Jose
... breaking down of food into smaller components that can be absorbed into a blood stream, for... ...
... breaking down of food into smaller components that can be absorbed into a blood stream, for... ...
sheet#8 - DENTISTRY 2012
... means we give him antibiotics till the inflammation resolves then come back to him after 4-6 weeks. Because the inflammation and edema and swelling will be more severe and it will be hard to make laparoscopic surgeries without scars and complications of the wound. Nowadays there are some professiona ...
... means we give him antibiotics till the inflammation resolves then come back to him after 4-6 weeks. Because the inflammation and edema and swelling will be more severe and it will be hard to make laparoscopic surgeries without scars and complications of the wound. Nowadays there are some professiona ...
Intracellular Digestion
... liver may be very different than it was when it entered. – One of the many functions the liver include regulating glucose levels in the blood and converting amino acids into carbohydrates. – From the liver the blood travels to the heart to be pumped to the rest of the body. ...
... liver may be very different than it was when it entered. – One of the many functions the liver include regulating glucose levels in the blood and converting amino acids into carbohydrates. – From the liver the blood travels to the heart to be pumped to the rest of the body. ...
Oral Drug Absorption
... Physiological Factors that Influence Drug Absorption from GIT • GI motility: Gastric emptying time and intestinal motility • GI perfusion • GI secretions • Presence of food ...
... Physiological Factors that Influence Drug Absorption from GIT • GI motility: Gastric emptying time and intestinal motility • GI perfusion • GI secretions • Presence of food ...
An amazing journey through the digestive tract! Learn underlined
... Pyloric Sphincter Opens to let chyme (or Valve) slowly enter the small intestine Closes to prevent backflow © updated 2008 by Michele McMullen ...
... Pyloric Sphincter Opens to let chyme (or Valve) slowly enter the small intestine Closes to prevent backflow © updated 2008 by Michele McMullen ...
Digestive System - Net Start Class
... liver may be very different than it was when it entered. – One of the many functions the liver include regulating glucose levels in the blood and converting amino acids into carbohydrates. – From the liver the blood travels to the heart to be pumped to the rest of the body. ...
... liver may be very different than it was when it entered. – One of the many functions the liver include regulating glucose levels in the blood and converting amino acids into carbohydrates. – From the liver the blood travels to the heart to be pumped to the rest of the body. ...
Pyloric Stenosis: A Cause of Vomiting in Dogs
... the small intestine. Small breeds, especially nervous individuals, seem to develop this condition more frequently than others. What are the symptoms? Intermittent vomiting within one to two hours of eating is the most common sign of pyloric stenosis. The food will appear undigested, pretty much look ...
... the small intestine. Small breeds, especially nervous individuals, seem to develop this condition more frequently than others. What are the symptoms? Intermittent vomiting within one to two hours of eating is the most common sign of pyloric stenosis. The food will appear undigested, pretty much look ...
Bile
... post- prandial heart burn, regurgitation at 1 hour Avoiding a large meal (fatty foods) and lay down or Bending, smoking , alcohol & coffee, tomatoes, onions & mint taking H2 blocker 60 minutes before eating neutralize existing stomach acids with Digel ...
... post- prandial heart burn, regurgitation at 1 hour Avoiding a large meal (fatty foods) and lay down or Bending, smoking , alcohol & coffee, tomatoes, onions & mint taking H2 blocker 60 minutes before eating neutralize existing stomach acids with Digel ...
Daniel
... The first part of the small intestine immediately beyond the stomach, leading to the jejunum. ...
... The first part of the small intestine immediately beyond the stomach, leading to the jejunum. ...
Answers to Test Your Understanding of Concepts
... from the periphery of each lobule where the hepatic artery and portal vein empty, through the sinusoids and then out the central vein. The liver cells (hepatocytes) of the lobules can remove hormones, drugs, and other biologically active molecules from the blood by (1) excretion of these compounds i ...
... from the periphery of each lobule where the hepatic artery and portal vein empty, through the sinusoids and then out the central vein. The liver cells (hepatocytes) of the lobules can remove hormones, drugs, and other biologically active molecules from the blood by (1) excretion of these compounds i ...
Digestion4
... Control of Digestive Gland Secretions • As with all body systems, the nervous system and endocrine system tightly control digestion • The amount of saliva produced, the amount of stomach acid produced, the timing and amount of pancreatic and gall bladder secretions and the rate of peristalsis all c ...
... Control of Digestive Gland Secretions • As with all body systems, the nervous system and endocrine system tightly control digestion • The amount of saliva produced, the amount of stomach acid produced, the timing and amount of pancreatic and gall bladder secretions and the rate of peristalsis all c ...
Nervous and hormonal control of GIT Learning Objectives
... strongly contracts gallbladder, expelling bile into small intestine. bile is important for emulsifying fatty substances, allowing them to be digested and absorbed. Cholecystokinin also inhibits stomach contraction moderately. Therefore, at the same time that this hormone causes emptying of the gallb ...
... strongly contracts gallbladder, expelling bile into small intestine. bile is important for emulsifying fatty substances, allowing them to be digested and absorbed. Cholecystokinin also inhibits stomach contraction moderately. Therefore, at the same time that this hormone causes emptying of the gallb ...
Digestive system
... neurons to control the smooth muscle of the digestive tract Hormonal control- a lot of digestion is controled by hormones, there are atleast 18 involved in digestion ...
... neurons to control the smooth muscle of the digestive tract Hormonal control- a lot of digestion is controled by hormones, there are atleast 18 involved in digestion ...
Gastrointestinal System
... • Hospitalization may be necessary for severe physical complications-tube or parenteral feedings may be utilized, but only as temporary intervention (not a cure for anorexia nervosa). ...
... • Hospitalization may be necessary for severe physical complications-tube or parenteral feedings may be utilized, but only as temporary intervention (not a cure for anorexia nervosa). ...
Digestive System Major Functions of the GI Tract Six Processes of
... Peristalsis and mass movements occur in the large intestine Mass movements are strong waver that move over colon 3-4 times daily Bulk (fiber) keeps stool soft and increases the strength of contractions When feces enter the rectum defecation reflex is initiated ...
... Peristalsis and mass movements occur in the large intestine Mass movements are strong waver that move over colon 3-4 times daily Bulk (fiber) keeps stool soft and increases the strength of contractions When feces enter the rectum defecation reflex is initiated ...
powerpoint version - University of Arizona
... -reabsorb water and ions at end of small intestine (ilieum) and from large intestine/colon -feces into cloaca/rectum for excretion -cloaca can also be site of urine modification (e.g., birds) -bacterial digestion in hindgut fermenters (especially in cecum) ...
... -reabsorb water and ions at end of small intestine (ilieum) and from large intestine/colon -feces into cloaca/rectum for excretion -cloaca can also be site of urine modification (e.g., birds) -bacterial digestion in hindgut fermenters (especially in cecum) ...
Chapter 7d Human Nutrition PowerPoint
... stimulates the muscles of the digestive tube and thus keeps food moving through it. sources: fruits, vegetables, and grains. Lack of roughage in the diet is one cause of constipation. ...
... stimulates the muscles of the digestive tube and thus keeps food moving through it. sources: fruits, vegetables, and grains. Lack of roughage in the diet is one cause of constipation. ...
Hormonal Control Of The Digestive System:
... part of the brain or from the spinal cord. They release a chemical called acetylcholine and another called adrenaline. Acetylcholine causes the muscle of the digestive organs to squeeze with more force and increase the "push" of food and juice through the digestive tract. Acetylcholine also causes t ...
... part of the brain or from the spinal cord. They release a chemical called acetylcholine and another called adrenaline. Acetylcholine causes the muscle of the digestive organs to squeeze with more force and increase the "push" of food and juice through the digestive tract. Acetylcholine also causes t ...
Digestive System
... A substance produced by a living organism that acts as a catalyst to bring about a specific biochemical reaction. Most enzymes are... ...
... A substance produced by a living organism that acts as a catalyst to bring about a specific biochemical reaction. Most enzymes are... ...
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
... • Removes Fe and stores it • Removes Vitamins A,D,E and K and stores them • Makes plasma proteins to maintain osmotic pressure ...
... • Removes Fe and stores it • Removes Vitamins A,D,E and K and stores them • Makes plasma proteins to maintain osmotic pressure ...
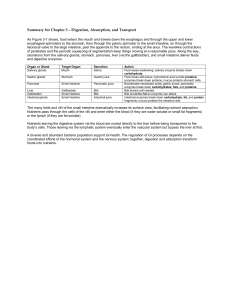
Summary for Chapter 3 – Digestion, Absorption, and
... enzymes break down proteins; mucus protects stomach cells. Bicarbonate neutralizes acidic gastric juices; pancreatic enzymes break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Bile stored until needed. Bile emulsifies fat so enzymes can attack. Intestinal enzymes break down carbohydrate, fat, and protein ...
... enzymes break down proteins; mucus protects stomach cells. Bicarbonate neutralizes acidic gastric juices; pancreatic enzymes break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Bile stored until needed. Bile emulsifies fat so enzymes can attack. Intestinal enzymes break down carbohydrate, fat, and protein ...
Adjustable gastric band

A laparoscopic adjustable gastric band, commonly called a lap-band, A band, or LAGB, is an inflatable silicone device placed around the top portion of the stomach to treat obesity, intended to slow consumption of food and thus reduce the amount of food consumed.Adjustable gastric band surgery is an example of bariatric surgery designed for obese patients with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or greater — or between 35 and 40 in cases of patients with certain comorbidities that are known to improve with weight loss, such as sleep apnea, diabetes, osteoarthritis, GERD, Hypertension (high blood pressure), or metabolic syndrome, among others.In February 2011, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) expanded approval of adjustable gastric bands to patients with a BMI between 30 to 40 and one weight-related medical condition, such as diabetes or high blood pressure. However, an adjustable gastric band may be used only after other methods such as diet and exercise have been tried.