Anxiety Disorders - Perfectionism and Psychopathology Lab
... Often events involve actual or threatened death, or serious injury These events can include natural disasters (floods) or human made disasters (war, rape, assault) Can involve actual involvement with event, witnessing or being indirectly involved ...
... Often events involve actual or threatened death, or serious injury These events can include natural disasters (floods) or human made disasters (war, rape, assault) Can involve actual involvement with event, witnessing or being indirectly involved ...
Personality Disorders
... symbolize underlying psychological conflict. • Learning theory: Conversion symptoms represent learned responses that are reinforced by avoidance of painful or anxiety-evoking situations. • Cognitive factors: Evidence is emerging that points to cognitive factors such as distorted thinking patterns. ...
... symbolize underlying psychological conflict. • Learning theory: Conversion symptoms represent learned responses that are reinforced by avoidance of painful or anxiety-evoking situations. • Cognitive factors: Evidence is emerging that points to cognitive factors such as distorted thinking patterns. ...
DSM 5
... and activities (RRBs). Because both components are required for diagnosis of ASD, social communication disorder is diagnosed if no RRBs are present. ...
... and activities (RRBs). Because both components are required for diagnosis of ASD, social communication disorder is diagnosed if no RRBs are present. ...
Memory
... depression… trapped in depressed mood; also exhibit anxiety or substance abuse. 2. Women are nearly twice as vulnerable to depression. Men tend to be more external. 3. Most major depressive episodes self-terminate. 4. Stressful events related to work, marriage, and close relationships often precede ...
... depression… trapped in depressed mood; also exhibit anxiety or substance abuse. 2. Women are nearly twice as vulnerable to depression. Men tend to be more external. 3. Most major depressive episodes self-terminate. 4. Stressful events related to work, marriage, and close relationships often precede ...
chapter 15 - Cengage Learning
... 19. State the causes, according to various theoretical models, of mood disorders. Describe how learned helplessness and attributional style may contribute to depression. (see “Causes of Mood Disorders”) 20. Define schizophrenia. Describe the disorganized thought and language characteristic of schizo ...
... 19. State the causes, according to various theoretical models, of mood disorders. Describe how learned helplessness and attributional style may contribute to depression. (see “Causes of Mood Disorders”) 20. Define schizophrenia. Describe the disorganized thought and language characteristic of schizo ...
Chapter Outline - Cengage Learning
... which has been helpful in reducing fears and panic attacks in agoraphobic individuals and those with specific phobias; cognitive strategies aimed at changing unrealistic thoughts; systematic desensitization; modeling. A combined approach that includes cognitive, behavioral, and biological components ...
... which has been helpful in reducing fears and panic attacks in agoraphobic individuals and those with specific phobias; cognitive strategies aimed at changing unrealistic thoughts; systematic desensitization; modeling. A combined approach that includes cognitive, behavioral, and biological components ...
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) is
... The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) is a comprehensive encyclopedia of psychological disorders first published by the American Psychiatric Association in 1952. The DSM is used as a classification system in order to provide a common language for psychiatrists, psychologist ...
... The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) is a comprehensive encyclopedia of psychological disorders first published by the American Psychiatric Association in 1952. The DSM is used as a classification system in order to provide a common language for psychiatrists, psychologist ...
Unit XII Textbook PowerPoint questions and answers
... 2. Which of the following is true of depression? a. Depression usually develops during middle age. b. Depression usually happens without major cognitive or behavioral changes. c. A major depressive episode usually gets worse and worse unless its treated. d. True depression us usually not related to ...
... 2. Which of the following is true of depression? a. Depression usually develops during middle age. b. Depression usually happens without major cognitive or behavioral changes. c. A major depressive episode usually gets worse and worse unless its treated. d. True depression us usually not related to ...
learning objectives chapter 12
... broadcasting, thought blocking, thought withdrawal, and thought insertions. Define hallucinations. (see “Symptoms of Schizophrenia”) 21. Describe the symptoms of the following DSM-IV categories of schizophrenia: paranoid, disorganized, catatonic, undifferentiated, and residual. Discuss alternative w ...
... broadcasting, thought blocking, thought withdrawal, and thought insertions. Define hallucinations. (see “Symptoms of Schizophrenia”) 21. Describe the symptoms of the following DSM-IV categories of schizophrenia: paranoid, disorganized, catatonic, undifferentiated, and residual. Discuss alternative w ...
Psychological Disorders
... Positive symptoms: characteristics of schizophrenia that are added to a person’s personality, such as hallucinations, delusions, inappropriate emotions, and word salad. Negative symptoms: characteristics of schizophrenia that are taken away from a person’s personality, such as flattening of the emot ...
... Positive symptoms: characteristics of schizophrenia that are added to a person’s personality, such as hallucinations, delusions, inappropriate emotions, and word salad. Negative symptoms: characteristics of schizophrenia that are taken away from a person’s personality, such as flattening of the emot ...
Document
... “hollow” and “thud”; sometimes called “The Thud Experiment” All were admitted to the psychiatric hospitals; most diagnosed ...
... “hollow” and “thud”; sometimes called “The Thud Experiment” All were admitted to the psychiatric hospitals; most diagnosed ...
jAnxiety Disorders - Dr. Ameneh Mirzael 2009
... • life time prevalence: 12.5% • most common mental d/o in women & 2nd most common d/o in men (after substancerelated d/o) • F:M = 2:1 • start at a young age (5-12 years) ...
... • life time prevalence: 12.5% • most common mental d/o in women & 2nd most common d/o in men (after substancerelated d/o) • F:M = 2:1 • start at a young age (5-12 years) ...
anxiety disorders
... phobias, agoraphobia has the strongest and most specific association with the genetic factor that represents proneness to phobias. • More than one-third of individuals with agoraphobia are completely homebound and unable to work. ...
... phobias, agoraphobia has the strongest and most specific association with the genetic factor that represents proneness to phobias. • More than one-third of individuals with agoraphobia are completely homebound and unable to work. ...
Unit 12 - Our Lady of Lourdes High School
... 2 or more distinct identities are present alternately controlling the person’s behavior Each personality has its own voice and mannerisms ...
... 2 or more distinct identities are present alternately controlling the person’s behavior Each personality has its own voice and mannerisms ...
Unit 1 Notes: Psychological Disorders Dysfunctional Behavior
... In the United States, the DSM-‐V (or Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders, 5th edition) is considered the authoritative source on diagnosing and treating psychological disorders The DSM-‐V di ...
... In the United States, the DSM-‐V (or Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders, 5th edition) is considered the authoritative source on diagnosing and treating psychological disorders The DSM-‐V di ...
Unit 1 Notes: Psychological Disorders
... The diathesis-stress model suggests that stress works with genetic factors in bringing on schizophrenia in genetically vulnerable individuals Sources of stress include early brain trauma, dysfunctional family environments and negative life events It is suggested that these factors combine to produce ...
... The diathesis-stress model suggests that stress works with genetic factors in bringing on schizophrenia in genetically vulnerable individuals Sources of stress include early brain trauma, dysfunctional family environments and negative life events It is suggested that these factors combine to produce ...
LEARNING OBJECTIVES To demonstrate mastery of this chapter
... b. psychoanalytic theory; c. behavioral theory; d. cognitive theory; e. the social and environmental stresses that cause women to experience depression more than men, including postpartum depression; f. the role of heredity; and g. the time or season of the year, including the cause, symptoms, and t ...
... b. psychoanalytic theory; c. behavioral theory; d. cognitive theory; e. the social and environmental stresses that cause women to experience depression more than men, including postpartum depression; f. the role of heredity; and g. the time or season of the year, including the cause, symptoms, and t ...
Anxiety and Somatoform Disorders
... physical complaint, such as paralysis of the legs, or blindness. Patients strongly believe there is impairment, but may show less distress than with a real loss. 3. Hypochondriasis is characterized by persistent preoccupation with one's health and physical condition, despite the fact that genuine ...
... physical complaint, such as paralysis of the legs, or blindness. Patients strongly believe there is impairment, but may show less distress than with a real loss. 3. Hypochondriasis is characterized by persistent preoccupation with one's health and physical condition, despite the fact that genuine ...
Section 9: Basic Psychiatric Terminology
... Anxiety Disorders 1. Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD): generalized, persistent state of anxiety not related to a certain stimulus. 2. Panic disorder: Discrete attacks of anxiety with no ...
... Anxiety Disorders 1. Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD): generalized, persistent state of anxiety not related to a certain stimulus. 2. Panic disorder: Discrete attacks of anxiety with no ...
Paranoid Schizophrenia
... but currently have no major symptoms Thinking is only mildly disturbed Emotional lives are impoverished This diagnosis could mean that the schizophrenia is in remission or becoming dormant – Remember the doctors who had entered themselves into ...
... but currently have no major symptoms Thinking is only mildly disturbed Emotional lives are impoverished This diagnosis could mean that the schizophrenia is in remission or becoming dormant – Remember the doctors who had entered themselves into ...
abnormal dissociative and schizophrenia
... number of receptor sites for the neurotransmitter dopamine. ...
... number of receptor sites for the neurotransmitter dopamine. ...
Dissociative Disorders - kyle
... only get attention when they behave badly, they may learn anti-social behavior. ...
... only get attention when they behave badly, they may learn anti-social behavior. ...
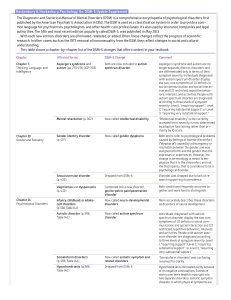
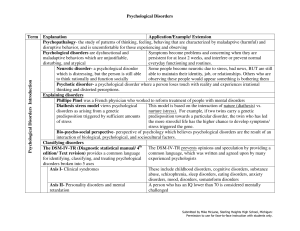
Psychological Disorders Term Explanation Application
... GABA reduces neural activity in the brain, which therefore could of serotonin and GABA, while also having explain symptoms of anxiety because people do not have enough GABA. In addition, norepinephrine speeds up neural activity in the excessive norepinephrine brain, providing an explanation for peop ...
... GABA reduces neural activity in the brain, which therefore could of serotonin and GABA, while also having explain symptoms of anxiety because people do not have enough GABA. In addition, norepinephrine speeds up neural activity in the excessive norepinephrine brain, providing an explanation for peop ...
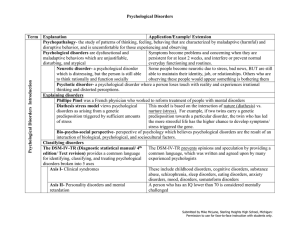
13A-Psychdisorder-table - Miami Beach Senior High School
... GABA reduces neural activity in the brain, which therefore could of serotonin and GABA, while also having explain symptoms of anxiety because people do not have enough excessive norepinephrine GABA. In addition, norepinephrine speeds up neural activity in the brain, providing an explanation for peop ...
... GABA reduces neural activity in the brain, which therefore could of serotonin and GABA, while also having explain symptoms of anxiety because people do not have enough excessive norepinephrine GABA. In addition, norepinephrine speeds up neural activity in the brain, providing an explanation for peop ...
Unit 12 Abnormal Psych Teacher
... People who have schizophrenia have abnormal brain activity before the onset of symptoms, showing that schizophrenia may be a developmental disorder. MRI studies show the gray matter in the brains of people with schizophrenia is markedly dense than people with no schizophrenia. Studies have sho ...
... People who have schizophrenia have abnormal brain activity before the onset of symptoms, showing that schizophrenia may be a developmental disorder. MRI studies show the gray matter in the brains of people with schizophrenia is markedly dense than people with no schizophrenia. Studies have sho ...