DNA cytosine methylation in plant development
... the silencing of both transposable elements (TEs) and endogenous genes, and loss of methylation may have severe functional consequences. The recent methylation profiling of the entire Arabidopsis genome has provided novel insights into the extent and pattern of cytosine methylation and its relations ...
... the silencing of both transposable elements (TEs) and endogenous genes, and loss of methylation may have severe functional consequences. The recent methylation profiling of the entire Arabidopsis genome has provided novel insights into the extent and pattern of cytosine methylation and its relations ...
Molecular pathogenesis of feline leukemia virus
... Feline leukemia virus (FeLV), which is subclassified into three subgroups of A, B and C, is a pathogenic retrovirus in cats. FeLVA is minimally pathogenic, FeLV-C can cause pure red cell aplasia, and FeLV-B is associated with a variety of pathogenic properties such as lymphoma, leukemia and anemia. ...
... Feline leukemia virus (FeLV), which is subclassified into three subgroups of A, B and C, is a pathogenic retrovirus in cats. FeLVA is minimally pathogenic, FeLV-C can cause pure red cell aplasia, and FeLV-B is associated with a variety of pathogenic properties such as lymphoma, leukemia and anemia. ...
Maternal uniparental disomyof chromosome 13
... Since Engel originally postulated the existence produced a true isochromosome since all the of UPD in 1980,' several examples have been polymorphic AC repeat alleles examined were reported involving all or part of chromosomes homozygous despite all being highly (>75%) 6,7,11,14,15,16,21,22, and the ...
... Since Engel originally postulated the existence produced a true isochromosome since all the of UPD in 1980,' several examples have been polymorphic AC repeat alleles examined were reported involving all or part of chromosomes homozygous despite all being highly (>75%) 6,7,11,14,15,16,21,22, and the ...
Significant enhancement of fatty acid composition in seeds of the
... selected. These 20-nt target sequences were oriented within each gene either in the same 50 to 30 direction as the reading frame of the gene (the ‘forward’ direction) or in the 50 to 30 direction on the opposite (reverse) strand of DNA. The location of each of these sites in the FAD2 genes of Cameli ...
... selected. These 20-nt target sequences were oriented within each gene either in the same 50 to 30 direction as the reading frame of the gene (the ‘forward’ direction) or in the 50 to 30 direction on the opposite (reverse) strand of DNA. The location of each of these sites in the FAD2 genes of Cameli ...
Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation in Age
... The most common DNA methylation form is the 5¶ methylcytosine. It occurs predominantly in the symmetric CG context. Approximately 70% to 80% of CG dinucleotides of the genome are normally methylated and are called CpG. In vertebrates, CpG dinucleotides tend to cluster together and form CpG islands. ...
... The most common DNA methylation form is the 5¶ methylcytosine. It occurs predominantly in the symmetric CG context. Approximately 70% to 80% of CG dinucleotides of the genome are normally methylated and are called CpG. In vertebrates, CpG dinucleotides tend to cluster together and form CpG islands. ...
Prediction and Validation of Gene-Disease Associations
... the association from just direct protein interactions to more distant connections in various ways. One kind of network that has proven to be particularly useful for predicting biological function is the functional interaction network, where a pair of genes is connected based on the integrated eviden ...
... the association from just direct protein interactions to more distant connections in various ways. One kind of network that has proven to be particularly useful for predicting biological function is the functional interaction network, where a pair of genes is connected based on the integrated eviden ...
Emerging model systems in evo-devo: cavefish and microevolution
... biologists have made considerable progress in understanding the molecular basis of developmental changes during evolution. In most cases, however, little is known about evolutionary forces that drive these changes. The use of appropriate model systems in microevolution will be necessary to determine ...
... biologists have made considerable progress in understanding the molecular basis of developmental changes during evolution. In most cases, however, little is known about evolutionary forces that drive these changes. The use of appropriate model systems in microevolution will be necessary to determine ...
Mechanisms and constraints shaping the evolution of body plan
... while in genome-based models transcription factor binding sites and genes encoding transcription factors (TFs) may evolve independently. When network-based models are combined with an initially small number of genes, this introduces a bias towards evolving interactions between genes present early du ...
... while in genome-based models transcription factor binding sites and genes encoding transcription factors (TFs) may evolve independently. When network-based models are combined with an initially small number of genes, this introduces a bias towards evolving interactions between genes present early du ...
Enhancers reside in a unique epigenetic environment during early
... expression are characterized by relatively low levels of DNA methylation (hypo-methylation), while inactive enhancers display hyper-methylation of the underlying DNA. The direct functional significance of the DNA methylation state of enhancers is, however, unclear for most loci. Results: In contrast ...
... expression are characterized by relatively low levels of DNA methylation (hypo-methylation), while inactive enhancers display hyper-methylation of the underlying DNA. The direct functional significance of the DNA methylation state of enhancers is, however, unclear for most loci. Results: In contrast ...
Epigenetic Signatures of AutismTrimethylated
... From: Epigenetic Signatures of AutismTrimethylated H3K4 Landscapes in Prefrontal Neurons Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69(3):314-324. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.151 ...
... From: Epigenetic Signatures of AutismTrimethylated H3K4 Landscapes in Prefrontal Neurons Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69(3):314-324. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.151 ...
Messenger RNA reprogramming by spliceosome-mediated
... expression of the pre-mRNA target can provide transsplicing with cell-type specificity, which can be further enhanced by regulating the expression pattern of the PTM. This advantage of target dependence is shared by all trans-splicing methodologies over techniques that use direct expression of genes ...
... expression of the pre-mRNA target can provide transsplicing with cell-type specificity, which can be further enhanced by regulating the expression pattern of the PTM. This advantage of target dependence is shared by all trans-splicing methodologies over techniques that use direct expression of genes ...
PPT - Bioinformatics.ca
... – Use multiple sources to increase coverage Zeeberg BR et al. Mistaken identifiers: gene name errors can be introduced inadvertently when using Excel in bioinformatics BMC ...
... – Use multiple sources to increase coverage Zeeberg BR et al. Mistaken identifiers: gene name errors can be introduced inadvertently when using Excel in bioinformatics BMC ...
- Lab Fabiana Perocchi
... same chromosomal position. Therefore, despite the importance of allele-specific expression, the extent of ADE on opposite strands or for non-coding sequences has remained ...
... same chromosomal position. Therefore, despite the importance of allele-specific expression, the extent of ADE on opposite strands or for non-coding sequences has remained ...
The Genetics of Microcephaly
... like the chromosomes, genes come in pairs, one inherited from father and the other inherited from mother. When one gene is faulty, the second copy of that gene usually compensates for it. However, males have a single X chromosome and only one copy of each gene that is located, is on this X chromosom ...
... like the chromosomes, genes come in pairs, one inherited from father and the other inherited from mother. When one gene is faulty, the second copy of that gene usually compensates for it. However, males have a single X chromosome and only one copy of each gene that is located, is on this X chromosom ...
WP4 - Tomsett
... Lane 2 = gcs3 plasmid control Lane 3 = gcs3 transformant Lane 4 = gcs4 plasmid control Lane 5 = gcs4 transformant Lane 6 = gsat1 plasmid control ...
... Lane 2 = gcs3 plasmid control Lane 3 = gcs3 transformant Lane 4 = gcs4 plasmid control Lane 5 = gcs4 transformant Lane 6 = gsat1 plasmid control ...
BMC Genomics - LCBB
... changes but also events that alter the chromosome structure, such as inversions, duplications or deletions [1]. Ancestral gene sequence inference has led to significant predictions of protein functional shift and positive selection [2]. For example, comparisons of orthologous chromosomal segments sh ...
... changes but also events that alter the chromosome structure, such as inversions, duplications or deletions [1]. Ancestral gene sequence inference has led to significant predictions of protein functional shift and positive selection [2]. For example, comparisons of orthologous chromosomal segments sh ...
New Construct Approaches for Efficient Gene Silencing in Plants
... Hua Yan, Robert Chretien, Jingsong Ye, and Caius M. Rommens* Simplot Plant Sciences, J.R. Simplot Company, Boise, Idaho 83706 ...
... Hua Yan, Robert Chretien, Jingsong Ye, and Caius M. Rommens* Simplot Plant Sciences, J.R. Simplot Company, Boise, Idaho 83706 ...
Coordination of replication and transcription along a Drosophila
... arrays of cDNAs have demonstrated a correlation between time of replication and the probability that a specific gene is expressed, it remained to be determined what step(s) in the replication initiation process are influenced by transcription. Similarly, because the prior studies lacked contiguous i ...
... arrays of cDNAs have demonstrated a correlation between time of replication and the probability that a specific gene is expressed, it remained to be determined what step(s) in the replication initiation process are influenced by transcription. Similarly, because the prior studies lacked contiguous i ...
Reveal—visual eQTL analytics
... 3.1 Association gene network The starting point of an analysis using Reveal is a list of SNPs and genes, and data from a patient cohort covering the presence of the sequence polymorphisms and the expression values of the genes. In addition, patients are assigned to one of two groups depending on the ...
... 3.1 Association gene network The starting point of an analysis using Reveal is a list of SNPs and genes, and data from a patient cohort covering the presence of the sequence polymorphisms and the expression values of the genes. In addition, patients are assigned to one of two groups depending on the ...
Ribosome profiling reveals post-transcriptional buffering of divergent
... Understanding the patterns and causes of phenotypic divergence is a central goal in evolutionary biology. Much work has shown that mRNA abundance is highly variable between closely related species. However, the extent and mechanisms of post-transcriptional gene regulatory evolution are largely unkno ...
... Understanding the patterns and causes of phenotypic divergence is a central goal in evolutionary biology. Much work has shown that mRNA abundance is highly variable between closely related species. However, the extent and mechanisms of post-transcriptional gene regulatory evolution are largely unkno ...
Role for CCG-trinucleotide repeats in the pathogenesis of chronic
... in this tumor further refines the minimal region of deletion. Our data are in concordance with previously published results10,11 (Figure 1) for the 11q-deleted region in CLL (all of which include the trinucleotide repeat TNR/11q#1; see below). Taken together with the published data, we further reduc ...
... in this tumor further refines the minimal region of deletion. Our data are in concordance with previously published results10,11 (Figure 1) for the 11q-deleted region in CLL (all of which include the trinucleotide repeat TNR/11q#1; see below). Taken together with the published data, we further reduc ...
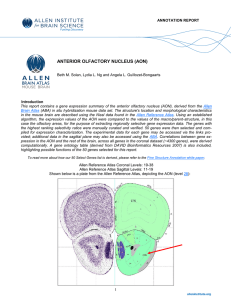
anterior olfactory nucleus (aon) - Dashboard
... In Situ Hybridization Expression Patterns of 50 Select Genes: The in situ hybridization (ISH) data below presents the anterior olfactory nucleus’ anatomical and cytoarchitectural characteristics in the context of actual gene expression. In addition to presenting molecularly defined borders, ISH gen ...
... In Situ Hybridization Expression Patterns of 50 Select Genes: The in situ hybridization (ISH) data below presents the anterior olfactory nucleus’ anatomical and cytoarchitectural characteristics in the context of actual gene expression. In addition to presenting molecularly defined borders, ISH gen ...
Evolutionary consequences of polyploidy in prokaryotes and the
... one intact copy of each of the several essential genes, but with other copies damaged by mutations, may be perfectly viable, but its chances to produce viable offspring may be negligible provided that intact genes are scattered over different chromosomes, and that each descendant gets a random set o ...
... one intact copy of each of the several essential genes, but with other copies damaged by mutations, may be perfectly viable, but its chances to produce viable offspring may be negligible provided that intact genes are scattered over different chromosomes, and that each descendant gets a random set o ...