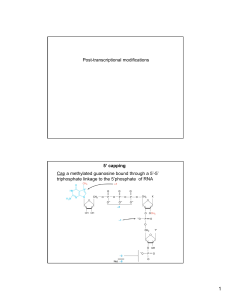
Post-transcriptional modifications Cap a
... Multiple copies of transgenes introduced into plant cells can interact with each other and with homologous host genes in trans, resulting in the inactivation of expression of both genes. This phenomenon called homology-dependent gene silencing (HDGS) occurs generally in plants and is similar to cert ...
... Multiple copies of transgenes introduced into plant cells can interact with each other and with homologous host genes in trans, resulting in the inactivation of expression of both genes. This phenomenon called homology-dependent gene silencing (HDGS) occurs generally in plants and is similar to cert ...
Isochores and Genes: Who`s in the Driver`s Seat?
... – Could it be episodic, with occasional large “advances” balanced (or not balanced) by slow “retreats” • Human chromosomes 3, 4, 6, 8, 15, and 20 may have iCGs continuing to form at one or both chromosome ends ...
... – Could it be episodic, with occasional large “advances” balanced (or not balanced) by slow “retreats” • Human chromosomes 3, 4, 6, 8, 15, and 20 may have iCGs continuing to form at one or both chromosome ends ...
No Slide Title
... are influenced not by one or two genes, but by dozens or hundreds. In this example, alleles at three loci control skin color. Environmental factors can also influence these polyfactorial characters. The distribution shown here is characteristic of polyfactorial characters. These characters vary cont ...
... are influenced not by one or two genes, but by dozens or hundreds. In this example, alleles at three loci control skin color. Environmental factors can also influence these polyfactorial characters. The distribution shown here is characteristic of polyfactorial characters. These characters vary cont ...
Cells - Troup County High School
... new alleles are randomly formed; one can only predict offspring (using Punnett squares) • The Law of Independent Assortment: each trait is inherited independently of other traits ...
... new alleles are randomly formed; one can only predict offspring (using Punnett squares) • The Law of Independent Assortment: each trait is inherited independently of other traits ...
Lecture 01. The subject and the main tasks of Medical Genetics
... contains the genetic instructions specifying the biological development of all cellular forms of life ...
... contains the genetic instructions specifying the biological development of all cellular forms of life ...
Extensions to Mendel`s laws of inheritance
... Ex: Type AB Blood, Speckled Chickens, Roan Cattle, Sickle-cell Anemia ...
... Ex: Type AB Blood, Speckled Chickens, Roan Cattle, Sickle-cell Anemia ...
1 word is genus and
... n. Mutation: When the gene code is changed in any way. o. Sex-Linked: traits found on the “X” chromosomes such as color blindness 42. Who determines the sex of the offspring? The male: sperm is either X or Y 43. Place the following in the correct sequence: DNA,protein,chromosome, gene a. Chromosome ...
... n. Mutation: When the gene code is changed in any way. o. Sex-Linked: traits found on the “X” chromosomes such as color blindness 42. Who determines the sex of the offspring? The male: sperm is either X or Y 43. Place the following in the correct sequence: DNA,protein,chromosome, gene a. Chromosome ...
click here
... 1. Independent assortment is based on the fact that the genes are NOT linked. In a dihybrid cross, you would expect a 9:3:3:1 ratio if genes are not linked. The three ratios shown are all expected results of a dihybrid (AaBb x AaBb) cross- all show a 9:3:3:1 ratio, or a variant of it. Ans: all of th ...
... 1. Independent assortment is based on the fact that the genes are NOT linked. In a dihybrid cross, you would expect a 9:3:3:1 ratio if genes are not linked. The three ratios shown are all expected results of a dihybrid (AaBb x AaBb) cross- all show a 9:3:3:1 ratio, or a variant of it. Ans: all of th ...
The community effect in animal development
... Where else does community effect, or similar communication, occur? ...
... Where else does community effect, or similar communication, occur? ...
(RNA and Protein Synthesis) Section 11.4 Questions
... 16. What shape does RNA typically form? _________________________ 17. What is the name of the first step of the DNA to RNA conversion? ____________________ 18. Does this first step of the conversion take place inside or outside of the nucleus? _________ 19. Where does the transcribed message go? __ ...
... 16. What shape does RNA typically form? _________________________ 17. What is the name of the first step of the DNA to RNA conversion? ____________________ 18. Does this first step of the conversion take place inside or outside of the nucleus? _________ 19. Where does the transcribed message go? __ ...
Edges of Life
... translated into a protein • Proteins make up machines, skeleton, and color of cells and therefore determine form and function ...
... translated into a protein • Proteins make up machines, skeleton, and color of cells and therefore determine form and function ...
Genetics - De Anza
... Type B - Glycolipid B on cell surface Type AB - Both glyocolipids A & B Type O - Neither glyocolipid A nor B ...
... Type B - Glycolipid B on cell surface Type AB - Both glyocolipids A & B Type O - Neither glyocolipid A nor B ...
Diploid zygote is very transient in lower eukaryotes
... genetically different haploid cells; mitosis produces 2 genetically identical diploid cells. ...
... genetically different haploid cells; mitosis produces 2 genetically identical diploid cells. ...
Review - Qc.edu
... 4. The central dogma of molecular biology: DNA to RNA to protein. DNA and its structure: sugar, phosphate, bases, principle of complementarity. Proteins, their structure and functions, enzymes, amino acids, active centers. Replication, transcription, translation. Classes of RNA molecules: messenger ...
... 4. The central dogma of molecular biology: DNA to RNA to protein. DNA and its structure: sugar, phosphate, bases, principle of complementarity. Proteins, their structure and functions, enzymes, amino acids, active centers. Replication, transcription, translation. Classes of RNA molecules: messenger ...
SMCarr passport for UPS
... Recessive IDs are typically more detrimental/severe in their effects than dominant IDs. Different pedigree/inheritance patterns if disease gene is located on sex chromosomes vs. autosomes. Y-linked diseases uncommon (very few genes; <100) * often affect fertility X-linked dominant diseases a ...
... Recessive IDs are typically more detrimental/severe in their effects than dominant IDs. Different pedigree/inheritance patterns if disease gene is located on sex chromosomes vs. autosomes. Y-linked diseases uncommon (very few genes; <100) * often affect fertility X-linked dominant diseases a ...
Bioprospecting of Genes and Allele Mining
... • Scientific bio-prospecting started later to identify the active ingredients present in different organisms and isolate or replicate them for largescale use. • Alexander Fleming’s discovery of the antibiotic penicillin is an example of bio-prospecting that happened accidentally. ...
... • Scientific bio-prospecting started later to identify the active ingredients present in different organisms and isolate or replicate them for largescale use. • Alexander Fleming’s discovery of the antibiotic penicillin is an example of bio-prospecting that happened accidentally. ...
Genetics Notes PDP - Lincoln Park High School
... Sex-linked genes: recessive alleles located on the X (p.178) o ALWAYS expressed in males…why? o b/c they only have 1 X o Women can be “carriers” (heterozygous) & show dominant phenotype o Ex: hemophilia ...
... Sex-linked genes: recessive alleles located on the X (p.178) o ALWAYS expressed in males…why? o b/c they only have 1 X o Women can be “carriers” (heterozygous) & show dominant phenotype o Ex: hemophilia ...
Comparative Genome Organization in plants: From Sequence and Markers to... and Chromosomes Summary
... They are the attachment site of microtubules during cell division. Centromeres are often composed of tandem repeats, which are highly conserved and are defined cytologically by primary constriction. Centromere-associated repeats represent a considerable percentage of the genomic DNA. Despite analysi ...
... They are the attachment site of microtubules during cell division. Centromeres are often composed of tandem repeats, which are highly conserved and are defined cytologically by primary constriction. Centromere-associated repeats represent a considerable percentage of the genomic DNA. Despite analysi ...
Genetics Journal Club
... Disruptions in this process can cause additional intermediates with cleaved precursor miRNAs or ac-pre-miRNAs, leading to alternative forms interfering with regulation of gene function and protein translation at multiple levels. ...
... Disruptions in this process can cause additional intermediates with cleaved precursor miRNAs or ac-pre-miRNAs, leading to alternative forms interfering with regulation of gene function and protein translation at multiple levels. ...
Day1VGN-Microarray-CSC2011ppt
... Arabidopsis ATH1 Genome Array This GeneChip contains 500,000 DNA oligos comprising 24,000 genes ...
... Arabidopsis ATH1 Genome Array This GeneChip contains 500,000 DNA oligos comprising 24,000 genes ...
Cracking Your Genetic Code VQs14
... 2. Your genome is a language whose alphabet consists of four chemicals, each known by its initial __________________________. Strings of these chemical letters spell out some 20,000 genes on 23 pairs of chromosomes. Genes code for proteins, molecules that do most of the work in our cells and help __ ...
... 2. Your genome is a language whose alphabet consists of four chemicals, each known by its initial __________________________. Strings of these chemical letters spell out some 20,000 genes on 23 pairs of chromosomes. Genes code for proteins, molecules that do most of the work in our cells and help __ ...
RNA polymerase II is the key enzyme in the process of transcription
... c. What is a CXXC-domain and what is its function? 2. One of the four core histones becomes conjugated with ubiquitin in a process that is coupled to transcriptional activation. Describe briefly this process and explain how this monoubiquitination mark is linked to the formation of another key activ ...
... c. What is a CXXC-domain and what is its function? 2. One of the four core histones becomes conjugated with ubiquitin in a process that is coupled to transcriptional activation. Describe briefly this process and explain how this monoubiquitination mark is linked to the formation of another key activ ...























