here
... A black hole forms when a mass is squashed inside it’s Schwarzschild Radius RS = 3 (M/Msun) km ...
... A black hole forms when a mass is squashed inside it’s Schwarzschild Radius RS = 3 (M/Msun) km ...
PowerPoint - Chandra X
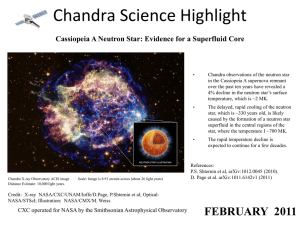
... in the Cassiopeia A supernova remnant over the past ten years have revealed a 4% decline in the neutron star’s surface temperature, which is ~2 MK. ...
... in the Cassiopeia A supernova remnant over the past ten years have revealed a 4% decline in the neutron star’s surface temperature, which is ~2 MK. ...
Stellar Evolution
... layers are driven away • Core becomes hot enough to produce Carbon (C) • Star contracts to normal size when helium is used up • Carbon core left over, White dwarf remains ...
... layers are driven away • Core becomes hot enough to produce Carbon (C) • Star contracts to normal size when helium is used up • Carbon core left over, White dwarf remains ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... Sheetthat not even – An object so massive and dense light can escape its gravity – The end result from a supernova of a star that has a mass greater than 3x the sun ...
... Sheetthat not even – An object so massive and dense light can escape its gravity – The end result from a supernova of a star that has a mass greater than 3x the sun ...
Death of Stars - Astronomy @ Walton High School
... boundary of a black hole (called the event horizon) it cannot escape back out again; not even light can escape which travels at 300,000 kilometres a second. Evidence from black holes comes from binary stars that get their solar material pulled into the hole. This often forms an accretion disc of mat ...
... boundary of a black hole (called the event horizon) it cannot escape back out again; not even light can escape which travels at 300,000 kilometres a second. Evidence from black holes comes from binary stars that get their solar material pulled into the hole. This often forms an accretion disc of mat ...
The Lives of Stars
... large truck. White dwarfs have no fuel, but they glow faintly from leftover energy. After billions of years, a white dwarf eventually stops glowing. Then it is called a black dwarf. ...
... large truck. White dwarfs have no fuel, but they glow faintly from leftover energy. After billions of years, a white dwarf eventually stops glowing. Then it is called a black dwarf. ...
Astr40 HWIII(new) - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... 4. Stars with lower mass have shorter lifetimes. (T or F) 5. A low mass star which finishes fusing all the H to He in its core, leaves the main sequence ...
... 4. Stars with lower mass have shorter lifetimes. (T or F) 5. A low mass star which finishes fusing all the H to He in its core, leaves the main sequence ...
Lifecycle of Stars
... 1) Once your teacher has approved each word timeline and you have recorded them on the back of this page, you will create a personal poster that visually displays the four life cycles. You will work in table teams to complete this process, but you will each create your own mini-poster. 2) Use your n ...
... 1) Once your teacher has approved each word timeline and you have recorded them on the back of this page, you will create a personal poster that visually displays the four life cycles. You will work in table teams to complete this process, but you will each create your own mini-poster. 2) Use your n ...
main sequence star
... the core of the star. The white dwarf is very dense and hot. The emit (release) less light than they did when they were stars. • As these white dwarfs cool they become fainter. • When there is no more energy being emitted (released), they are called black dwarfs. ...
... the core of the star. The white dwarf is very dense and hot. The emit (release) less light than they did when they were stars. • As these white dwarfs cool they become fainter. • When there is no more energy being emitted (released), they are called black dwarfs. ...
File
... 8-25 X larger than our Sun Consume their fuel very fast – die more quickly and more violently Star expands into a Supergiant which causes the core to collapse and the outer portion to explode creating a Supernova then a Neutron Star ...
... 8-25 X larger than our Sun Consume their fuel very fast – die more quickly and more violently Star expands into a Supergiant which causes the core to collapse and the outer portion to explode creating a Supernova then a Neutron Star ...
Properties of Main Sequence Stars
... Determine approximate values of the luminosity, temperature, mass and radius of an O5 and M5 main sequence star using the HR diagram on the accompanying page or use the HR diagrams in the text (Unit 59). ...
... Determine approximate values of the luminosity, temperature, mass and radius of an O5 and M5 main sequence star using the HR diagram on the accompanying page or use the HR diagrams in the text (Unit 59). ...
Useful Things to Study (#2)
... What is a comet nucleus made of? How about the tail? What are meteors? What is the Titius-Bode Law (aka Bode’s Law)? What is a dwarf planet? The destructive power of a collision with an asteroid or comet nucleus comes from the kinetic energy of the object hitting the Earth. Since kinetic energy is 1 ...
... What is a comet nucleus made of? How about the tail? What are meteors? What is the Titius-Bode Law (aka Bode’s Law)? What is a dwarf planet? The destructive power of a collision with an asteroid or comet nucleus comes from the kinetic energy of the object hitting the Earth. Since kinetic energy is 1 ...
Great Migrations & other natural history tales
... Observations show that many stars are surrounded by dust and sometimes detectable gas, in the form of the so-called debris disks or replenished dust disks, originally called Vega-type disks. The Sun has a zodiacal light disk, which is a week manifestation of the same phenomenon. Beta Pictoris (or b ...
... Observations show that many stars are surrounded by dust and sometimes detectable gas, in the form of the so-called debris disks or replenished dust disks, originally called Vega-type disks. The Sun has a zodiacal light disk, which is a week manifestation of the same phenomenon. Beta Pictoris (or b ...
Black Hole Video Questions
... 8. If a space probe were to look out of a black hole it would see (blackness) (light being sucked in) (nothing). 9. If a space probe were to look into of a black hole it would see the center of the black hole called the (accretion disk) (event horizon) (singularity). 10. Most black holes are about ( ...
... 8. If a space probe were to look out of a black hole it would see (blackness) (light being sucked in) (nothing). 9. If a space probe were to look into of a black hole it would see the center of the black hole called the (accretion disk) (event horizon) (singularity). 10. Most black holes are about ( ...
1 - Alice Pevyhouse
... 4.Astronomers identify the “birth” of a real star with what activity in the star? 5.When a single star of mass equal to our Sun dies, it will ultimatly become a 6. In a collapsing star of high mass, when electrons and protons are squeezed together with enormous force in the core of the star, they tu ...
... 4.Astronomers identify the “birth” of a real star with what activity in the star? 5.When a single star of mass equal to our Sun dies, it will ultimatly become a 6. In a collapsing star of high mass, when electrons and protons are squeezed together with enormous force in the core of the star, they tu ...
Lifetimes of stars
... Stellar Lifetimes • The Sun (and all stars) will eventually run out of fuel (hydrogen in regions where it is hot enough for fusion). • If all the hydrogen in the Sun could fuse to helium, the Sun’s lifetime would be 100 billion years. • But, by the time about 10% of the Sun’s H has been converted in ...
... Stellar Lifetimes • The Sun (and all stars) will eventually run out of fuel (hydrogen in regions where it is hot enough for fusion). • If all the hydrogen in the Sun could fuse to helium, the Sun’s lifetime would be 100 billion years. • But, by the time about 10% of the Sun’s H has been converted in ...
PHYS 175 Fall 2014 Final Recitation Ch. 16 The Sun
... Photons released in the core (where fusion takes place) collide almost instantaneously with other core constituents. This energy gradually flows outward, until the density of the sun decreases sufficiently to allow for radiative diffusion of the energy. Again, the photons still undergo many collisio ...
... Photons released in the core (where fusion takes place) collide almost instantaneously with other core constituents. This energy gradually flows outward, until the density of the sun decreases sufficiently to allow for radiative diffusion of the energy. Again, the photons still undergo many collisio ...
More stellar evolution…bloated stars and compact cores
... What we see is the outside (photosphere) of the star. While this is going on in the core, the post-main sequence star moves around on the HertzsprungRussell diagram ...
... What we see is the outside (photosphere) of the star. While this is going on in the core, the post-main sequence star moves around on the HertzsprungRussell diagram ...
Forces in stars
... and a mass of 2 million million million million million kg (about 300 000 times that of the Earth). This enormous mass means a very high gravitational pull – a person weighing 600 N on the surface of the Earth would have the colossal weight of 16400N if they stood on the 'surface' of the Sun. As muc ...
... and a mass of 2 million million million million million kg (about 300 000 times that of the Earth). This enormous mass means a very high gravitational pull – a person weighing 600 N on the surface of the Earth would have the colossal weight of 16400N if they stood on the 'surface' of the Sun. As muc ...
ppt - Slides by Prof Christian
... pressure can no longer hold up against gravity. WDs with more than ~ 1.4 solar masses can not exist! Chandrasekhar Limit = 1.4 Msun ...
... pressure can no longer hold up against gravity. WDs with more than ~ 1.4 solar masses can not exist! Chandrasekhar Limit = 1.4 Msun ...
Cygnus X-1
Cygnus X-1 (abbreviated Cyg X-1) is a well-known galactic X-ray source, thought to be a black hole, in the constellation Cygnus. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the strongest X-ray sources seen from Earth, producing a peak X-ray flux density of 6977229999999999999♠2.3×10−23 Wm−2 Hz−1 (7003230000000000000♠2.3×103 Jansky). Cygnus X-1 was the first X-ray source widely accepted to be a black hole and it remains among the most studied astronomical objects in its class. The compact object is now estimated to have a mass about 14.8 times the mass of the Sun and has been shown to be too small to be any known kind of normal star, or other likely object besides a black hole. If so, the radius of its event horizon is about 7004440000000000000♠44 km.Cygnus X-1 belongs to a high-mass X-ray binary system about 7019574266339685654♠6070 ly from the Sun that includes a blue supergiant variable star designated HDE 226868 which it orbits at about 0.2 AU, or 20% of the distance from the Earth to the Sun. A stellar wind from the star provides material for an accretion disk around the X-ray source. Matter in the inner disk is heated to millions of degrees, generating the observed X-rays. A pair of jets, arranged perpendicular to the disk, are carrying part of the energy of the infalling material away into interstellar space.This system may belong to a stellar association called Cygnus OB3, which would mean that Cygnus X-1 is about five million years old and formed from a progenitor star that had more than 7001400000000000000♠40 solar masses. The majority of the star's mass was shed, most likely as a stellar wind. If this star had then exploded as a supernova, the resulting force would most likely have ejected the remnant from the system. Hence the star may have instead collapsed directly into a black hole.Cygnus X-1 was the subject of a friendly scientific wager between physicists Stephen Hawking and Kip Thorne in 1975, with Hawking betting that it was not a black hole. He conceded the bet in 1990 after observational data had strengthened the case that there was indeed a black hole in the system. This hypothesis has not been confirmed due to a lack of direct observation but has generally been accepted from indirect evidence.