Solid Tumour Section Soft tissue tumors: t(X;20)(p11.23;q13.33) in biphasic synovial sarcoma
... with relatively well-defined borders and a grey cut surface. No necrosis was seen. In histological sections stained with H and E, the tumor was mainly composed of uniform, closely packed spindle cells, with a high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio and finely dispersed chromatin. The tumor cells were arrange ...
... with relatively well-defined borders and a grey cut surface. No necrosis was seen. In histological sections stained with H and E, the tumor was mainly composed of uniform, closely packed spindle cells, with a high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio and finely dispersed chromatin. The tumor cells were arrange ...
Genetic Inheritance: Punnett Squares, Probability, and Genetic
... Disclaimer: Anything listed on this sheet is fair game for the test. It may not appear in the exact words, or in this order, and some things may be omitted on the actual test. I will focus on your understanding of difficult concepts. This means I will most likely give you hypothetical, real world si ...
... Disclaimer: Anything listed on this sheet is fair game for the test. It may not appear in the exact words, or in this order, and some things may be omitted on the actual test. I will focus on your understanding of difficult concepts. This means I will most likely give you hypothetical, real world si ...
Lecture 15 Genetic Regulation
... A Role for Minerals in Genetic Expression Summary: Metal ions are not passive components of biological systems as once thought. Recent studies have shown that Fe, Cu, or Zn are capable of regulating the expression of genes that code for that metal’s storage or transport proteins ...
... A Role for Minerals in Genetic Expression Summary: Metal ions are not passive components of biological systems as once thought. Recent studies have shown that Fe, Cu, or Zn are capable of regulating the expression of genes that code for that metal’s storage or transport proteins ...
Genetics Unit Test
... 1. ___________genetic makeup; the set of genes that an individual has 2. ____________the physical appearance of an individual 3. ____________an organism with 2 identical genes for a trait. 4. ____________an organism with 2 different genes for a trait 5. _____________Each parent has 2 genes for each ...
... 1. ___________genetic makeup; the set of genes that an individual has 2. ____________the physical appearance of an individual 3. ____________an organism with 2 identical genes for a trait. 4. ____________an organism with 2 different genes for a trait 5. _____________Each parent has 2 genes for each ...
Document
... of specific genes? (In other words, why are genes always turned on or expressed at the same level?) ...
... of specific genes? (In other words, why are genes always turned on or expressed at the same level?) ...
Chapter 11 Powerpoint File
... • Although each cell now has 4 chromatids something is different. Because each pair of homologous chromosomes was separated, neither of the daughter cells has two complete sets of chromosomes that it would have in a diploid cell • The two sets have been shuffled ...
... • Although each cell now has 4 chromatids something is different. Because each pair of homologous chromosomes was separated, neither of the daughter cells has two complete sets of chromosomes that it would have in a diploid cell • The two sets have been shuffled ...
ppt - Barley World
... Controlling gene flow to organic table beet • Spatial separation and pinning • RR sugarbeet - females only For more on sugarbeet seed production see CSS450/460 ...
... Controlling gene flow to organic table beet • Spatial separation and pinning • RR sugarbeet - females only For more on sugarbeet seed production see CSS450/460 ...
Document
... Using DNA that encodes a functional, therapeutic NCL gene to replace the mutated or missing NCL gene Injection of the viral vector containing the corrective NCL gene into the brain of affected ...
... Using DNA that encodes a functional, therapeutic NCL gene to replace the mutated or missing NCL gene Injection of the viral vector containing the corrective NCL gene into the brain of affected ...
Mammalian X Chromosome Inactivation
... 1. Present at homologous sites on pairs of chromosomes 2. Always genetically inert 3. DNA sequences that are not organized into genes 4. Telomeric and centromeric regions Features of Facultative Heterochromatin 1. Referred to as silent chromatin 2. Potential to become heterochromatic (Barr body) ...
... 1. Present at homologous sites on pairs of chromosomes 2. Always genetically inert 3. DNA sequences that are not organized into genes 4. Telomeric and centromeric regions Features of Facultative Heterochromatin 1. Referred to as silent chromatin 2. Potential to become heterochromatic (Barr body) ...
Slide 1
... • Master control genes called homeotic genes regulate groups of other genes that determine what body parts will develop in which locations. These are used on a fertilized egg in preparation for building a fetus. Undifferentiated cells must have new genes expressed while others are silenced. Click he ...
... • Master control genes called homeotic genes regulate groups of other genes that determine what body parts will develop in which locations. These are used on a fertilized egg in preparation for building a fetus. Undifferentiated cells must have new genes expressed while others are silenced. Click he ...
Chapter 3 Genetics Study Guide
... 2. Describe Mendel’s experiment with pea plants. What was the outcome in both fractions and percentages? Mendel crossed a purebred Tall with a purebred short. In the first generation, he got all tall and the short disappeared. In the second generation he got 3 tall and one short so the short reappea ...
... 2. Describe Mendel’s experiment with pea plants. What was the outcome in both fractions and percentages? Mendel crossed a purebred Tall with a purebred short. In the first generation, he got all tall and the short disappeared. In the second generation he got 3 tall and one short so the short reappea ...
Practice Exam 3
... c. There is a struggle for limited resources, and only a fraction of offspring will survive d. Individuals whose characteristics are best suited to the environment generally leave more offspring than those whose characteristics are less well studied. e. Organisms interact with their environment. 20. ...
... c. There is a struggle for limited resources, and only a fraction of offspring will survive d. Individuals whose characteristics are best suited to the environment generally leave more offspring than those whose characteristics are less well studied. e. Organisms interact with their environment. 20. ...
Chapter 15
... RNA polymerases are the primary enzymes responsible for this process 1. Promoters- process starts at RNA polymerase binding sites (promoters) on the DNA template strand. Promoters are short sequences that are not transcribed by the polymerase that binds to them. Ex: TATA box25 nucleotides upstream f ...
... RNA polymerases are the primary enzymes responsible for this process 1. Promoters- process starts at RNA polymerase binding sites (promoters) on the DNA template strand. Promoters are short sequences that are not transcribed by the polymerase that binds to them. Ex: TATA box25 nucleotides upstream f ...
The diagram below shows the arrangement of chromatin (thick black
... polymerase from accessing the coding regions. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that RNA polymerase is involved in transcribing DNA into mRNA, but does not understand that histone acetylation increases gene expression by exposing DNA in order for transcription to ...
... polymerase from accessing the coding regions. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that RNA polymerase is involved in transcribing DNA into mRNA, but does not understand that histone acetylation increases gene expression by exposing DNA in order for transcription to ...
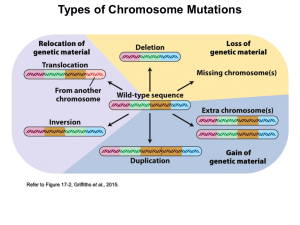
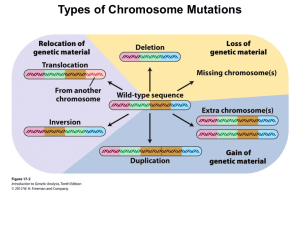
Looking Beyond Our DNA - Federation of American Societies for
... of the cells in the body have the same DNA sequence, but differences in the “punctuation” in certain genes determine when and how they are turned on (gene activation). It is these differences in the activation of genes that result in a broad array of cell types with various functions (i.e., muscle, ...
... of the cells in the body have the same DNA sequence, but differences in the “punctuation” in certain genes determine when and how they are turned on (gene activation). It is these differences in the activation of genes that result in a broad array of cell types with various functions (i.e., muscle, ...
The Unseen Genome: Beyond DNA
... outside the DNA sequence altogether. The tools of genetic engineering worked best on conventional genes and proteins, however, so scientists looked hardest where the light was brightest. In recent years, geneticists have been exploring the less visible parts of the genome more thoroughly, in search ...
... outside the DNA sequence altogether. The tools of genetic engineering worked best on conventional genes and proteins, however, so scientists looked hardest where the light was brightest. In recent years, geneticists have been exploring the less visible parts of the genome more thoroughly, in search ...
Results
... domain-containing proteins from C. lavandulifolium, Arabidopsis and Oryza sativa. Amino acid sequences were aligned using ClustalW and a neighbor-joining tree was constructed with a 1000-bootstrap replication support. The subfamilies within the NAC family, as designated by Ooka et al. [8] were group ...
... domain-containing proteins from C. lavandulifolium, Arabidopsis and Oryza sativa. Amino acid sequences were aligned using ClustalW and a neighbor-joining tree was constructed with a 1000-bootstrap replication support. The subfamilies within the NAC family, as designated by Ooka et al. [8] were group ...
Genomics and Behavior “Central Dogma” Outline
... • Partner preference behavior has been examined in only a few species of voles • It may be that many non-monogamous species show some form of partner preference that is affected by vasopressin • The effects of the vasopressin promoter may depend on the expression of other genes ...
... • Partner preference behavior has been examined in only a few species of voles • It may be that many non-monogamous species show some form of partner preference that is affected by vasopressin • The effects of the vasopressin promoter may depend on the expression of other genes ...
Mammalian X Chromosome Inactivation
... 1. Present at homologous sites on pairs of chromosomes 2. Always genetically inert 3. DNA sequences that are not organized into genes 4. Telomeric and centromeric regions Features of Facultative Heterochromatin 1. Referred to as silent chromatin 2. Potential to become heterochromatic (Barr body) ...
... 1. Present at homologous sites on pairs of chromosomes 2. Always genetically inert 3. DNA sequences that are not organized into genes 4. Telomeric and centromeric regions Features of Facultative Heterochromatin 1. Referred to as silent chromatin 2. Potential to become heterochromatic (Barr body) ...
The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... along inside edge of nuclear envelope selection of which X will inactivate occurs randomly & independently in each embryonic cell …. females are a mosaic of the 2 X chromosomes ...
... along inside edge of nuclear envelope selection of which X will inactivate occurs randomly & independently in each embryonic cell …. females are a mosaic of the 2 X chromosomes ...
How can jellyfish shed light on the subject? One of the
... express their newly acquired jellyfish gene and produce the fluorescent protein which causes them to glow a brilliant green color under ultraviolet light. In this activity, students will learn about the process of moving genes from one organism to another with the aid of a plasmid. In addition to on ...
... express their newly acquired jellyfish gene and produce the fluorescent protein which causes them to glow a brilliant green color under ultraviolet light. In this activity, students will learn about the process of moving genes from one organism to another with the aid of a plasmid. In addition to on ...