Genetics - TeacherWeb
... • Branch of biology dealing with genes and heredity • Genes: bits of DNA on chromosomes • Usually 2 genes for a trait Dominant Gene: always seen in the population – represented by a capital letter Recessive Gene: overpowered by the dominant gene – represented by a small ...
... • Branch of biology dealing with genes and heredity • Genes: bits of DNA on chromosomes • Usually 2 genes for a trait Dominant Gene: always seen in the population – represented by a capital letter Recessive Gene: overpowered by the dominant gene – represented by a small ...
Development Through the Lifespan
... Development Through the Lifespan Chapter 2 Biological and Environmental Foundations ...
... Development Through the Lifespan Chapter 2 Biological and Environmental Foundations ...
File - S
... and diabetes are also common cases of hereditary diseases which depend on the combination of genes. ...
... and diabetes are also common cases of hereditary diseases which depend on the combination of genes. ...
Evolution Study Guide Part 2
... These mutations can be neutral (no effect), negative (possible disease), or beneficial. Mutations are important for evolution only if they are mutations in the germ cells because these genes pass onto future generations. 2. Genetic Recombination and Sexual Reproduction is the most common way of gene ...
... These mutations can be neutral (no effect), negative (possible disease), or beneficial. Mutations are important for evolution only if they are mutations in the germ cells because these genes pass onto future generations. 2. Genetic Recombination and Sexual Reproduction is the most common way of gene ...
Using a parallel approach to help evolution
... Control case runs all independent Genetic Algorithms •Test case injects “good genes” into the Genetic Algorithms ...
... Control case runs all independent Genetic Algorithms •Test case injects “good genes” into the Genetic Algorithms ...
HealthGrid Conference
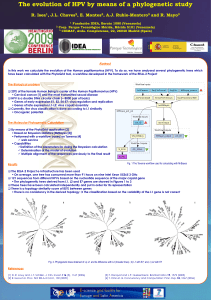
... Definition of the parameters for doing the Bayesian calculation Determination of the model of evolution Multiple alignment of the sequences previously to the final result Fig. 1 The Taverna workflow used for calculating with MrBayes ...
... Definition of the parameters for doing the Bayesian calculation Determination of the model of evolution Multiple alignment of the sequences previously to the final result Fig. 1 The Taverna workflow used for calculating with MrBayes ...
BIOLOGY Chapter 14: Evolution: A History and a Process Name
... Section Goal: The student will explain the significance of gene pools in understanding evolution, tell how genetic drift, gene flow, mutation and natural selection contribute to changes in a gene pool, explain what is meant be the term fitness and describe recent evidence for microevolution on the G ...
... Section Goal: The student will explain the significance of gene pools in understanding evolution, tell how genetic drift, gene flow, mutation and natural selection contribute to changes in a gene pool, explain what is meant be the term fitness and describe recent evidence for microevolution on the G ...
Physical Anthropology Study Guide for Exam 1 Evolutionary Theory
... Mutation Genetic drift Founders' effect Gene flow Speciation Chronospecies Anagenesis Divergent evolution Cladogenesis Convergent evolution Punctuated equilbrium Human Adaptability Adaptation: -genetic -physiological -cultural Acclimatization Sickle-cell anemia Lactose intolerance High altitude Berg ...
... Mutation Genetic drift Founders' effect Gene flow Speciation Chronospecies Anagenesis Divergent evolution Cladogenesis Convergent evolution Punctuated equilbrium Human Adaptability Adaptation: -genetic -physiological -cultural Acclimatization Sickle-cell anemia Lactose intolerance High altitude Berg ...
Chorionic Gonadotropin (CG) 태반성 성선자극호르몬
... Primates and an Evolutionary History of Selection Glenn A. Maston & Maryellen Ruvolo Department of Anthropology, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts Abstract ...
... Primates and an Evolutionary History of Selection Glenn A. Maston & Maryellen Ruvolo Department of Anthropology, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts Abstract ...
Fragile Sites and Cancer Powerpoint
... • Staining of metaphase chromosomes, one area failed to stain giving the appearance of a gap. • Gaps were susceptible to chromosome breakage. • Cause of fragility is unknown. ...
... • Staining of metaphase chromosomes, one area failed to stain giving the appearance of a gap. • Gaps were susceptible to chromosome breakage. • Cause of fragility is unknown. ...
meiosis generates new combinations of alleles
... mutations in the DNA. These forms are called alleles. Property of having different forms is called ...
... mutations in the DNA. These forms are called alleles. Property of having different forms is called ...
The Code of Life: Topic 3
... • Gene expression! • You have 23 pairs of chromosomes. • In each pair you get one from your mother and one from your father. • Each chromosome in a pair holds all the same genes as the other. • So what determines which gene is expressed when you develop? • ie how do you get your mother's eyes or you ...
... • Gene expression! • You have 23 pairs of chromosomes. • In each pair you get one from your mother and one from your father. • Each chromosome in a pair holds all the same genes as the other. • So what determines which gene is expressed when you develop? • ie how do you get your mother's eyes or you ...
Identification of Coding Sequences
... probabilities for the transition from one part of a gene to another. In this model, used by the GENSCAN algorithm, each circle or diamond represents a functional unit in the gene. For example Eint is the initial exon and Eterm is the last. The arrows represent the probability of a transition from on ...
... probabilities for the transition from one part of a gene to another. In this model, used by the GENSCAN algorithm, each circle or diamond represents a functional unit in the gene. For example Eint is the initial exon and Eterm is the last. The arrows represent the probability of a transition from on ...
BI475 Ch15 SQ
... 2. Summarize current thinking regarding the processes that led to evolution of the first genomes. Be careful to distinguish between the RNA world and the DNA world and to indicate how the transition from the former to latter is thought to have occurred. 3. Which periods during the last 1.5 billion y ...
... 2. Summarize current thinking regarding the processes that led to evolution of the first genomes. Be careful to distinguish between the RNA world and the DNA world and to indicate how the transition from the former to latter is thought to have occurred. 3. Which periods during the last 1.5 billion y ...
12.4 Notes - Trimble County Schools
... • Recessive – traits that only appear when paired with another allele that is recessive (type O) • Genotype – a pair of allele genes • Phenotype – the outward appearance of an individual ...
... • Recessive – traits that only appear when paired with another allele that is recessive (type O) • Genotype – a pair of allele genes • Phenotype – the outward appearance of an individual ...
uses_lecturenotes.pdf
... • Presymptomatic testing for predicting adult-onset disorders such as Huntington's disease • Presymptomatic testing for estimating the risk of developing adult-onset cancers and Alzheimer's disease • Confirmational diagnosis of a symptomatic individual • Forensic/identity testing 2.) Gene therapy – ...
... • Presymptomatic testing for predicting adult-onset disorders such as Huntington's disease • Presymptomatic testing for estimating the risk of developing adult-onset cancers and Alzheimer's disease • Confirmational diagnosis of a symptomatic individual • Forensic/identity testing 2.) Gene therapy – ...
Slide 1
... Motor Control • Define system based on physical description of architecture, including limbs and joints ...
... Motor Control • Define system based on physical description of architecture, including limbs and joints ...
Schol Biol: Genetics
... • Chitin synthase (shell structure) • HSP70 (stress) Biochemical measurements • Carbonic anhydrase activity ...
... • Chitin synthase (shell structure) • HSP70 (stress) Biochemical measurements • Carbonic anhydrase activity ...
Estimation Over Multiple Undirected Graphs
... Graphical models are useful in analyzing complex systems involving a large number of interacting units. For example, in gene expression analysis, one key challenge is reconstruction of gene networks, describing gene-gene interactions. Observed attributes of genes, such as gene expressions, are used ...
... Graphical models are useful in analyzing complex systems involving a large number of interacting units. For example, in gene expression analysis, one key challenge is reconstruction of gene networks, describing gene-gene interactions. Observed attributes of genes, such as gene expressions, are used ...
7.3 Gene Linkage and Mapping
... Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance-based on research of Thomas Morgan Hunt • Genes are located on chromosomes and the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis accounts for inheritance patterns. “Random Assortment” • Chromosomes exchange homologous genes during meiosis explains how linked genes can sepa ...
... Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance-based on research of Thomas Morgan Hunt • Genes are located on chromosomes and the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis accounts for inheritance patterns. “Random Assortment” • Chromosomes exchange homologous genes during meiosis explains how linked genes can sepa ...