CH225h - Oregon State chemistry
... The rms speeds are inversely proportional to the square root of mass, so the ratio of Ar speed / He speed is ≈ sqrt (4/40) ≈ 0.3 (b) If Ar, He, and Xe are mixed with equal partial pressures in a gas sample, which will effuse most rapidly through a small hole in the container ? Explain briefly. He. E ...
... The rms speeds are inversely proportional to the square root of mass, so the ratio of Ar speed / He speed is ≈ sqrt (4/40) ≈ 0.3 (b) If Ar, He, and Xe are mixed with equal partial pressures in a gas sample, which will effuse most rapidly through a small hole in the container ? Explain briefly. He. E ...
- Gondwana University, Gadchiroli
... (B) Statements of first law of thermodynamics, definition of internal energy & enthalpy, heat capacity at constant volume & at constant pressure, Joule-Thomson experiment, Joule Thomson coefficient & Inversion temperature, calculations of W,Q,ΔE & ΔH for expansion of gases for isothermal & adiabatic ...
... (B) Statements of first law of thermodynamics, definition of internal energy & enthalpy, heat capacity at constant volume & at constant pressure, Joule-Thomson experiment, Joule Thomson coefficient & Inversion temperature, calculations of W,Q,ΔE & ΔH for expansion of gases for isothermal & adiabatic ...
GENERAL CHEMISTRY II QUIZ 5 November 10, 2009
... 0.600 mol of O2 are placed in a 2.00 L flask at 600 K, what are the equilibrium concentrations of all species? N2(g) + ...
... 0.600 mol of O2 are placed in a 2.00 L flask at 600 K, what are the equilibrium concentrations of all species? N2(g) + ...
4. Which of the following describes how a Keq value is related to the
... Use the following equilibrium system to answer the next TWO questions. 4NH3(g) + 3O2(g) ⇌ 2N2(g) 6H2O(l) ;ΔH = -1530 kJ ...
... Use the following equilibrium system to answer the next TWO questions. 4NH3(g) + 3O2(g) ⇌ 2N2(g) 6H2O(l) ;ΔH = -1530 kJ ...
Chapter 8
... Energy and Chemical Bonds • A chemical – Potential - attractive forces in an ionic compound or sharing of electrons covalent compound – Kinetic – (often in form of heat) occurs when bonds are broken and particles allowed to move – To determine the energy of a reaction it is necessary to keep track ...
... Energy and Chemical Bonds • A chemical – Potential - attractive forces in an ionic compound or sharing of electrons covalent compound – Kinetic – (often in form of heat) occurs when bonds are broken and particles allowed to move – To determine the energy of a reaction it is necessary to keep track ...
Equilibrium
... 2. Gas particles are tiny compared to the distances between them, so volume of gas is negligible 3. Gas particles are constantly in motion. The collisions cause pressure of the gas 4. Gas particles neither attract nor repel each other 5. The average kinetic energy of gases are proportional to the k ...
... 2. Gas particles are tiny compared to the distances between them, so volume of gas is negligible 3. Gas particles are constantly in motion. The collisions cause pressure of the gas 4. Gas particles neither attract nor repel each other 5. The average kinetic energy of gases are proportional to the k ...
Thermo-charged capacitors and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
... of the Gibbs free energy of the system ∆G = ∆H − T ∆S should be negative. The enthalpy variation for constant pressure systems is given by ∆H = ∆E + ∆W , where ∆E is the system internal energy variation and ∆W is the work produced. ∆H is equal to 0 since, from the First Law of Thermodynamics, ∆H = ∆ ...
... of the Gibbs free energy of the system ∆G = ∆H − T ∆S should be negative. The enthalpy variation for constant pressure systems is given by ∆H = ∆E + ∆W , where ∆E is the system internal energy variation and ∆W is the work produced. ∆H is equal to 0 since, from the First Law of Thermodynamics, ∆H = ∆ ...
On a Universal Tendency in Nature to the Dissipation
... The object of the present communication is to call attention to the remarkable consequences which follow from Carnot's proposition, that there is an absolute waste of mechanical energy available to man when heat is allowed to pass from one body to another at a lower temperature, by any means not ful ...
... The object of the present communication is to call attention to the remarkable consequences which follow from Carnot's proposition, that there is an absolute waste of mechanical energy available to man when heat is allowed to pass from one body to another at a lower temperature, by any means not ful ...
Contents and Concepts
... A spontaneous process is one that occurs by itself. As we will see, the entropy of the system increases in a spontaneous process. ...
... A spontaneous process is one that occurs by itself. As we will see, the entropy of the system increases in a spontaneous process. ...
Experimental Enthalpy of Fusion and Heat Capacity
... As already indicated, the only other experimental heat capacity data have been obtained by adiabatic calorimetry [12] but, where the comparison is possible (300-350 K), they differ substantially (by about 8%) from ours. It should be stressed that the thermodynamic evaluation performed by Pankratz [1 ...
... As already indicated, the only other experimental heat capacity data have been obtained by adiabatic calorimetry [12] but, where the comparison is possible (300-350 K), they differ substantially (by about 8%) from ours. It should be stressed that the thermodynamic evaluation performed by Pankratz [1 ...
Thermodynamics
... Not speed of reaction (kinetics) A reaction can be thermodynamically favored but still be ...
... Not speed of reaction (kinetics) A reaction can be thermodynamically favored but still be ...
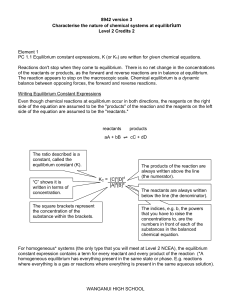
Wanganui High School
... For homogeneous* systems (the only type that you will meet at Level 2 NCEA), the equilibrium constant expression contains a term for every reactant and every product of the reaction (*A homogeneous equilibrium has everything present in the same state or phase. E.g. reactions where everything is a ga ...
... For homogeneous* systems (the only type that you will meet at Level 2 NCEA), the equilibrium constant expression contains a term for every reactant and every product of the reaction (*A homogeneous equilibrium has everything present in the same state or phase. E.g. reactions where everything is a ga ...
Chemical Thermodynamics Survival Kit
... number of moles of water is not taken into consideration (obviously, the ideal gas law cannot be applied to a liquid). ...
... number of moles of water is not taken into consideration (obviously, the ideal gas law cannot be applied to a liquid). ...
CHEM WKST: EQUILIBRIUM / LE CHATELIER`S PRINCIPLE
... g) A catalyst is added. no shift 8) For the reaction: N2(g) + 6HCl(g) ⇄ 2NH3(g) + 3Cl2(g); ΔH = +461 kJ Indicate what happens to [HCl] if the following changes occur. a) More N2 is added. [HCl] ↓ b) Some NH3 is removed. [HCl] ↓ c) The temperature is increased. [HCl] ↓ d) The pressure is lowered. [HC ...
... g) A catalyst is added. no shift 8) For the reaction: N2(g) + 6HCl(g) ⇄ 2NH3(g) + 3Cl2(g); ΔH = +461 kJ Indicate what happens to [HCl] if the following changes occur. a) More N2 is added. [HCl] ↓ b) Some NH3 is removed. [HCl] ↓ c) The temperature is increased. [HCl] ↓ d) The pressure is lowered. [HC ...