Excretory System
... Function of the Kidney • The principal function of the kidney is to filter blood in order to remove cellular waste products from the body. • At any given time, 20 % of blood is in the kidneys. Humans can function with one kidney. • If one ceases to work, the other increases in size to handle the wor ...
... Function of the Kidney • The principal function of the kidney is to filter blood in order to remove cellular waste products from the body. • At any given time, 20 % of blood is in the kidneys. Humans can function with one kidney. • If one ceases to work, the other increases in size to handle the wor ...
Acute-on-chronic kidney disease
... Distinguishing acute kidney injury from CKD Previous creatinine measurements are the most useful tool for confirming and assessing the severity of acute kidney injury. The length of time between creatinine measurements will vary from patient to patient and clinical judgement is required to interpret ...
... Distinguishing acute kidney injury from CKD Previous creatinine measurements are the most useful tool for confirming and assessing the severity of acute kidney injury. The length of time between creatinine measurements will vary from patient to patient and clinical judgement is required to interpret ...
Excretory System ppt
... Function of the Kidney • The principal function of the kidney is to filter blood in order to remove cellular waste products from the body. • At any given time, 20 % of blood is in the kidneys. Humans can function with one kidney. • If one ceases to work, the other increases in size to handle the wor ...
... Function of the Kidney • The principal function of the kidney is to filter blood in order to remove cellular waste products from the body. • At any given time, 20 % of blood is in the kidneys. Humans can function with one kidney. • If one ceases to work, the other increases in size to handle the wor ...
Excretory System PPT
... Function of the Kidney • The principal function of the kidney is to filter blood in order to remove cellular waste products from the body. • At any given time, 20 % of blood is in the kidneys. Humans can function with one kidney. • If one ceases to work, the other increases in size to handle the wor ...
... Function of the Kidney • The principal function of the kidney is to filter blood in order to remove cellular waste products from the body. • At any given time, 20 % of blood is in the kidneys. Humans can function with one kidney. • If one ceases to work, the other increases in size to handle the wor ...
Medullary Sponge Kidney What are the kidneys and What is medullary sponge
... blood in urine; kidney stones; and urinary tract infections (UTIs). But these prob lems do not usually appear until the ages of 30 to 40. MSK affects about 1 person per 5,000 to 20,000 people in the United States.1 Researchers have reported that up to 20 percent of people who form kidney stones hav ...
... blood in urine; kidney stones; and urinary tract infections (UTIs). But these prob lems do not usually appear until the ages of 30 to 40. MSK affects about 1 person per 5,000 to 20,000 people in the United States.1 Researchers have reported that up to 20 percent of people who form kidney stones hav ...
27-Premedical_excre
... Function of Tubules Most of these functions concern the reabsorption and secretion of various solutes such as ions (sodium), carbohydrates (glucose), and amino ...
... Function of Tubules Most of these functions concern the reabsorption and secretion of various solutes such as ions (sodium), carbohydrates (glucose), and amino ...
Excretory System
... Function of the Kidney • The principal function of the kidney is to filter blood in order to remove cellular waste products from the body. • At any given time, 20 % of blood is in the kidneys. Humans can function with one kidney. • If one ceases to work, the other increases in size to handle the wor ...
... Function of the Kidney • The principal function of the kidney is to filter blood in order to remove cellular waste products from the body. • At any given time, 20 % of blood is in the kidneys. Humans can function with one kidney. • If one ceases to work, the other increases in size to handle the wor ...
Understanding Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
... healthy kidneys filter waste but keep proteins like albumin inside your body, finding protein in your urine means that your kidneys are not functioning as they should. The normal rate for microalbumin is less than 30. If your number is higher or is increasing from the last time you were tested, your ...
... healthy kidneys filter waste but keep proteins like albumin inside your body, finding protein in your urine means that your kidneys are not functioning as they should. The normal rate for microalbumin is less than 30. If your number is higher or is increasing from the last time you were tested, your ...
Bio 221 The Urinary System Spring 2006
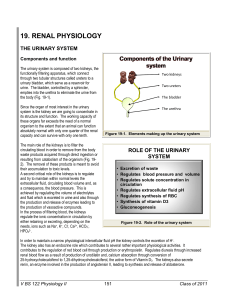
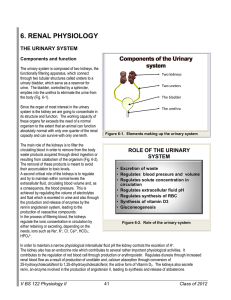
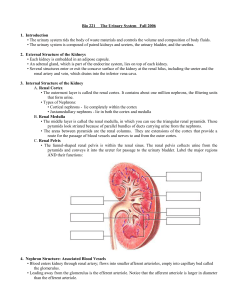
... • Each kidney is embedded in an adipose capsule. • An adrenal gland, which is part of the endocrine system, lies on top of each kidney. • Several structures enter or exit the concave surface of the kidney at the renal hilus, including the ureter and the renal artery and vein, which drains into the i ...
... • Each kidney is embedded in an adipose capsule. • An adrenal gland, which is part of the endocrine system, lies on top of each kidney. • Several structures enter or exit the concave surface of the kidney at the renal hilus, including the ureter and the renal artery and vein, which drains into the i ...
Renal blood flow
... increased in chronic renal failure (CRF), although this increase may not be clinically apparent until the GFR is reduced to very low levels. • Weight gain is usually associated with volume expansion and is offset by the concomitant loss of lean body mass. ...
... increased in chronic renal failure (CRF), although this increase may not be clinically apparent until the GFR is reduced to very low levels. • Weight gain is usually associated with volume expansion and is offset by the concomitant loss of lean body mass. ...
Altered Renal Function
... • Slow development (years) • Alterations in salt and water balance not apparent until renal function is less than 25% of normal. • Common causes: – Chronic glomerulonephritis – Chronic pyelonephritis ...
... • Slow development (years) • Alterations in salt and water balance not apparent until renal function is less than 25% of normal. • Common causes: – Chronic glomerulonephritis – Chronic pyelonephritis ...
URINARY SYSTEM
... • Multiple renal veins contribute to the formation of the left and right renal veins, both of which are anterior to the renal arteries • Importantly, the longer left renal vein crosses the midline anterior to the abdominal aorta and posterior to the superior mesenteric artery and can be compressed ...
... • Multiple renal veins contribute to the formation of the left and right renal veins, both of which are anterior to the renal arteries • Importantly, the longer left renal vein crosses the midline anterior to the abdominal aorta and posterior to the superior mesenteric artery and can be compressed ...
27-Premedical_excre
... Function of Tubules Most of these functions concern the reabsorption and secretion of various solutes such as ions (sodium), carbohydrates (glucose), and amino ...
... Function of Tubules Most of these functions concern the reabsorption and secretion of various solutes such as ions (sodium), carbohydrates (glucose), and amino ...
Kidney Health - SurvivorshipGuidelines.org
... care provider’s recommendations. People with low levels of blood salts and minerals may need to take supplements (prescribed by a healthcare provider). This can be important for long-term health. For example, persistently low levels of blood magnesium can lead to heart problems. Copyright 2008 © Chi ...
... care provider’s recommendations. People with low levels of blood salts and minerals may need to take supplements (prescribed by a healthcare provider). This can be important for long-term health. For example, persistently low levels of blood magnesium can lead to heart problems. Copyright 2008 © Chi ...
lec26
... a. Attempt to maximize cardiac output and improve intravascular volume b. Diuretics often worsen renal failure but may be necessary to prevent pulmonary edema c. In general, potassium sparing diuretics should be avoided (high risk hyperkalemia) e. Dopamine or mannitol can be tried, but are usually n ...
... a. Attempt to maximize cardiac output and improve intravascular volume b. Diuretics often worsen renal failure but may be necessary to prevent pulmonary edema c. In general, potassium sparing diuretics should be avoided (high risk hyperkalemia) e. Dopamine or mannitol can be tried, but are usually n ...
What are kidneys? - Kidney Health New Zealand
... • Glomerulonephritis – this is an inflammation of the kidneys that can follow some infections. The urine looks dark and your child may look puffy in the face. Post streptococcal infections (the bug that can cause skin and throat infections) are seen more frequently in New Zealand children than in m ...
... • Glomerulonephritis – this is an inflammation of the kidneys that can follow some infections. The urine looks dark and your child may look puffy in the face. Post streptococcal infections (the bug that can cause skin and throat infections) are seen more frequently in New Zealand children than in m ...
PPT File - Northeast Regional Ag Expo 2016
... - group of diseases that injure the part of the kidney that filters blood (called glomeruli). When the kidney is injured, it cannot get rid of wastes and extra fluid in the body. If the illness continues, the kidneys may stop working completely, resulting in kidney failure. ...
... - group of diseases that injure the part of the kidney that filters blood (called glomeruli). When the kidney is injured, it cannot get rid of wastes and extra fluid in the body. If the illness continues, the kidneys may stop working completely, resulting in kidney failure. ...
CASE REPORT
... Kidney calices – A05.810.453.537.503 Renal artery – A07.231.114.745 Renal vein – A07.231.908.752 INTRODUCTION: The occurrence of horseshoe kidney is about 0.25% in general population, (1) and are seen in approximately 1 out of 300 pyelographies. (2,3) Horseshoe kidney is found in 1 out of 1000 necro ...
... Kidney calices – A05.810.453.537.503 Renal artery – A07.231.114.745 Renal vein – A07.231.908.752 INTRODUCTION: The occurrence of horseshoe kidney is about 0.25% in general population, (1) and are seen in approximately 1 out of 300 pyelographies. (2,3) Horseshoe kidney is found in 1 out of 1000 necro ...
Pathophysiology of kidney. Kidney insufficiency
... followed by deformation of the bones (if hipocalciemia in children), osteoporosis (reduced bone density without deformation of the bones); osteosclerosis (increased bone density). ...
... followed by deformation of the bones (if hipocalciemia in children), osteoporosis (reduced bone density without deformation of the bones); osteosclerosis (increased bone density). ...
Kidney Homeostasis
... experiment that allows them to investigate one physiological effect of consuming coffee (e.g. Effects on blood pressure, urine output, etc.) ...
... experiment that allows them to investigate one physiological effect of consuming coffee (e.g. Effects on blood pressure, urine output, etc.) ...
urinary system - Practicum-Health-Science-I-2011-2012
... • Small calculi may be eliminated in the urine, but larger stones often become lodged in the renal pelvis or ureter ...
... • Small calculi may be eliminated in the urine, but larger stones often become lodged in the renal pelvis or ureter ...
Chronic kidney disease

Chronic kidney disease (CKD), also known as chronic renal disease, is a progressive loss in renal function over a period of months or years. The symptoms of worsening kidney function are not specific, and might include feeling generally unwell and experiencing a reduced appetite. Often, chronic kidney disease is diagnosed as a result of screening of people known to be at risk of kidney problems, such as those with high blood pressure or diabetes and those with a blood relative with CKD. This disease may also be identified when it leads to one of its recognized complications, such as cardiovascular disease, anemia, or pericarditis. It is differentiated from acute kidney disease in that the reduction in kidney function must be present for over 3 months.Chronic kidney disease is identified by a blood test for creatinine, which is a breakdown product of muscle metabolism. Higher levels of creatinine indicate a lower glomerular filtration rate and as a result a decreased capability of the kidneys to excrete waste products. Creatinine levels may be normal in the early stages of CKD, and the condition is discovered if urinalysis (testing of a urine sample) shows the kidney is allowing the loss of protein or red blood cells into the urine. To fully investigate the underlying cause of kidney damage, various forms of medical imaging, blood tests, and sometimes a renal biopsy (removing a small sample of kidney tissue) are employed to find out if a reversible cause for the kidney malfunction is present.Recent professional guidelines classify the severity of CKD in five stages, with stage 1 being the mildest and usually causing few symptoms and stage 5 being a severe illness with poor life expectancy if untreated. Stage 5 CKD is often called end-stage kidney disease, end-stage renal disease, or end-stage kidney failure, and is largely synonymous with the now outdated terms chronic renal failure or chronic kidney failure; and usually means the patient requires renal replacement therapy, which may involve a form of dialysis, but ideally constitutes a kidney transplant.Screening of at-risk people is important because treatments exist that delay the progression of CKD. If an underlying cause of CKD, such as vasculitis, or obstructive nephropathy (blockage to the drainage system of the kidneys) is found, it may be treated directly to slow the damage. In more advanced stages, treatments may be required for anemia and renal bone disease (also called renal osteodystrophy, secondary hyperparathyroidism or chronic kidney disease - mineral bone disorder (CKD-MBD)). Chronic kidney disease resulted in 956,000 deaths in 2013 up from 409,000 deaths in 1990.