section 4 powerpoint
... Tycho’s observations of Mars relative to the Sun separated by the planet’s 687d orbital period (with Earth at different parts of its orbit) and used them to triangulate the location of Mars, which was at the same point of its orbit. ...
... Tycho’s observations of Mars relative to the Sun separated by the planet’s 687d orbital period (with Earth at different parts of its orbit) and used them to triangulate the location of Mars, which was at the same point of its orbit. ...
Solar System Unit
... In August of 2006, Pluto lost its status as a planet. (1) A "planet" is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbor ...
... In August of 2006, Pluto lost its status as a planet. (1) A "planet" is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbor ...
The Newtonian Revolution: The discovery of natural law
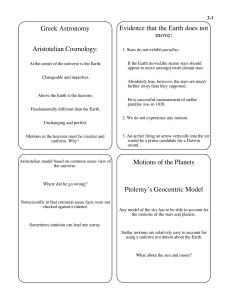
... and COMPEL the rest of the Solar System to do ALL of the moving… • As observations improved after Ptolemy’s death, this is what forced epicycles on top of epicycles, and deferrents away from the centers. • His construction is essentially what we would call today a Fourier de-composition of the motio ...
... and COMPEL the rest of the Solar System to do ALL of the moving… • As observations improved after Ptolemy’s death, this is what forced epicycles on top of epicycles, and deferrents away from the centers. • His construction is essentially what we would call today a Fourier de-composition of the motio ...
Formation of the Solar System
... 7. Asteroids orbit the Sun and range from a few kilometers to about ______ kilometers in diameter. 8. Most asteroids are located between the orbits of _________________ in the asteroid belt. 9. Asteroids are thought to be _____________ that never formed planets. 10. A meteoroid is a broken fragment ...
... 7. Asteroids orbit the Sun and range from a few kilometers to about ______ kilometers in diameter. 8. Most asteroids are located between the orbits of _________________ in the asteroid belt. 9. Asteroids are thought to be _____________ that never formed planets. 10. A meteoroid is a broken fragment ...
Document
... Uranus has the coldest temperature of -224⁰C Uranus is tipped over on its side with an axial tilt of 98⁰. It is described as “Rolling around the Sun on it’s side.” Uranus Has 27 moons and 13 rings. ...
... Uranus has the coldest temperature of -224⁰C Uranus is tipped over on its side with an axial tilt of 98⁰. It is described as “Rolling around the Sun on it’s side.” Uranus Has 27 moons and 13 rings. ...
Jupiter
... different layers is determined by the study of the planet gravitational potential measured by different spacecraft. If there is the inner core, prove the theory of planet formation from a disk of planetesimals. Jupiter is so massive that it has not yet released the heat accumulated in its formation ...
... different layers is determined by the study of the planet gravitational potential measured by different spacecraft. If there is the inner core, prove the theory of planet formation from a disk of planetesimals. Jupiter is so massive that it has not yet released the heat accumulated in its formation ...
Document
... The Sun, planets, asteroids, comets, planetesimals all revolve in the same direction with some exceptions. ...
... The Sun, planets, asteroids, comets, planetesimals all revolve in the same direction with some exceptions. ...
SKY SCIENCE study guide_2
... 4) What is a comet? Asteroid? Meteoroid? Meteor? Meteorite? 5) List some examples of things in space that EMIT and that REFLECT light. 6) What is another name for our North star? Why is it so important? 7) Which constellation does the big dipper belong to? 8) What is a constellation? 9) What is the ...
... 4) What is a comet? Asteroid? Meteoroid? Meteor? Meteorite? 5) List some examples of things in space that EMIT and that REFLECT light. 6) What is another name for our North star? Why is it so important? 7) Which constellation does the big dipper belong to? 8) What is a constellation? 9) What is the ...
Creating a 2-D Model of the Solar System using Physics
... Update the positions of the planets one at a time and iteratively, where at each step the planet’s acceleration is updated based on the position of each other body ...
... Update the positions of the planets one at a time and iteratively, where at each step the planet’s acceleration is updated based on the position of each other body ...
CST Prep- 8th Grade Astronomy
... 1. The theory of how the universe was created is called the ____________________. 2. Which equation states that matter and energy are interchangeable? __________________ 3. All matter in the Universe today came from an original pin prick of limitless __________________. 4. Is the universe contractin ...
... 1. The theory of how the universe was created is called the ____________________. 2. Which equation states that matter and energy are interchangeable? __________________ 3. All matter in the Universe today came from an original pin prick of limitless __________________. 4. Is the universe contractin ...
Folie 1
... • The atmosphere is transparent to visible light, but mostly opaque to infrared. • The Infrared "opacity" comes from absorption bands of H2O, CO2, CH4 and ...
... • The atmosphere is transparent to visible light, but mostly opaque to infrared. • The Infrared "opacity" comes from absorption bands of H2O, CO2, CH4 and ...
Newton derives Kepler`s laws
... b) What is the kinetic energy of Jupiter in motion around the Sun? ...
... b) What is the kinetic energy of Jupiter in motion around the Sun? ...
Slide 1
... 6.1 An Inventory of the Solar System Now known: Solar system has 165 moons, one star, eight planets (added Uranus and Neptune), eight asteroids and more than 100 Kuiper belt objects more than 300 km in diameter, smaller asteroids, comets, and meteoroids ...
... 6.1 An Inventory of the Solar System Now known: Solar system has 165 moons, one star, eight planets (added Uranus and Neptune), eight asteroids and more than 100 Kuiper belt objects more than 300 km in diameter, smaller asteroids, comets, and meteoroids ...
Intro L4 IQ
... once per year. The seasonal (annual) changing of constellations depends upon revolution. Diurnal changes, for example, the transit of stars during the course of the night (or the sun during the day) are caused by the Earth’s rotation. Diurnal changes are far more obvious than annual changes ...
... once per year. The seasonal (annual) changing of constellations depends upon revolution. Diurnal changes, for example, the transit of stars during the course of the night (or the sun during the day) are caused by the Earth’s rotation. Diurnal changes are far more obvious than annual changes ...
Astronomy Objective 1 1. An asteroid is a small, rocky object that
... 1. An asteroid is a small, rocky object that orbits the sun; most are located in a band between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. 2. An astronomical unit (AU) is the average distance between the Earth and the sun; approximately 150 million kilometers (93 million miles). 3. Astronomy is the scientific ...
... 1. An asteroid is a small, rocky object that orbits the sun; most are located in a band between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. 2. An astronomical unit (AU) is the average distance between the Earth and the sun; approximately 150 million kilometers (93 million miles). 3. Astronomy is the scientific ...
AUST – HORIZON AND BEYOND part 1
... The word planet is derived from the Greek word planetes which means ‘wanderer’. ...
... The word planet is derived from the Greek word planetes which means ‘wanderer’. ...
Space Key Word Search
... VARIABLE STAR - a type of star whose brightness changes over time, usually in a predictable way. ...
... VARIABLE STAR - a type of star whose brightness changes over time, usually in a predictable way. ...
Galaxy and Beyond
... the Sun (can range from 30 - 50 Aus) Astronomical Unit (AU) - is distance b/w Earth & Sun (about 93 million miles) ...
... the Sun (can range from 30 - 50 Aus) Astronomical Unit (AU) - is distance b/w Earth & Sun (about 93 million miles) ...
History of Astronomy Notes
... Explains apparent changes in brightness for some planets. Explains some of the observed non-uniform motions of the Sun, Moon, and Planets. Can fine-tune the model by adding epicycles. Failures of Ptolemy’s System: It was really, REALLY complicated. ...
... Explains apparent changes in brightness for some planets. Explains some of the observed non-uniform motions of the Sun, Moon, and Planets. Can fine-tune the model by adding epicycles. Failures of Ptolemy’s System: It was really, REALLY complicated. ...
Outer or Jovian Planets - Academic Computer Center
... • The spin axis of Uranus is tilted so that it lies nearly in its orbital ...
... • The spin axis of Uranus is tilted so that it lies nearly in its orbital ...
Name Class Date Our Solar System The solar system consists of our
... Earth’s Sun is an average-sized star. The Sun is more than a million times greater in volume than Earth. The other stars we see in the night sky are like the Sun or even larger but are so far away that they look like tiny points of light. Distances between stars are vast compared to distances within ...
... Earth’s Sun is an average-sized star. The Sun is more than a million times greater in volume than Earth. The other stars we see in the night sky are like the Sun or even larger but are so far away that they look like tiny points of light. Distances between stars are vast compared to distances within ...
Earth Science Library wk 2 (WP)
... into it maintaining that Copernicus did not mean to suggest that the Earth actually moved, but rather that the model was a convenient mathematical tool for determining planetary positions. ...
... into it maintaining that Copernicus did not mean to suggest that the Earth actually moved, but rather that the model was a convenient mathematical tool for determining planetary positions. ...
The Other Distant Giants Are Kindred Planets with Individual Quirks
... In addition to a shroud of atmospheric haze, Uranus and Neptune are concealed from our understanding by their immense distances from us. Uranus is barely visible to the naked eye, so it remained unrecognized as a planet until modern times with the aid of a telescope. The existence of Neptune was ded ...
... In addition to a shroud of atmospheric haze, Uranus and Neptune are concealed from our understanding by their immense distances from us. Uranus is barely visible to the naked eye, so it remained unrecognized as a planet until modern times with the aid of a telescope. The existence of Neptune was ded ...
Definition of planet

The definition of planet, since the word was coined by the ancient Greeks, has included within its scope a wide range of celestial bodies. Greek astronomers employed the term asteres planetai (ἀστέρες πλανῆται), ""wandering stars"", for star-like objects which apparently moved over the sky. Over the millennia, the term has included a variety of different objects, from the Sun and the Moon to satellites and asteroids.By the end of the 19th century the word planet, though it had yet to be defined, had become a working term applied only to a small set of objects in the Solar System. After 1992, however, astronomers began to discover many additional objects beyond the orbit of Neptune, as well as hundreds of objects orbiting other stars. These discoveries not only increased the number of potential planets, but also expanded their variety and peculiarity. Some were nearly large enough to be stars, while others were smaller than Earth's moon. These discoveries challenged long-perceived notions of what a planet could be.The issue of a clear definition for planet came to a head in 2005 with the discovery of the trans-Neptunian object Eris, a body more massive than the smallest then-accepted planet, Pluto. In its 2006 response, the International Astronomical Union (IAU), recognised by astronomers as the world body responsible for resolving issues of nomenclature, released its decision on the matter. This definition, which applies only to the Solar System, states that a planet is a body that orbits the Sun, is massive enough for its own gravity to make it round, and has ""cleared its neighbourhood"" of smaller objects around its orbit. Under this new definition, Pluto and the other trans-Neptunian objects do not qualify as planets. The IAU's decision has not resolved all controversies, and while many scientists have accepted the definition, some in the astronomical community have rejected it outright.