NOVA: Cracking Your Genetic Code - Tri-City
... If she found out she was predisposed to getting breast cancer, what things could she have done that she may not have done otherwise? ...
... If she found out she was predisposed to getting breast cancer, what things could she have done that she may not have done otherwise? ...
microarrays1
... Define distributions over the whole array or a control group. Use mean/variance to determine the significance, normalization…statisticians like this stuff ...
... Define distributions over the whole array or a control group. Use mean/variance to determine the significance, normalization…statisticians like this stuff ...
ppt
... melanogaster. When females heterozygous for these genes were crossed with scute bristled, ruby eyed males, the following classes and numbers of progeny (out of 1000) ...
... melanogaster. When females heterozygous for these genes were crossed with scute bristled, ruby eyed males, the following classes and numbers of progeny (out of 1000) ...
7th Grade Science Notes
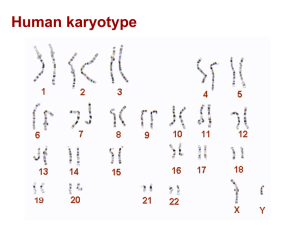
... Genes that are on these chromosomes are called “sex-linked” genes. Each male carries an X and a Y chromosome. Each female carries two X chromosomes. If a disease or abnormality occurs on the X chromosome, it will always be expressed in the male because they have only one X. It may not be expressed i ...
... Genes that are on these chromosomes are called “sex-linked” genes. Each male carries an X and a Y chromosome. Each female carries two X chromosomes. If a disease or abnormality occurs on the X chromosome, it will always be expressed in the male because they have only one X. It may not be expressed i ...
Permutation to assess the generalizability of the reduction in error
... the squared values of the Kolmogorov Smirnov statistic (unweighted this time ie 0.0 to 1.0) from the subsets as described above. In this scoring system high scores in any single subset will effect the gene ranking more than medium scores across all subsets. From the 20 highest scoring genes random g ...
... the squared values of the Kolmogorov Smirnov statistic (unweighted this time ie 0.0 to 1.0) from the subsets as described above. In this scoring system high scores in any single subset will effect the gene ranking more than medium scores across all subsets. From the 20 highest scoring genes random g ...
Detection of different genes heredity
... (unresponsive) to androgens (male hormones). Instead, they are born looking externally like normal girls. Internally, there is a short blind-pouch vagina and no uterus, fallopian tubes or ovaries. There are testes in the abdomen or the inguinal canal. ...
... (unresponsive) to androgens (male hormones). Instead, they are born looking externally like normal girls. Internally, there is a short blind-pouch vagina and no uterus, fallopian tubes or ovaries. There are testes in the abdomen or the inguinal canal. ...
Basic Principles of Genetics: Printable Crossword Puzzle
... parent, are possible. 9. An alternate form of the same gene. 11. The genetic makeup of an individual for a trait or for all of his/her inherited traits—not the observable or detectable characteristics. 12. An inheritance pattern in which a gene will have a different effect depending on the gender of ...
... parent, are possible. 9. An alternate form of the same gene. 11. The genetic makeup of an individual for a trait or for all of his/her inherited traits—not the observable or detectable characteristics. 12. An inheritance pattern in which a gene will have a different effect depending on the gender of ...
General Genetics - Montgomery College
... • Law of Independent Assortment: genes residing on different chromosomes separate without regard for one another – describes the broad range of variation seen in organisms ...
... • Law of Independent Assortment: genes residing on different chromosomes separate without regard for one another – describes the broad range of variation seen in organisms ...
Chapter 4 Heredity and Evolution
... Members of each gene pair separate so each gamete contains one member of a pair. fertilization Full number of chromosomes is restored and members of gene pairs are reunited. ...
... Members of each gene pair separate so each gamete contains one member of a pair. fertilization Full number of chromosomes is restored and members of gene pairs are reunited. ...
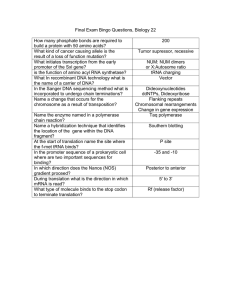
How many phosphate bonds are required to build a protein with 50
... Name a change that occurs for the chromosome as a result of transposition? Name the enzyme named in a polymerase chain reaction? Name a hybridization technique that identifies the location of the gene within the DNA fragment? At the start of translation name the site where the f-met tRNA binds? In t ...
... Name a change that occurs for the chromosome as a result of transposition? Name the enzyme named in a polymerase chain reaction? Name a hybridization technique that identifies the location of the gene within the DNA fragment? At the start of translation name the site where the f-met tRNA binds? In t ...
bot 458h1f - plant molecular biology and biotechnology
... This course introduces students to major features of gene expression and signal transduction in plants. Topics include strategies for generating transgenic plants and regulating gene expression, as well as the importance of signal transduction in plant growth and survival. Strategies on how to manip ...
... This course introduces students to major features of gene expression and signal transduction in plants. Topics include strategies for generating transgenic plants and regulating gene expression, as well as the importance of signal transduction in plant growth and survival. Strategies on how to manip ...
Section 7.1: Chromosomes and Phenotype
... 1. How does phenotype depend on the interaction of alleles? 2. Describe how many genes interact to produce one trait. 3. How does the environment interact with genotype? ...
... 1. How does phenotype depend on the interaction of alleles? 2. Describe how many genes interact to produce one trait. 3. How does the environment interact with genotype? ...
Genetics Vocabulary Crossword Puzzle Across
... 19. a strand of DNA that contains genes 20. The number of chromosomes in a gamete is called the ______ number. (In humans it is 23) 21. the genetic make-up of an individual; often represented by 2 letters (ex: TT, Tt, tt) 22. two of the same alleles (ex: TT, tt) ...
... 19. a strand of DNA that contains genes 20. The number of chromosomes in a gamete is called the ______ number. (In humans it is 23) 21. the genetic make-up of an individual; often represented by 2 letters (ex: TT, Tt, tt) 22. two of the same alleles (ex: TT, tt) ...
APOC1 gene rs4420638 SNP
... with Internet recourses. You need to find on ClinVar (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar) all genetic variants that are related to Multiple Sclerosis. Once found, select only ones that have germline allele origin and that are related to “risk factors”. • Download (small button in the lower right co ...
... with Internet recourses. You need to find on ClinVar (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar) all genetic variants that are related to Multiple Sclerosis. Once found, select only ones that have germline allele origin and that are related to “risk factors”. • Download (small button in the lower right co ...
Modification of Mendel
... sugar chain to which the A and B sugars are added. A rare mutation Ih Ih prevents proper formation so that the A and B sugars cannot be added even though the enzyme for doing that is being made. (Diagram next slide) A second gene is masking the normal phenotype. ...
... sugar chain to which the A and B sugars are added. A rare mutation Ih Ih prevents proper formation so that the A and B sugars cannot be added even though the enzyme for doing that is being made. (Diagram next slide) A second gene is masking the normal phenotype. ...
My Slides - people.vcu.edu
... • Are traits for offspring ‘in-between’ or outside the range of parent values? • How often do several loci influence a trait in a natural population? – How hard will it be to find these loci? ...
... • Are traits for offspring ‘in-between’ or outside the range of parent values? • How often do several loci influence a trait in a natural population? – How hard will it be to find these loci? ...
Slide 1
... combining withfrom yourtheir partner’s one from their dad. We will look at size genes today. Turn over the cards to see which gene characteristics (allelles) your lambfrom will carry Each remove the two size gene cards the pack and place them Record your lamb’s gene characteristics on your sheet col ...
... combining withfrom yourtheir partner’s one from their dad. We will look at size genes today. Turn over the cards to see which gene characteristics (allelles) your lambfrom will carry Each remove the two size gene cards the pack and place them Record your lamb’s gene characteristics on your sheet col ...
Powerpoint Presentation: Gene Therapy
... (commonly used) Direct introduction (“golden bullets”) Liposomes Endocytosis of DNA bound to cell surface receptors (low efficiency) Artificial chromosome (under development)) ...
... (commonly used) Direct introduction (“golden bullets”) Liposomes Endocytosis of DNA bound to cell surface receptors (low efficiency) Artificial chromosome (under development)) ...
Unit 3- Section 2
... Deletion-A portion of the chromosome is lost and the information is lost with it. Duplication-A portion from the homologous chromosome is added Inversion- A portion is added but it attaches in the ...
... Deletion-A portion of the chromosome is lost and the information is lost with it. Duplication-A portion from the homologous chromosome is added Inversion- A portion is added but it attaches in the ...
Logan Rayborns Biology CrosswordsM
... 10. the study of heredity and the variation of inherited characteristics. 12. A diploid organism is heterozygous at a gene locus when its cells contain two different alleles of a gene. 14. used to measure the chances or likelihood of an event to occur, a hypothesis being correct, or a scientific pre ...
... 10. the study of heredity and the variation of inherited characteristics. 12. A diploid organism is heterozygous at a gene locus when its cells contain two different alleles of a gene. 14. used to measure the chances or likelihood of an event to occur, a hypothesis being correct, or a scientific pre ...
AP Biology
... 17. In reference to Figure 11.6 – Summarize the 2 methods an organism may use to regulate a metabolic pathway. Give one advantage and one disadvantage of each method. ...
... 17. In reference to Figure 11.6 – Summarize the 2 methods an organism may use to regulate a metabolic pathway. Give one advantage and one disadvantage of each method. ...
C-13 Part II Non-Mendelian inheritance
... Polygenic inheritance occurs when multiple genes are involved in controlling the phenotype of a trait. The phenotype is an accumulation of contributions by multiple genes. These traits show continuous variation and are referred to as quantitative traits. For example – human height ...
... Polygenic inheritance occurs when multiple genes are involved in controlling the phenotype of a trait. The phenotype is an accumulation of contributions by multiple genes. These traits show continuous variation and are referred to as quantitative traits. For example – human height ...