direction of the comet's motion. 15) The Trojan asteroids are found a) orbiting around the Kuiper Belt body Hector. b) with the others, between Mars and Jupiter; their r ...
Stars - Red, Blue, Old, New pt.3
... • While the He is being converted to C in the core, there is a zone of H to He fusion surrounding the core • When the core is all C, further changes occur and C to O fusion starts (with zones of He to C and H to He surrounding) • Stars get an “onion” structure ...
... • While the He is being converted to C in the core, there is a zone of H to He fusion surrounding the core • When the core is all C, further changes occur and C to O fusion starts (with zones of He to C and H to He surrounding) • Stars get an “onion” structure ...
Class 11 and 12 lecture slides (giant planets)
... • What are the consequences of a Jupiter-size planet migrating inwards? (c.f. Triton) • Systems with hot Jupiters are likely to be lacking any other large bodies • So the timing of gas dissipation is crucial to the eventual appearance of the planetary system (and the possibility of habitable planets ...
... • What are the consequences of a Jupiter-size planet migrating inwards? (c.f. Triton) • Systems with hot Jupiters are likely to be lacking any other large bodies • So the timing of gas dissipation is crucial to the eventual appearance of the planetary system (and the possibility of habitable planets ...
CHAPTER 1 Planets of the Solar System
... Uranus, and Neptune), and the five known dwarf planets (Ceres, Pluto, Makemake, Haumea, and Eris). In the image above, relative sizes of the Sun, planets, and dwarf planets and their positions relative to each other are correct, but the relative distances are not. Eight Planets Since the time of Cop ...
... Uranus, and Neptune), and the five known dwarf planets (Ceres, Pluto, Makemake, Haumea, and Eris). In the image above, relative sizes of the Sun, planets, and dwarf planets and their positions relative to each other are correct, but the relative distances are not. Eight Planets Since the time of Cop ...
Early Astronomy and Gravity
... From Ptolemy to Copernicus • Ptolemy’s geocentric system was very complicated, but also very accurate. It lasted for nearly 1500 years! • But most people still thought that the “perfect reality” was a bunch of “nested spheres” as Aristotle originally suggested. • Copernicus wrote about heliocentric ...
... From Ptolemy to Copernicus • Ptolemy’s geocentric system was very complicated, but also very accurate. It lasted for nearly 1500 years! • But most people still thought that the “perfect reality” was a bunch of “nested spheres” as Aristotle originally suggested. • Copernicus wrote about heliocentric ...
File
... A. Fill in the blanks (use the following list) [ 10 /10] asteroid astronomical unit comet constellation eclipse geocentric heliocentric light year luminosity meteor meteorite nebula nuclear fusion red shift retrograde motion revolution rotation spectroscope solar system solar nebula theory star suns ...
... A. Fill in the blanks (use the following list) [ 10 /10] asteroid astronomical unit comet constellation eclipse geocentric heliocentric light year luminosity meteor meteorite nebula nuclear fusion red shift retrograde motion revolution rotation spectroscope solar system solar nebula theory star suns ...
CHAPTER 1 Planets of the Solar System
... Uranus, and Neptune), and the five known dwarf planets (Ceres, Pluto, Makemake, Haumea, and Eris). In the image above, relative sizes of the Sun, planets, and dwarf planets and their positions relative to each other are correct, but the relative distances are not. Eight Planets Since the time of Cop ...
... Uranus, and Neptune), and the five known dwarf planets (Ceres, Pluto, Makemake, Haumea, and Eris). In the image above, relative sizes of the Sun, planets, and dwarf planets and their positions relative to each other are correct, but the relative distances are not. Eight Planets Since the time of Cop ...
New Worlds Observer
... Exo-planets are the planets that circle stars other than our Sun. There are probably 10,000 exo-planets within 10pc (30 light years) of the Earth. Indirect means have now found over 200. If we can observe them directly, we will have a new field of astronomy every bit as rich as extragalactic. ...
... Exo-planets are the planets that circle stars other than our Sun. There are probably 10,000 exo-planets within 10pc (30 light years) of the Earth. Indirect means have now found over 200. If we can observe them directly, we will have a new field of astronomy every bit as rich as extragalactic. ...
Unit 7 Planets Day 1!
... I can classify the inner and outer planets by looking at their characteristics. ...
... I can classify the inner and outer planets by looking at their characteristics. ...
The Solar System
... surfaces. We call the nearest planets(meaning wanderers) the Solar System. It is made up of eight planets orbiting the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. Our Solar System began to form about five billion years ago from a cloud of dust and gas. This dust and gas began ...
... surfaces. We call the nearest planets(meaning wanderers) the Solar System. It is made up of eight planets orbiting the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. Our Solar System began to form about five billion years ago from a cloud of dust and gas. This dust and gas began ...
Week Two
... During meteor showers, the material that falls to Earth is left over from the dust tail of comets ...
... During meteor showers, the material that falls to Earth is left over from the dust tail of comets ...
The Solar System
... the same planets that the ancient Greeks had known—Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn. Since Galileo’s time, astronomers have discovered two more planets—Uranus and Neptune. Astronomers have also identified many other objects in the solar system, such as comets and asteroids. Today we ...
... the same planets that the ancient Greeks had known—Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn. Since Galileo’s time, astronomers have discovered two more planets—Uranus and Neptune. Astronomers have also identified many other objects in the solar system, such as comets and asteroids. Today we ...
Astronomy
... e. The tides are the daily, periodic rise and fall of water level caused by the gravitational pull of the sun and moon. f. Water occurs on Earth as a solid (ice), a liquid, or a gas (water vapor) due to its position in the solar system. g. The sun consists largely of hydrogen gas. Its energy comes f ...
... e. The tides are the daily, periodic rise and fall of water level caused by the gravitational pull of the sun and moon. f. Water occurs on Earth as a solid (ice), a liquid, or a gas (water vapor) due to its position in the solar system. g. The sun consists largely of hydrogen gas. Its energy comes f ...
Beginnings - Big Picture
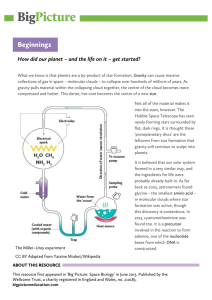
... It seems that the early solar system – including the early Earth – was laced with some of the basic chemicals from which life is built. But what turned an inanimate, prehistoric ‘soup’ of chemicals into the first organisms we would classify as alive? The most famous experiment into the origin of li ...
... It seems that the early solar system – including the early Earth – was laced with some of the basic chemicals from which life is built. But what turned an inanimate, prehistoric ‘soup’ of chemicals into the first organisms we would classify as alive? The most famous experiment into the origin of li ...
Slide 1
... places that are far, far away. time light Telescopes are _________ machines, because the _________ that comes to you through them left their star or galaxy ...
... places that are far, far away. time light Telescopes are _________ machines, because the _________ that comes to you through them left their star or galaxy ...
Chapter 11 Review
... Why are the distances between bodies in the solar system not measured in light-years? Why is it best to use a long baseline when determining distances using triangulation? Explain why parallax is not a good technique for determining distances of stars that are extremely far away (that is, greater th ...
... Why are the distances between bodies in the solar system not measured in light-years? Why is it best to use a long baseline when determining distances using triangulation? Explain why parallax is not a good technique for determining distances of stars that are extremely far away (that is, greater th ...
Group 1 Notes for Week 8 - UGA Physics and Astronomy
... But this isn’t the whole picture. Young stars have powerful STELLAR WINDS: streams of charged particles continually leaving the surface of the star at very high speeds. It’s not powerful enough to blow a planet off of its course/orbit, but it can move dust particles around very easily. So, for about ...
... But this isn’t the whole picture. Young stars have powerful STELLAR WINDS: streams of charged particles continually leaving the surface of the star at very high speeds. It’s not powerful enough to blow a planet off of its course/orbit, but it can move dust particles around very easily. So, for about ...
Definition of planet

The definition of planet, since the word was coined by the ancient Greeks, has included within its scope a wide range of celestial bodies. Greek astronomers employed the term asteres planetai (ἀστέρες πλανῆται), ""wandering stars"", for star-like objects which apparently moved over the sky. Over the millennia, the term has included a variety of different objects, from the Sun and the Moon to satellites and asteroids.By the end of the 19th century the word planet, though it had yet to be defined, had become a working term applied only to a small set of objects in the Solar System. After 1992, however, astronomers began to discover many additional objects beyond the orbit of Neptune, as well as hundreds of objects orbiting other stars. These discoveries not only increased the number of potential planets, but also expanded their variety and peculiarity. Some were nearly large enough to be stars, while others were smaller than Earth's moon. These discoveries challenged long-perceived notions of what a planet could be.The issue of a clear definition for planet came to a head in 2005 with the discovery of the trans-Neptunian object Eris, a body more massive than the smallest then-accepted planet, Pluto. In its 2006 response, the International Astronomical Union (IAU), recognised by astronomers as the world body responsible for resolving issues of nomenclature, released its decision on the matter. This definition, which applies only to the Solar System, states that a planet is a body that orbits the Sun, is massive enough for its own gravity to make it round, and has ""cleared its neighbourhood"" of smaller objects around its orbit. Under this new definition, Pluto and the other trans-Neptunian objects do not qualify as planets. The IAU's decision has not resolved all controversies, and while many scientists have accepted the definition, some in the astronomical community have rejected it outright.