Anatomy Lab - Doctors2Be
... forming renal papilla it’s open to the Minor calyces Major calyces Renal pelvis fills most of the sinus Cortex extends into medulla as renal columns ...
... forming renal papilla it’s open to the Minor calyces Major calyces Renal pelvis fills most of the sinus Cortex extends into medulla as renal columns ...
Sodium Disorders
... species, purine depletion, and phospholipases probably have a role in these changes in morphology and polarity as well as in the subsequent cell death that occurs as a result of necrosis and apoptosis. There is a sloughing of viable and nonviable cells into the tubular lumen, resulting in the format ...
... species, purine depletion, and phospholipases probably have a role in these changes in morphology and polarity as well as in the subsequent cell death that occurs as a result of necrosis and apoptosis. There is a sloughing of viable and nonviable cells into the tubular lumen, resulting in the format ...
Acute Renal Failure
... species, purine depletion, and phospholipases probably have a role in these changes in morphology and polarity as well as in the subsequent cell death that occurs as a result of necrosis and apoptosis. There is a sloughing of viable and nonviable cells into the tubular lumen, resulting in the format ...
... species, purine depletion, and phospholipases probably have a role in these changes in morphology and polarity as well as in the subsequent cell death that occurs as a result of necrosis and apoptosis. There is a sloughing of viable and nonviable cells into the tubular lumen, resulting in the format ...
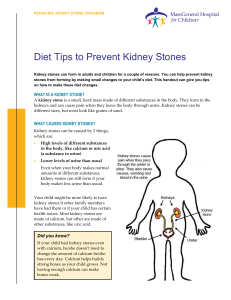
Diet Tips to Help Prevent Kidney Stones
... Kidney stones can form in adults and children for a couple of reasons. You can help prevent kidney stones from forming by making small changes to your child’s diet. This handout can give you tips on how to make these diet changes. ...
... Kidney stones can form in adults and children for a couple of reasons. You can help prevent kidney stones from forming by making small changes to your child’s diet. This handout can give you tips on how to make these diet changes. ...
File
... rid your body of harmful wastes, extra salt, and extra water. Hemodialysis helps control blood pressure and helps your body keep the proper balance of important chemicals such as potassium, sodium, calcium, and bicarbonate. – Dialysis can replace part of the function of your kidneys. Diet, medicatio ...
... rid your body of harmful wastes, extra salt, and extra water. Hemodialysis helps control blood pressure and helps your body keep the proper balance of important chemicals such as potassium, sodium, calcium, and bicarbonate. – Dialysis can replace part of the function of your kidneys. Diet, medicatio ...
Excretory System
... rid your body of harmful wastes, extra salt, and extra water. Hemodialysis helps control blood pressure and helps your body keep the proper balance of important chemicals such as potassium, sodium, calcium, and bicarbonate. – Dialysis can replace part of the function of your kidneys. Diet, medicatio ...
... rid your body of harmful wastes, extra salt, and extra water. Hemodialysis helps control blood pressure and helps your body keep the proper balance of important chemicals such as potassium, sodium, calcium, and bicarbonate. – Dialysis can replace part of the function of your kidneys. Diet, medicatio ...
Kidney Homeostasis
... Please go to the following interactive site to learn more about the kidney: http://www.biologymad.com/resources/kidney.swf ...
... Please go to the following interactive site to learn more about the kidney: http://www.biologymad.com/resources/kidney.swf ...
Unit 14 PowerPoint
... Tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Actually an extension of the renal pelvis – 25 to 30 cm long (10 to 12 inches) ...
... Tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Actually an extension of the renal pelvis – 25 to 30 cm long (10 to 12 inches) ...
Urinary System Part 1
... • Renal tubule extends from glomerular capsule and ends at the collecting duct – Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule – Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) – Loop of Henle – Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) ...
... • Renal tubule extends from glomerular capsule and ends at the collecting duct – Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule – Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) – Loop of Henle – Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) ...
6. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
... kidney also has an endocrine role which contributes to several rather important physiological activities. It contributes to the regulation of red blood cell through production or erythropoietin. Regulates diuresis through increased renal blood flow as a result of production of urodilatin and, calciu ...
... kidney also has an endocrine role which contributes to several rather important physiological activities. It contributes to the regulation of red blood cell through production or erythropoietin. Regulates diuresis through increased renal blood flow as a result of production of urodilatin and, calciu ...
study on spectrum of renal diseases in elderly patients
... blood pressure.In established nephropathy arterial blood pressure is elevated but ...
... blood pressure.In established nephropathy arterial blood pressure is elevated but ...
The Urinary System
... Left kidney lies at the level from the lower border of T11 to L2; the 12th rib is behind its middle part of the post surface Right kidney lies slightly lower than the left kidney, at the level from the upper border of T12 to L3; the 12th rib is behind its upper part of the post surface Renal hilum a ...
... Left kidney lies at the level from the lower border of T11 to L2; the 12th rib is behind its middle part of the post surface Right kidney lies slightly lower than the left kidney, at the level from the upper border of T12 to L3; the 12th rib is behind its upper part of the post surface Renal hilum a ...
Unit 23.4: The Excretory System
... The kidneys themselves are also regulated by hormones. For example, antidiuretic hormone from the hypothalamus stimulates the kidneys to produce more concentrated urine when the body is low on water. Kidney Disease and Dialysis A person can live a normal, healthy life with just one kidney. However, ...
... The kidneys themselves are also regulated by hormones. For example, antidiuretic hormone from the hypothalamus stimulates the kidneys to produce more concentrated urine when the body is low on water. Kidney Disease and Dialysis A person can live a normal, healthy life with just one kidney. However, ...
AH Renal I
... • 3rd leading cause of renal failure – Affects BOTH kidneys equally – Can spread to tubules, interstitial, vascular areas ...
... • 3rd leading cause of renal failure – Affects BOTH kidneys equally – Can spread to tubules, interstitial, vascular areas ...
Kidney Function Rapid Tests Package insert
... 2. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): This type involves the gradual loss of kidney function. It happens slowly and may go unnoticed for years. People with CKD are more susceptible to heart attacks and strokes. Most kidney problems fall under this category. 3. End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD): This conditi ...
... 2. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): This type involves the gradual loss of kidney function. It happens slowly and may go unnoticed for years. People with CKD are more susceptible to heart attacks and strokes. Most kidney problems fall under this category. 3. End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD): This conditi ...
Last chapter, we examined the liver, one of the most intricate organs
... ones are always being produced to replace the ones that get removed by the spleen at the end of their useful life. These young red blood cells are known as reticulocytes because they still have a fine reticulum of nuclear material visible for a few days after they leave the bone marrow. Mature red b ...
... ones are always being produced to replace the ones that get removed by the spleen at the end of their useful life. These young red blood cells are known as reticulocytes because they still have a fine reticulum of nuclear material visible for a few days after they leave the bone marrow. Mature red b ...
Kidneys - India Renal Foundation
... independently. In other words, a person can lead a normal life even with one kidney. Kidneys are the chief excretory organs of body . The main function of the kidney is to excrete waste products. Apart from excretion, kidneys perform other important functions also which are balancing the body fluid, ...
... independently. In other words, a person can lead a normal life even with one kidney. Kidneys are the chief excretory organs of body . The main function of the kidney is to excrete waste products. Apart from excretion, kidneys perform other important functions also which are balancing the body fluid, ...
Evidence Based Medicine Journal Article Review
... • Depends on site, partial or complete, acute or chronic and duration of obstruction. • Generally if diagnosed early and obstruction relieved, recovery is good with return to normal kidney function. • Late diagnosis – chronic renal failure. ...
... • Depends on site, partial or complete, acute or chronic and duration of obstruction. • Generally if diagnosed early and obstruction relieved, recovery is good with return to normal kidney function. • Late diagnosis – chronic renal failure. ...
Osmoregulation and Excretion
... Osmoregulation: The Basics • Osmoconformers – Isoosmotic with surroundings • Osmoregulators- Control internal environment independently from environment • Stenohaline – Animals that cannot tolerate large changes in external osmolarity • Euryhaline – Animals that can survive large fluctuation in ext ...
... Osmoregulation: The Basics • Osmoconformers – Isoosmotic with surroundings • Osmoregulators- Control internal environment independently from environment • Stenohaline – Animals that cannot tolerate large changes in external osmolarity • Euryhaline – Animals that can survive large fluctuation in ext ...
Chronic kidney disease

Chronic kidney disease (CKD), also known as chronic renal disease, is a progressive loss in renal function over a period of months or years. The symptoms of worsening kidney function are not specific, and might include feeling generally unwell and experiencing a reduced appetite. Often, chronic kidney disease is diagnosed as a result of screening of people known to be at risk of kidney problems, such as those with high blood pressure or diabetes and those with a blood relative with CKD. This disease may also be identified when it leads to one of its recognized complications, such as cardiovascular disease, anemia, or pericarditis. It is differentiated from acute kidney disease in that the reduction in kidney function must be present for over 3 months.Chronic kidney disease is identified by a blood test for creatinine, which is a breakdown product of muscle metabolism. Higher levels of creatinine indicate a lower glomerular filtration rate and as a result a decreased capability of the kidneys to excrete waste products. Creatinine levels may be normal in the early stages of CKD, and the condition is discovered if urinalysis (testing of a urine sample) shows the kidney is allowing the loss of protein or red blood cells into the urine. To fully investigate the underlying cause of kidney damage, various forms of medical imaging, blood tests, and sometimes a renal biopsy (removing a small sample of kidney tissue) are employed to find out if a reversible cause for the kidney malfunction is present.Recent professional guidelines classify the severity of CKD in five stages, with stage 1 being the mildest and usually causing few symptoms and stage 5 being a severe illness with poor life expectancy if untreated. Stage 5 CKD is often called end-stage kidney disease, end-stage renal disease, or end-stage kidney failure, and is largely synonymous with the now outdated terms chronic renal failure or chronic kidney failure; and usually means the patient requires renal replacement therapy, which may involve a form of dialysis, but ideally constitutes a kidney transplant.Screening of at-risk people is important because treatments exist that delay the progression of CKD. If an underlying cause of CKD, such as vasculitis, or obstructive nephropathy (blockage to the drainage system of the kidneys) is found, it may be treated directly to slow the damage. In more advanced stages, treatments may be required for anemia and renal bone disease (also called renal osteodystrophy, secondary hyperparathyroidism or chronic kidney disease - mineral bone disorder (CKD-MBD)). Chronic kidney disease resulted in 956,000 deaths in 2013 up from 409,000 deaths in 1990.