Unit 12: Abnormal Psychology
... • The nearly 1-in-100 odds of any person developing schizophrenia become about 1 in 10 if a family member has it, and close to 1 in 2 if an identical twin has the disorder. • Adoption studies confirm the genetic contribution to schizophrenia. An adopted child’s probability of developing the disorde ...
... • The nearly 1-in-100 odds of any person developing schizophrenia become about 1 in 10 if a family member has it, and close to 1 in 2 if an identical twin has the disorder. • Adoption studies confirm the genetic contribution to schizophrenia. An adopted child’s probability of developing the disorde ...
Psychotic Disorders
... Schizoaffective disorder Meets criteria for major depressive or manic episode and psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia 2 weeks of psychotic symptoms in absence of mood symptoms Mood symptoms represent significant portion of time both in active and ...
... Schizoaffective disorder Meets criteria for major depressive or manic episode and psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia 2 weeks of psychotic symptoms in absence of mood symptoms Mood symptoms represent significant portion of time both in active and ...
Disorders Classification + Answer Key
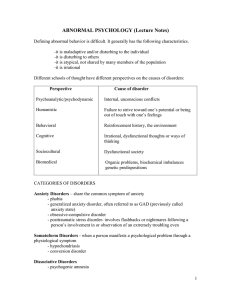
... Directions: Using the cards provided by your instructor determine to which category of illnesses belongs. In the second column find the characteristics that best suit each of the categories of illnesses. In the third column create your own example of an individual experiencing one of the disorders i ...
... Directions: Using the cards provided by your instructor determine to which category of illnesses belongs. In the second column find the characteristics that best suit each of the categories of illnesses. In the third column create your own example of an individual experiencing one of the disorders i ...
Psych B – Module 29
... Biological Factors – Brain Function • The brain of those with schizophrenia operates differently than the normal brain. • The frontal lobes show less activity. • Those with schizophrenia have a larger number of receptor sites for the neurotransmitter dopamine. ...
... Biological Factors – Brain Function • The brain of those with schizophrenia operates differently than the normal brain. • The frontal lobes show less activity. • Those with schizophrenia have a larger number of receptor sites for the neurotransmitter dopamine. ...
Psych B
... Biological Factors – Brain Function • The brain of those with schizophrenia operates differently than the normal brain. • The frontal lobes show less activity. • Those with schizophrenia have a larger number of receptor sites for the neurotransmitter dopamine. ...
... Biological Factors – Brain Function • The brain of those with schizophrenia operates differently than the normal brain. • The frontal lobes show less activity. • Those with schizophrenia have a larger number of receptor sites for the neurotransmitter dopamine. ...
Abnormal Psychology
... – 4. Frequent negative thoughts, faulty attribution of blame, low self-esteem (cognitive) – 5. Loss of energy, restlessness (physical) – 6. May last six or more months • 12% of adult population will be affected by this • Can turn into a major depressive episode – Thoughts of suicide, death ...
... – 4. Frequent negative thoughts, faulty attribution of blame, low self-esteem (cognitive) – 5. Loss of energy, restlessness (physical) – 6. May last six or more months • 12% of adult population will be affected by this • Can turn into a major depressive episode – Thoughts of suicide, death ...
Psychological Disorders
... – The causes often seem to work in tandem with each other to increase likelihood of particular disorder – No one ‘guess’ is likely to cause the disorder in isolation ...
... – The causes often seem to work in tandem with each other to increase likelihood of particular disorder – No one ‘guess’ is likely to cause the disorder in isolation ...
Personality Disorders
... Personality disorder - - DSM - long term, stable pattern of unusual and inflexible personality traits that lead to functional impairment or distress ...
... Personality disorder - - DSM - long term, stable pattern of unusual and inflexible personality traits that lead to functional impairment or distress ...
File
... A major mood disorder accompanied by psychotic symptoms is called an affective psychosis. Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) which occurs during the winter months is another common form of depression. SAD is typically treated with phototherapy. Biological, psychoanalytic, cognitive, and behavio ...
... A major mood disorder accompanied by psychotic symptoms is called an affective psychosis. Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) which occurs during the winter months is another common form of depression. SAD is typically treated with phototherapy. Biological, psychoanalytic, cognitive, and behavio ...
Signs and Symptoms in Psychiatry
... psychiatry signs and symptoms are not so clearly demarcated as in other fields of medicine; they often overlap. Because of this, disorders in psychiatry are often described as syndromes—a constellation of signs and symptoms that together make up a recognizable condition. Schizophrenia, for example, ...
... psychiatry signs and symptoms are not so clearly demarcated as in other fields of medicine; they often overlap. Because of this, disorders in psychiatry are often described as syndromes—a constellation of signs and symptoms that together make up a recognizable condition. Schizophrenia, for example, ...
Ch 14 Objectives
... 12. Explain how genetic, neurochemical, and neuroanatomical factors may be related to the development of mood disorders. 13. Explain how cognitive factors, interpersonal factors, and stress may be related to the development of mood disorders. 14. Describe the general characteristics (symptoms) of sc ...
... 12. Explain how genetic, neurochemical, and neuroanatomical factors may be related to the development of mood disorders. 13. Explain how cognitive factors, interpersonal factors, and stress may be related to the development of mood disorders. 14. Describe the general characteristics (symptoms) of sc ...
psychological disorders
... similarity between symptoms of amphetamine psychosis and acute paranoid schizophrenia AP results from an overproduction of dopamine Phenothiazines relieve symptoms of schizophrenia increased number of dopamine receptor sites in schizophrenics But... ...
... similarity between symptoms of amphetamine psychosis and acute paranoid schizophrenia AP results from an overproduction of dopamine Phenothiazines relieve symptoms of schizophrenia increased number of dopamine receptor sites in schizophrenics But... ...
Anxiety and Somatoform Disorders
... Thoughts of a person with schizophrenia may jump from topic to topic in an illogical way. • Other symptoms they experience may include decreased ability to function, social withdrawal, loss of social skills, and loss of normal emotional responsiveness. Some may even go into a catatonic stupor which ...
... Thoughts of a person with schizophrenia may jump from topic to topic in an illogical way. • Other symptoms they experience may include decreased ability to function, social withdrawal, loss of social skills, and loss of normal emotional responsiveness. Some may even go into a catatonic stupor which ...
Psychological Disorders Defining Abnormal Behavior
... – Individual experiences a major depressive episode and depressed characteristics for at least two weeks or longer – Vegetative symptoms of depression • Dysthymic disorder – Generally more chronic and has fewer symptoms than major depressive disorder ...
... – Individual experiences a major depressive episode and depressed characteristics for at least two weeks or longer – Vegetative symptoms of depression • Dysthymic disorder – Generally more chronic and has fewer symptoms than major depressive disorder ...
Psychological Disorders
... patient seeks treatment • Axis II - an enduring personality disorder that may contribute to axis I ...
... patient seeks treatment • Axis II - an enduring personality disorder that may contribute to axis I ...
Review Unit 12 Disorders 2014-2015
... “What goes up, must come down” – Men and women affected equally ...
... “What goes up, must come down” – Men and women affected equally ...
Chapter 13 - Psychological Disorders
... Agoraphobia: Anxiety characterized by marked fear and avoidance of being alone in a place from which escape might be difficult or embarrassing (such as airplanes, tunnels, being in crowds) Social phobia: Fear of, and desire to avoid, situations in which one might be exposed to scrutiny by others ...
... Agoraphobia: Anxiety characterized by marked fear and avoidance of being alone in a place from which escape might be difficult or embarrassing (such as airplanes, tunnels, being in crowds) Social phobia: Fear of, and desire to avoid, situations in which one might be exposed to scrutiny by others ...
Chapter 10
... (d) Takes please in few, if any, activities. (e) Lacks close friends or confidants other than 1st degree relatives (f) Appears to indifferent to the praise or criticisms of others (g) Shows emotional coldness, detachment, or flattened affect. 3. Schizotypal Personality disorder A pervasive pattern o ...
... (d) Takes please in few, if any, activities. (e) Lacks close friends or confidants other than 1st degree relatives (f) Appears to indifferent to the praise or criticisms of others (g) Shows emotional coldness, detachment, or flattened affect. 3. Schizotypal Personality disorder A pervasive pattern o ...
Major Depressive Episode
... these experiences, that determine growth and development of personality ...
... these experiences, that determine growth and development of personality ...