Ch.1 Notes - Green Local Schools
... cell specialization elaboration of one function and reduction of others ...
... cell specialization elaboration of one function and reduction of others ...
answers - Biology Resources
... cell wall are not living materials. 4 High temperature kills most living materials (by denaturing their proteins, e.g. enzymes and structures in the cell membrane). 5 It seems likely that a living process in the cytoplasm controls the diffusion of the pigment. Diffusion of pigment is prevented when ...
... cell wall are not living materials. 4 High temperature kills most living materials (by denaturing their proteins, e.g. enzymes and structures in the cell membrane). 5 It seems likely that a living process in the cytoplasm controls the diffusion of the pigment. Diffusion of pigment is prevented when ...
Appearance of cell-wall associated red pigment/s in stressed
... walls by water-saturated phenol, dimethyl sulphoxide and dimethylformamide. The chemical nature of the pigment(s) remains unknown. Some recently discovered in cell walls of vascular plants pigments related to anthocyanidins or anthocyanidin-like compounds [1-3]. However, as generally believed, speci ...
... walls by water-saturated phenol, dimethyl sulphoxide and dimethylformamide. The chemical nature of the pigment(s) remains unknown. Some recently discovered in cell walls of vascular plants pigments related to anthocyanidins or anthocyanidin-like compounds [1-3]. However, as generally believed, speci ...
SQUID ocean Sciences 122 - deb-or-ah
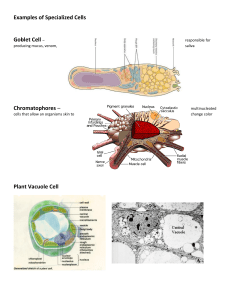
... Many of these creatures have special pigment cells called chromatophores in their skin. By controlling the size of the cells they can vary their color and even create changing patterns. Chromatophores are connected to the nervous system, and their size is determined by muscular contractions. ...
... Many of these creatures have special pigment cells called chromatophores in their skin. By controlling the size of the cells they can vary their color and even create changing patterns. Chromatophores are connected to the nervous system, and their size is determined by muscular contractions. ...
Chromatophore

Chromatophores are pigment-containing and light-reflecting cells, or groups of cells, found in bacteria and a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, have a class of cells called melanocytes for coloration.Chromatophores are largely responsible for generating skin and eye colour in cold-blooded animals and are generated in the neural crest during embryonic development. Mature chromatophores are grouped into subclasses based on their colour (more properly ""hue"") under white light: xanthophores (yellow), erythrophores (red), iridophores (reflective / iridescent), leucophores (white), melanophores (black/brown), and cyanophores (blue). The term chromatophore can also refer to coloured, membrane-associated vesicles found in some forms of photosynthetic bacteria.Some species can rapidly change colour through mechanisms that translocate pigment and reorient reflective plates within chromatophores. This process, often used as a type of camouflage, is called physiological colour change or metachrosis. Cephalopods such as the octopus have complex chromatophore organs controlled by muscles to achieve this, whereas vertebrates such as chameleons generate a similar effect by cell signalling. Such signals can be hormones or neurotransmitters and may be initiated by changes in mood, temperature, stress or visible changes in the local environment. Chromatophores are studied by scientists to understand human disease and as a tool in drug discovery.