Chapter 12
... Sex chromosomes are nonidentical but still homologous Homologous chromosomes interact, then segregate from one another during meiosis ...
... Sex chromosomes are nonidentical but still homologous Homologous chromosomes interact, then segregate from one another during meiosis ...
Figure 13-1
... True or False? Correct the false statement. A = TRUE; B = False 20. ___________________ In bacteria, a promoter is cluster of related genes plus its control sequences to turn on or off transcription. 21. ___________________ A protein produced by a transgenic bacteria is different from the same prot ...
... True or False? Correct the false statement. A = TRUE; B = False 20. ___________________ In bacteria, a promoter is cluster of related genes plus its control sequences to turn on or off transcription. 21. ___________________ A protein produced by a transgenic bacteria is different from the same prot ...
7-2.6 Standard Notes
... As the Punnett square shows, TT, Tt, and tt are all possible genotypes for the height of the offspring. The offspring with the genotypes TT and Tt will have a phenotype of tall; the offspring with the genotype of tt will have a phenotype of short. If the two alleles are the same (TT or tt), the geno ...
... As the Punnett square shows, TT, Tt, and tt are all possible genotypes for the height of the offspring. The offspring with the genotypes TT and Tt will have a phenotype of tall; the offspring with the genotype of tt will have a phenotype of short. If the two alleles are the same (TT or tt), the geno ...
SIMPLE PATTERNS OF INHERITANCE
... The nucleus of a diploid cell contains two sets of chromosomes, which are found in homologous pairs. One member of each pair is inherited from the mother and the other from the father. The maternal and paternal sets of homologous chromosomes are functionally equivalent; each set carries a full compl ...
... The nucleus of a diploid cell contains two sets of chromosomes, which are found in homologous pairs. One member of each pair is inherited from the mother and the other from the father. The maternal and paternal sets of homologous chromosomes are functionally equivalent; each set carries a full compl ...
Eye Color
... 20,000 or 25,000 genes in the human body. A pedigree is a chart that tells someone all of the possible known phenotypes. Phenotypes are physical traits you inherit from you parents. Genotype is internally coded inheritable information carried by a living organism. Recessive is when you produce littl ...
... 20,000 or 25,000 genes in the human body. A pedigree is a chart that tells someone all of the possible known phenotypes. Phenotypes are physical traits you inherit from you parents. Genotype is internally coded inheritable information carried by a living organism. Recessive is when you produce littl ...
Contemporary Biology Per
... Study Guide - Test #7, Section 8.4 & Chapter 9 1. Cells regulate gene transcription because they do not always need a gene’s product. A gene is said to be __________ or “turned on” when it is ____________ to mRNA. 2. E. coli contains about 2000 genes, three of which are called ____ genes, each codin ...
... Study Guide - Test #7, Section 8.4 & Chapter 9 1. Cells regulate gene transcription because they do not always need a gene’s product. A gene is said to be __________ or “turned on” when it is ____________ to mRNA. 2. E. coli contains about 2000 genes, three of which are called ____ genes, each codin ...
HOW SAGE WORKS (Reference http://www
... are called nucleotides. The alphabet of nucleotides is very small (with only four letters), but it suffices to spell out the unique, long words that make up the genetic code. Cells and viruses contain molecular tools that can transform DNA into RNA. Researchers use a method called "sequencing" to re ...
... are called nucleotides. The alphabet of nucleotides is very small (with only four letters), but it suffices to spell out the unique, long words that make up the genetic code. Cells and viruses contain molecular tools that can transform DNA into RNA. Researchers use a method called "sequencing" to re ...
Extranuclear Inheritance
... w Uses its own DNA polymerase w Occurs at any time in the cell cycle w Single origin of replication ...
... w Uses its own DNA polymerase w Occurs at any time in the cell cycle w Single origin of replication ...
Genetics - Faculty Web Sites
... don't start life as very short individuals - they become short over time, growing more slowly than their sisters and friends with each passing year. Studies have shown that a medicine called recombinant human growth hormone, or GH, can improve the height of girls with Turner syndrome. However, these ...
... don't start life as very short individuals - they become short over time, growing more slowly than their sisters and friends with each passing year. Studies have shown that a medicine called recombinant human growth hormone, or GH, can improve the height of girls with Turner syndrome. However, these ...
Genetic and dietary factors causing changes in gene activity through
... Gains in cells treated with the chemotherapy agent DAC, which inhibits all three enzymes. It is currently not known how this is causing gains in methylation but they are likely to be very important for efficacy Supplementation with folic acid seems to give gains in methylation genome-wide, both for ...
... Gains in cells treated with the chemotherapy agent DAC, which inhibits all three enzymes. It is currently not known how this is causing gains in methylation but they are likely to be very important for efficacy Supplementation with folic acid seems to give gains in methylation genome-wide, both for ...
Midas_2 - PhagesDB
... I deleted gene number 31, since there was too much overlap with the next gene, and there was no coding potential at all with genemark just glimmer, when I try to adjust the ORF it no longer has coding potential with Glimmer, so I deleted it. This was a tough call since it was a gene that originally ...
... I deleted gene number 31, since there was too much overlap with the next gene, and there was no coding potential at all with genemark just glimmer, when I try to adjust the ORF it no longer has coding potential with Glimmer, so I deleted it. This was a tough call since it was a gene that originally ...
Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life
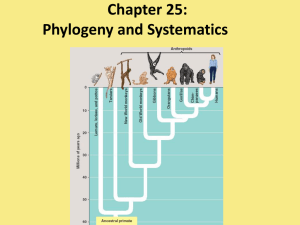
... • a hard to tell how long ago they shared a common ancestor; must also look at fossil ...
... • a hard to tell how long ago they shared a common ancestor; must also look at fossil ...
Supplementary Figure Legends
... (A) GO analysis (by DAVID) of the 100 genes whose expression is most highly correlated ...
... (A) GO analysis (by DAVID) of the 100 genes whose expression is most highly correlated ...
REVIEW 5: GENETICS 1. Chromosomes
... a. Can only be passed on if they occur in reproductive cells (sperm or egg). b. Gene mutations may cause a change in a gene which can change the _Shape _ of the _ Protein produced from that gene. This will have an effect on the way the protein works (if it still works at all). ...
... a. Can only be passed on if they occur in reproductive cells (sperm or egg). b. Gene mutations may cause a change in a gene which can change the _Shape _ of the _ Protein produced from that gene. This will have an effect on the way the protein works (if it still works at all). ...
CP-Ch10-MendelianGenetics
... locations on the same chromosome • Can cause inactivation of gene • Important sources of variation between ...
... locations on the same chromosome • Can cause inactivation of gene • Important sources of variation between ...
Genome of Drosophila species
... Remarks of Genomic Content The genomic sequence has shed light on some of the processes common to all cells, such as replication, chromosome segregation, and iron metabolism There are new findings about important classes of chromosomal proteins that allow insights into gene regulation and the c ...
... Remarks of Genomic Content The genomic sequence has shed light on some of the processes common to all cells, such as replication, chromosome segregation, and iron metabolism There are new findings about important classes of chromosomal proteins that allow insights into gene regulation and the c ...
Section 2: Energy Flow in Ecosystems
... • The splicing of eukaryotic genes creates additional opportunities for variation over time. • Because each exon encodes a different part of a protein, cells can occasionally shuffle exons between genes and thus make new proteins. • The thousands of proteins in human cells appear to result from shuf ...
... • The splicing of eukaryotic genes creates additional opportunities for variation over time. • Because each exon encodes a different part of a protein, cells can occasionally shuffle exons between genes and thus make new proteins. • The thousands of proteins in human cells appear to result from shuf ...
Why the
... handle this inequity by doubling the activity of the X versions of lost Y genes in males. Others employ a more complex strategy. First they increase the activity of X genes in both males and females, a maneuver that replenishes protein levels in males but creates an excess in females. Some animals, ...
... handle this inequity by doubling the activity of the X versions of lost Y genes in males. Others employ a more complex strategy. First they increase the activity of X genes in both males and females, a maneuver that replenishes protein levels in males but creates an excess in females. Some animals, ...
Chapter 10
... 1. Typical females have two X chromosomes; males have one a) Dosage compensation in mammals involves the inactivation of one X chromosome in female cells b) Fruit fly males accomplish this by making their single X chromosome more active 2. The Barr body is a dark area of highly condensed chromatin, ...
... 1. Typical females have two X chromosomes; males have one a) Dosage compensation in mammals involves the inactivation of one X chromosome in female cells b) Fruit fly males accomplish this by making their single X chromosome more active 2. The Barr body is a dark area of highly condensed chromatin, ...
Slide 1
... carriers of the defective gene (two carriers have to mate to produce an affected individual). Why is the prevalence of this defect so high? ...
... carriers of the defective gene (two carriers have to mate to produce an affected individual). Why is the prevalence of this defect so high? ...
ASE FS21 GM handout (DOC 756Kb)
... Click on the chromosome column, you will be able to zoom in (and out) until you can clearly see individual genes, Surf around the genome for a few minutes and get a feel for the genome Can you identify Gene structure, specifically Introns and Exons A gene sequence with introns and exons is the genom ...
... Click on the chromosome column, you will be able to zoom in (and out) until you can clearly see individual genes, Surf around the genome for a few minutes and get a feel for the genome Can you identify Gene structure, specifically Introns and Exons A gene sequence with introns and exons is the genom ...