The Integumentary System Skin
... Placoid cells, or denticles are tooth-like scales that cover sharks, rays, and skates. These develop from the dermal layer of the skin Many extinct agnatha (jawless fish) had scales similar to that of sharks, but nowadays the only covering is skin ...
... Placoid cells, or denticles are tooth-like scales that cover sharks, rays, and skates. These develop from the dermal layer of the skin Many extinct agnatha (jawless fish) had scales similar to that of sharks, but nowadays the only covering is skin ...
No Slide Title
... Photons possess different wavelengths that represent different energy levels. Different wavelengths seen as different colors. Pigment molecules possess different abilities to absorb wavelengths and appear as different colors. Chlorophyll is the major pigment molecule and appears as green. Plants ...
... Photons possess different wavelengths that represent different energy levels. Different wavelengths seen as different colors. Pigment molecules possess different abilities to absorb wavelengths and appear as different colors. Chlorophyll is the major pigment molecule and appears as green. Plants ...
Multicellular Protists
... Multicellular Protists (algae) • Primary producers • “ Plant-like” seaweeds – Lack true leaves, stems & roots – May be filamentous, grow in mats or crusts, sheets, or kelp ...
... Multicellular Protists (algae) • Primary producers • “ Plant-like” seaweeds – Lack true leaves, stems & roots – May be filamentous, grow in mats or crusts, sheets, or kelp ...
history of cell biology and parts of a microscope
... It can be used only in low power objective. ...
... It can be used only in low power objective. ...
Developmental Stages of Finfishes
... • Development is a process by which an organism reaches its adulthood. • Development in fish is continuous ...
... • Development is a process by which an organism reaches its adulthood. • Development in fish is continuous ...
Integumentary+System
... Color is yellow to brown to black Amount of melanin produced depends upon genetics and exposure to sunlight ...
... Color is yellow to brown to black Amount of melanin produced depends upon genetics and exposure to sunlight ...
Integument 3
... Cells are identical in the type and number of chromosomes it contains. Each cell has its own nucleus with identical DNA If a cell containing 46 chromosomes undergoes mitosis, how many chromosomes does each of its daughter cells contain? ...
... Cells are identical in the type and number of chromosomes it contains. Each cell has its own nucleus with identical DNA If a cell containing 46 chromosomes undergoes mitosis, how many chromosomes does each of its daughter cells contain? ...
Life Science Study Guide
... Scientists classify animals based on common characteristics such as antenna, number of legs, wings, backbones, etc. It show scientists how organisms are alike or different. How are vertebrates and invertebrates different? Give examples of each. Vertebrates are animals with a backbone. They include m ...
... Scientists classify animals based on common characteristics such as antenna, number of legs, wings, backbones, etc. It show scientists how organisms are alike or different. How are vertebrates and invertebrates different? Give examples of each. Vertebrates are animals with a backbone. They include m ...
BergSpr16 - MINDS@UW Home
... Fish specimens were obtained from UW-Stevens Point, which included ten different bodies of water (lakes, rivers, and streams). Approximately ten specimens from each body of water were examined. (N=73). First, each fish was photographed and total length was recorded (mm). Subsequently, one square cen ...
... Fish specimens were obtained from UW-Stevens Point, which included ten different bodies of water (lakes, rivers, and streams). Approximately ten specimens from each body of water were examined. (N=73). First, each fish was photographed and total length was recorded (mm). Subsequently, one square cen ...
Chapter 7 Photosynthesis_student version
... Hot, dry climates plants continue photosynthesis while conserving water ...
... Hot, dry climates plants continue photosynthesis while conserving water ...
Mechanisms of Animal Growth and Development
... Hormonal control of development (general aspects of hormone action, hormonal control of: sex differentiation in mamales, brain development and behavior in vertebrate, insect metamorphosis, amphibian metamorphosis). Organismic growth (measurment and mechanisms of growth, growth hormones, growth facto ...
... Hormonal control of development (general aspects of hormone action, hormonal control of: sex differentiation in mamales, brain development and behavior in vertebrate, insect metamorphosis, amphibian metamorphosis). Organismic growth (measurment and mechanisms of growth, growth hormones, growth facto ...
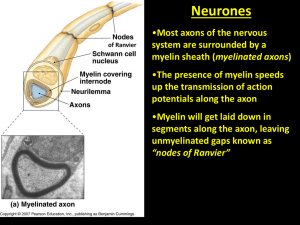
Myelin Sheaths Plant Hormone Intro
... • The part of a shoot sensitive to light is the tip. • The part of the shoot which responds to the stimulus is the part just below the tip. • These two parts of the shoot must be communicating with one another by means hormones. • Plant hormones are chemical that affect the activities of particular ...
... • The part of a shoot sensitive to light is the tip. • The part of the shoot which responds to the stimulus is the part just below the tip. • These two parts of the shoot must be communicating with one another by means hormones. • Plant hormones are chemical that affect the activities of particular ...
Understanding Skin Colour
... We all have a basic skin colour that is genetically determined and sets the rate at which melanin is produced without regard to sun exposure. Skin can be made darker by exposure to the sun in most people by exposure to sunlight. We are not sure about so many things in relation to melanin production ...
... We all have a basic skin colour that is genetically determined and sets the rate at which melanin is produced without regard to sun exposure. Skin can be made darker by exposure to the sun in most people by exposure to sunlight. We are not sure about so many things in relation to melanin production ...
Chapter 5 the integumentary system
... _____ directions – keeps hair from _________ _______); three growth phases (anagen, catagen, telogen); as the hair grows, __________ digest sheath around hair shaft at skin’s surface; alopecia; sebaceous gland; arrector ______ ...
... _____ directions – keeps hair from _________ _______); three growth phases (anagen, catagen, telogen); as the hair grows, __________ digest sheath around hair shaft at skin’s surface; alopecia; sebaceous gland; arrector ______ ...
PDF
... about the involvement of signalling by the receptor tyrosine kinases Kit and ErbB in the establishment of MSCs in zebrafish. On p. 1003, Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard and colleagues investigate the embryonic origin of the melanophores that emerge during juvenile development and that contribute to the ...
... about the involvement of signalling by the receptor tyrosine kinases Kit and ErbB in the establishment of MSCs in zebrafish. On p. 1003, Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard and colleagues investigate the embryonic origin of the melanophores that emerge during juvenile development and that contribute to the ...
PDF
... about the involvement of signalling by the receptor tyrosine kinases Kit and ErbB in the establishment of MSCs in zebrafish. On p. 1003, Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard and colleagues investigate the embryonic origin of the melanophores that emerge during juvenile development and that contribute to the ...
... about the involvement of signalling by the receptor tyrosine kinases Kit and ErbB in the establishment of MSCs in zebrafish. On p. 1003, Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard and colleagues investigate the embryonic origin of the melanophores that emerge during juvenile development and that contribute to the ...
Sensitivity of A-549 human lung cancer cells to nanoporous zinc
... photodynamic therapy. The ZnO NPs structure possesses a high surface to volume ratio due to its porosity and ZnO NPs can be used as an efficient photosensitizer carrier system. We were able to grow ZnO NPs on the tip of borosilicate glass capillaries (0.5 µm diameter) and conjugated this with Photof ...
... photodynamic therapy. The ZnO NPs structure possesses a high surface to volume ratio due to its porosity and ZnO NPs can be used as an efficient photosensitizer carrier system. We were able to grow ZnO NPs on the tip of borosilicate glass capillaries (0.5 µm diameter) and conjugated this with Photof ...
Nerve tissue
... • Golgi type II • axon terminates in the immediate area of the cell body • stellate cells ...
... • Golgi type II • axon terminates in the immediate area of the cell body • stellate cells ...
Chemistry: Chemical Reactions Exam Review SNC2P
... How does an ionic compound form? What is/are the difference(s) between ionic compound and polyatomic compound? How do you write formulas for ionic compounds and polyatomic compounds? How do you name ionic compounds and polyatomic compounds? ...
... How does an ionic compound form? What is/are the difference(s) between ionic compound and polyatomic compound? How do you write formulas for ionic compounds and polyatomic compounds? How do you name ionic compounds and polyatomic compounds? ...
Sometimes It’s Good to be a Chicken
... Skin Cancer Prevention The earlier we start practicing sun safety, the longer we will keep our skin healthy. ...
... Skin Cancer Prevention The earlier we start practicing sun safety, the longer we will keep our skin healthy. ...
Ch34
... Plants grow in a fixed location. If the environment becomes unfavorable, the plant must cope or die. Plants are capable of sensing environmental changes and make adjustments. The ultimate control of plant growth and development is genetic. Location of a cell in the plant body and environment influen ...
... Plants grow in a fixed location. If the environment becomes unfavorable, the plant must cope or die. Plants are capable of sensing environmental changes and make adjustments. The ultimate control of plant growth and development is genetic. Location of a cell in the plant body and environment influen ...
Chromatophore

Chromatophores are pigment-containing and light-reflecting cells, or groups of cells, found in bacteria and a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, have a class of cells called melanocytes for coloration.Chromatophores are largely responsible for generating skin and eye colour in cold-blooded animals and are generated in the neural crest during embryonic development. Mature chromatophores are grouped into subclasses based on their colour (more properly ""hue"") under white light: xanthophores (yellow), erythrophores (red), iridophores (reflective / iridescent), leucophores (white), melanophores (black/brown), and cyanophores (blue). The term chromatophore can also refer to coloured, membrane-associated vesicles found in some forms of photosynthetic bacteria.Some species can rapidly change colour through mechanisms that translocate pigment and reorient reflective plates within chromatophores. This process, often used as a type of camouflage, is called physiological colour change or metachrosis. Cephalopods such as the octopus have complex chromatophore organs controlled by muscles to achieve this, whereas vertebrates such as chameleons generate a similar effect by cell signalling. Such signals can be hormones or neurotransmitters and may be initiated by changes in mood, temperature, stress or visible changes in the local environment. Chromatophores are studied by scientists to understand human disease and as a tool in drug discovery.