Seating Chart for Wednesday PHOTO ID REQUIRED! SIT IN YOUR ASSIGNED ROW!
... • So light falls back. • “Schwarzschild radius” or “event horizon” = radius around mass concentration within which light can no longer escape to outside. ...
... • So light falls back. • “Schwarzschild radius” or “event horizon” = radius around mass concentration within which light can no longer escape to outside. ...
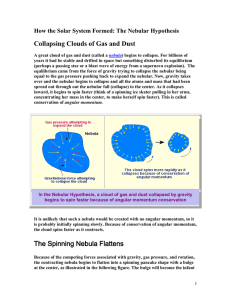
How the Solar System Formed: The Nebular
... all revolve in the same direction. All debris (matter) orbits the sun (except moons). The most dense materials are closest to the Sun. All the planets and most of the moons and asteroids are about the same age. The same materials (but in different proportions) make up all the objects in the solar sy ...
... all revolve in the same direction. All debris (matter) orbits the sun (except moons). The most dense materials are closest to the Sun. All the planets and most of the moons and asteroids are about the same age. The same materials (but in different proportions) make up all the objects in the solar sy ...
Chapter 1 - Colorado Mesa University
... • Our earth orbits our sun at a distance of ~ 150 million km, what we call an Astronomical Unit or AU and is tilted 23.6 degrees to its orbital plane. • Our sun orbits the center of the Milky Way about 8.5 kPc out. ...
... • Our earth orbits our sun at a distance of ~ 150 million km, what we call an Astronomical Unit or AU and is tilted 23.6 degrees to its orbital plane. • Our sun orbits the center of the Milky Way about 8.5 kPc out. ...
HO-04 5a Astro Unit Content
... Much of the above information could usefully be represented in a Venn diagram. Students will be able to make, record, and then clearly share accurate results from “naked-eye” observations of objects in the sky (e.g., clouds, planes, sun, moon, stars). They will use their recorded observations to fin ...
... Much of the above information could usefully be represented in a Venn diagram. Students will be able to make, record, and then clearly share accurate results from “naked-eye” observations of objects in the sky (e.g., clouds, planes, sun, moon, stars). They will use their recorded observations to fin ...
pptx
... The large impact theory is widely believed to be correct. The iron core of the impacting planet could have merged with the Earth’s core, while the Moon formed from crust and mantle thrown into space. This explains why the Moon is similar in composition to the Earth’s crust and mantle, but has as ver ...
... The large impact theory is widely believed to be correct. The iron core of the impacting planet could have merged with the Earth’s core, while the Moon formed from crust and mantle thrown into space. This explains why the Moon is similar in composition to the Earth’s crust and mantle, but has as ver ...
Practice questions for Stars File
... 1. Describe the difference in the stages of the life cycle for a large and massive star compared to an average star 2. Describe the fuel use changes from birth to death for a black hole 3. Describe the fuel use changes from birth to death for a neutron star 4. Explain how the energy changes are invo ...
... 1. Describe the difference in the stages of the life cycle for a large and massive star compared to an average star 2. Describe the fuel use changes from birth to death for a black hole 3. Describe the fuel use changes from birth to death for a neutron star 4. Explain how the energy changes are invo ...
`earthlike` and second the probability that they have suitable climate
... However when a planet is orbiting a star, it tugs the position of the star back and forth as it goes around. Thus the position of the star is oscillating and is moving toward the observer half the time and away from the the other half the time. Correspondingly the light from the star is blue shifted ...
... However when a planet is orbiting a star, it tugs the position of the star back and forth as it goes around. Thus the position of the star is oscillating and is moving toward the observer half the time and away from the the other half the time. Correspondingly the light from the star is blue shifted ...
Heliocentric Models and Modern Astronomy
... Kepler’s laws of heliocentric planetary motions consistent will all of Tycho Brahe’s data but obtained very strong support only after vindication by accurate + unprecedented observations taken by Galileo Galilei with the recently invented telescope ...
... Kepler’s laws of heliocentric planetary motions consistent will all of Tycho Brahe’s data but obtained very strong support only after vindication by accurate + unprecedented observations taken by Galileo Galilei with the recently invented telescope ...
UP8.LP2.OtherCelestialBodies
... after moons. Asteroids are rocky bodies that revolve around the Sun. Asteroids vary in shapes and sizes but are mostly made of iron, nickel, and stone. Most asteroids in the solar system can be found between Mars and Jupiter – this is called the asteroid belt. ...
... after moons. Asteroids are rocky bodies that revolve around the Sun. Asteroids vary in shapes and sizes but are mostly made of iron, nickel, and stone. Most asteroids in the solar system can be found between Mars and Jupiter – this is called the asteroid belt. ...
oceanworlds1
... The Earth is not the only planet in the solar system with an ocean. Scattered throughout the outer reaches are icy asteroids, moons, and dwarf planets; any of which could contain a large buried body of water. This intriguing possibility suggests we should refocus our exploration efforts if we want t ...
... The Earth is not the only planet in the solar system with an ocean. Scattered throughout the outer reaches are icy asteroids, moons, and dwarf planets; any of which could contain a large buried body of water. This intriguing possibility suggests we should refocus our exploration efforts if we want t ...
PhysicsSG-Gravitation-91109R
... period of 1.00 seconds. What is the speed of a point on the equator of the star? b) What is g at the surface of this neutron star? c) A 1.00 kg mass has a weight on earth of 9.80 N. What would be its weight on the star? d) How many revolutions per minute are made by a satellite orbiting 1.00 km abov ...
... period of 1.00 seconds. What is the speed of a point on the equator of the star? b) What is g at the surface of this neutron star? c) A 1.00 kg mass has a weight on earth of 9.80 N. What would be its weight on the star? d) How many revolutions per minute are made by a satellite orbiting 1.00 km abov ...
Astronomy Unit Test Review Sheet
... 2. What is an optical telescope? What is the difference between a reflecting and a refracting telescope? What other types of telescopes do scientists use to gather information? Optical telescopes are used to see visible light from far away. Refracting uses a glass lens and a reflecting telescope use ...
... 2. What is an optical telescope? What is the difference between a reflecting and a refracting telescope? What other types of telescopes do scientists use to gather information? Optical telescopes are used to see visible light from far away. Refracting uses a glass lens and a reflecting telescope use ...
Extra-Solar Planets
... – Effect of Jupiter on the Sun gives a Vmax of ~20m/sec – BUT that of Earth is a 1/10 m – 30 times less than can be detected at present ...
... – Effect of Jupiter on the Sun gives a Vmax of ~20m/sec – BUT that of Earth is a 1/10 m – 30 times less than can be detected at present ...
Due Date: Thursday, November 16, 2006
... The most significant difference between a high-mass star and the Sun will be their lifetime! Look at the HR diagram in Figure 11.1. The lifetime of Spica (10 Msun) is only about 10 million years. The lifetime of Achernar (6 Msun) is only 100 million years…so when we really should not expect the Sun ...
... The most significant difference between a high-mass star and the Sun will be their lifetime! Look at the HR diagram in Figure 11.1. The lifetime of Spica (10 Msun) is only about 10 million years. The lifetime of Achernar (6 Msun) is only 100 million years…so when we really should not expect the Sun ...
Pale Blue Dot - Pacific Science Center
... What is Astrobiology? Is there life on other planets? This is a complex question and we simply do not know. Earth is the only planet known to harbor life. As such it is the only model we have for comparison. When we look for life we look for life as we know it and that means we look for water. Wher ...
... What is Astrobiology? Is there life on other planets? This is a complex question and we simply do not know. Earth is the only planet known to harbor life. As such it is the only model we have for comparison. When we look for life we look for life as we know it and that means we look for water. Wher ...
Relative Sizes and Colors of Planets in the Solar System
... Go to the “Chart Tools” section on the menu bar and click on “Layout”. Click the Grid Lines tab and choose “none” for the horizontal and vertical grid lines. Click the Axis tab and choose “none” for both the vertical and the horizontal axis. To insert the name of each planet, (still in the “Layout” ...
... Go to the “Chart Tools” section on the menu bar and click on “Layout”. Click the Grid Lines tab and choose “none” for the horizontal and vertical grid lines. Click the Axis tab and choose “none” for both the vertical and the horizontal axis. To insert the name of each planet, (still in the “Layout” ...
4B-Astronomer-Notes
... modern astronomy. • The most important aspect of Copernicus' work is that it forever changed the place of man in the cosmos. • While a student at the University of Kraków, he discovered several logical contradictions in the existing astronomical system taught at that time, which put the earth at the ...
... modern astronomy. • The most important aspect of Copernicus' work is that it forever changed the place of man in the cosmos. • While a student at the University of Kraków, he discovered several logical contradictions in the existing astronomical system taught at that time, which put the earth at the ...
Solar System
... Venus is the 2nd planet in the solar system Similar to the size of Earth Its atmosphere consists of carbon dioxide, and clouds with sulfuric acid droplets It takes 225 days to orbit the Sun 1 time 117 Earth days = 1 Venus day Venus’ temperature on its surface can reach 880 degrees F. It’s known as E ...
... Venus is the 2nd planet in the solar system Similar to the size of Earth Its atmosphere consists of carbon dioxide, and clouds with sulfuric acid droplets It takes 225 days to orbit the Sun 1 time 117 Earth days = 1 Venus day Venus’ temperature on its surface can reach 880 degrees F. It’s known as E ...
Georgia Milestones Review Earth
... 12. Water in a gas state is called _____________________________. 13. Give an example of evaporation. _________________________________________________________ 14. Give 4 examples of precipitation. _______________________________________ 15. Is Earth’s axis straight or tilted? ________________ 16. W ...
... 12. Water in a gas state is called _____________________________. 13. Give an example of evaporation. _________________________________________________________ 14. Give 4 examples of precipitation. _______________________________________ 15. Is Earth’s axis straight or tilted? ________________ 16. W ...
Document
... direction to most other planets. It has no natural satellite. It is named after the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows. Because Venus is an inferior planet from E ...
... direction to most other planets. It has no natural satellite. It is named after the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows. Because Venus is an inferior planet from E ...
Slide 1
... “SCIENTISTS ESTIMATE THAT THE DUST CLOUD THAT OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED IN WAS AT LEAST 24 BILLION KILOMETERS ACROSS AND CONTAINED MATERIALS FROM AT LEAST TWO PREVIOUS GENERATIONS OF STARS.” “You Are Here, A Portable History of the Universe,” Christopher Potter ...
... “SCIENTISTS ESTIMATE THAT THE DUST CLOUD THAT OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED IN WAS AT LEAST 24 BILLION KILOMETERS ACROSS AND CONTAINED MATERIALS FROM AT LEAST TWO PREVIOUS GENERATIONS OF STARS.” “You Are Here, A Portable History of the Universe,” Christopher Potter ...
Orrery

An orrery is a mechanical model of the solar system that illustrates or predicts the relative positions and motions of the planets and moons, usually according to the heliocentric model. It may also represent the relative sizes of these bodies; but since accurate scaling is often not practical due to the actual large ratio differences, a subdued approximation may be used instead. Though the Greeks had working planetaria, the first orrery that was a planetarium of the modern era was produced in 1704, and one was presented to Charles Boyle, 4th Earl of Orrery — whence came the name. They are typically driven by a clockwork mechanism with a globe representing the Sun at the centre, and with a planet at the end of each of the arms.