Part 1: Prokaryotic Regulation Questions to answer
... Define each of the following terms and explain how each provides a eukaryotic cell with the ability to regulate gene expression: a. nucleosomes b. DNA methylation c. Transcription factors/enhancers d. alternative splicing e. mRNA degradation f. RNA interference (RNAi) g. Protein processing and degra ...
... Define each of the following terms and explain how each provides a eukaryotic cell with the ability to regulate gene expression: a. nucleosomes b. DNA methylation c. Transcription factors/enhancers d. alternative splicing e. mRNA degradation f. RNA interference (RNAi) g. Protein processing and degra ...
Bi190 Advanced Genetics 2011 Lecture 11/ho10 Genome to Function
... fraction (20%-40%) of genes are essential or have discernable phenotypes. One can analyze phenotypes more carefully, or look at genetic interactions, or run selection experiments, e.g. with bar-coded yeast deletion strains. Targeted knockouts are best made by gene replacement, using the Rothstein me ...
... fraction (20%-40%) of genes are essential or have discernable phenotypes. One can analyze phenotypes more carefully, or look at genetic interactions, or run selection experiments, e.g. with bar-coded yeast deletion strains. Targeted knockouts are best made by gene replacement, using the Rothstein me ...
Ch. 18 - ltcconline.net
... 7. Lac operon- genes produce enzymes to deal with lactose – inducible operon – turns on gene b. inducer 8. regulatory gene ...
... 7. Lac operon- genes produce enzymes to deal with lactose – inducible operon – turns on gene b. inducer 8. regulatory gene ...
Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... • Understand how recombination of genes affect genetic variability • Understand how frequency of recombination of linked genes is related to their loci distance from one another • Be familiar with patterns of inheritance for genes on sex chromosomes • Be familiar with errors that may occur in chromo ...
... • Understand how recombination of genes affect genetic variability • Understand how frequency of recombination of linked genes is related to their loci distance from one another • Be familiar with patterns of inheritance for genes on sex chromosomes • Be familiar with errors that may occur in chromo ...
Genetic Disorders & Diseases
... In order to have the disease, one would have to inherit two copies (alleles) of the abnormal gene, one from each parent ...
... In order to have the disease, one would have to inherit two copies (alleles) of the abnormal gene, one from each parent ...
Print Preview - C:\WINDOWS\TEMP\e3temp_6820\.aptcache
... sex chromosomes; Do not directly determine an determine an organism’s sex organism’s sex Inheritance of sex chromosomes: Punnett Square should indicate that females (XX) can only pass on an X chromosome and males (XY) can only pass on either Autosomal gene expression: Two alleles that one X or one Y ...
... sex chromosomes; Do not directly determine an determine an organism’s sex organism’s sex Inheritance of sex chromosomes: Punnett Square should indicate that females (XX) can only pass on an X chromosome and males (XY) can only pass on either Autosomal gene expression: Two alleles that one X or one Y ...
File - Mr. Krueger`s Biology
... sex chromosomes; Do not directly determine an determine an organism’s sex organism’s sex Inheritance of sex chromosomes: Punnett Square should indicate that females (XX) can only pass on an X chromosome and males (XY) can only pass on either Autosomal gene expression: Two alleles that one X or one Y ...
... sex chromosomes; Do not directly determine an determine an organism’s sex organism’s sex Inheritance of sex chromosomes: Punnett Square should indicate that females (XX) can only pass on an X chromosome and males (XY) can only pass on either Autosomal gene expression: Two alleles that one X or one Y ...
Keystone Vocabulary 61-70
... information for living organisms and is capable of self replication and the synthesis of ribonucleic acid (RNA) 63. Homologous Structure: A physical characteristic in different organisms that is similar because it was inherited from a common ancestor. 64. Interphase: The longest lasting phase of the ...
... information for living organisms and is capable of self replication and the synthesis of ribonucleic acid (RNA) 63. Homologous Structure: A physical characteristic in different organisms that is similar because it was inherited from a common ancestor. 64. Interphase: The longest lasting phase of the ...
7 Self study questions
... 1. Explain why ORF scanning is a feasible way of identifying genes in a prokaryotic DNA sequence. 2. What modifications are introduced when ORF scanning is applied to a eukaryotic DNA sequence? 3. Describe how homology searching is used to locate genes in a DNA sequence and to assign possible functi ...
... 1. Explain why ORF scanning is a feasible way of identifying genes in a prokaryotic DNA sequence. 2. What modifications are introduced when ORF scanning is applied to a eukaryotic DNA sequence? 3. Describe how homology searching is used to locate genes in a DNA sequence and to assign possible functi ...
Tmm - OpenWetWare
... Chip_Platform GPL96: Affymetrix GeneChip Human Genome U133 Array Set HG-U133A for 712X712 ...
... Chip_Platform GPL96: Affymetrix GeneChip Human Genome U133 Array Set HG-U133A for 712X712 ...
Robust Gene Dys-Regulation in Alzheimer`s Brains
... Further, they identified 12 genes whose gene expression has strong correlation with disease progression. The relevance of these genes to disease progression was also validated in an independent dataset. Also, the researchers found an intriguing transcriptional “cushion” for these 100 selected genes ...
... Further, they identified 12 genes whose gene expression has strong correlation with disease progression. The relevance of these genes to disease progression was also validated in an independent dataset. Also, the researchers found an intriguing transcriptional “cushion” for these 100 selected genes ...
Genes Are the Codes for Polypeptides
... 1. Begin by having students sketch a gene individually in journals and develop two or three questions that they have about their gene. 2. Students get into groups of 4 students and develop white boards with a sketch and 2-3 questions. 3. Class discusses sketches and questions in a “board meeting.” 4 ...
... 1. Begin by having students sketch a gene individually in journals and develop two or three questions that they have about their gene. 2. Students get into groups of 4 students and develop white boards with a sketch and 2-3 questions. 3. Class discusses sketches and questions in a “board meeting.” 4 ...
Quiz 3, February 6, 2003
... a. MUTATION is the original source of genetic variation within populations. b. NATURAL SELECTION is a process by which individuals with particular heritable characters survive and reproduce at a higher rate than other individuals in a population. c. GENETIC DRIFT is a random process that is most inf ...
... a. MUTATION is the original source of genetic variation within populations. b. NATURAL SELECTION is a process by which individuals with particular heritable characters survive and reproduce at a higher rate than other individuals in a population. c. GENETIC DRIFT is a random process that is most inf ...
The Human Genome
... “very delicate.” Leading the life of a normal youngster was impossible because any cut or bump could lead to death. It was necessary to keep him always under strict surveillance. In spite of all the protection, he died at the age of 31 as the result of a minor fall. ...
... “very delicate.” Leading the life of a normal youngster was impossible because any cut or bump could lead to death. It was necessary to keep him always under strict surveillance. In spite of all the protection, he died at the age of 31 as the result of a minor fall. ...
genetics
... mitochondria and plastids in plant cells have their own DNA which consists of small rings. This DNA is responsible for the production of proteins essential to the organization and function of their internal membranes (electron transport chain, ATP synthase).In humans the mitochondria in every cell o ...
... mitochondria and plastids in plant cells have their own DNA which consists of small rings. This DNA is responsible for the production of proteins essential to the organization and function of their internal membranes (electron transport chain, ATP synthase).In humans the mitochondria in every cell o ...
Week10
... and evolve the genotypes directly • This is more efficient because no conversion is needed – the genotypes are applied directly to the problem at hand • Usually the elements can be specially designed to make the process work faster and more efficiently than real evolution ...
... and evolve the genotypes directly • This is more efficient because no conversion is needed – the genotypes are applied directly to the problem at hand • Usually the elements can be specially designed to make the process work faster and more efficiently than real evolution ...
Lecture 24 Evolution Genotype vs. Phenotype Ontogeny Genotype
... • A mapping from bit-strings to potential solutions – best if each possible string generates a legal potential solution – choice of mapping is important – can use strings over other finite alphabets ...
... • A mapping from bit-strings to potential solutions – best if each possible string generates a legal potential solution – choice of mapping is important – can use strings over other finite alphabets ...
Genetics Challenge Name 1. The abbreviation for deoxyribonucleic
... 8. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are rod-shaped structures found in the nucleus of every cell in an organism. ...
... 8. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are rod-shaped structures found in the nucleus of every cell in an organism. ...
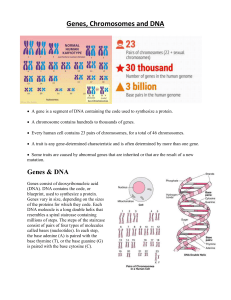
Genes Chromosomes and DNA
... A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or that are the result of a new mutation. ...
... A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or that are the result of a new mutation. ...
WHAT IS BIOTECHNOLOGY? WHAT IS GENE TECHNOLOGY?
... Recent advances in biotechnology provide ways of introducing very precise changes to genetic material that allow, for the first time, the transfer of properties of a single gene from one organism to another. These new techniques, commonly referred to as "gene technology", involve the modification of ...
... Recent advances in biotechnology provide ways of introducing very precise changes to genetic material that allow, for the first time, the transfer of properties of a single gene from one organism to another. These new techniques, commonly referred to as "gene technology", involve the modification of ...
Genetic Engineering
... • Genetic engineering takes genes from one organism, and places them into the chromosomes of another organism. It alters an organism's genetic code, and works because there is only one code for life • The set of instructions for which a gene is responsible work whichever organism the gene is in, e.g ...
... • Genetic engineering takes genes from one organism, and places them into the chromosomes of another organism. It alters an organism's genetic code, and works because there is only one code for life • The set of instructions for which a gene is responsible work whichever organism the gene is in, e.g ...
“FA” Gene Mutations in Familial Breast Cancer The cancer
... FANCD1/BRCA2, may be mutated in 10-20% of cases in which there is a strong family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer. These genes were originally identified as the most common genetic causes of the hereditary breast/ovarian cancer syndrome. In that disorder, only one of the two copies of the ge ...
... FANCD1/BRCA2, may be mutated in 10-20% of cases in which there is a strong family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer. These genes were originally identified as the most common genetic causes of the hereditary breast/ovarian cancer syndrome. In that disorder, only one of the two copies of the ge ...
1. Introduction 2. Fact or Fiction?
... DNA (in 23 pairs) that virtually each cell of the human body contains and that, together, contain all the genes. Other species have more or fewer chromosomes. ...
... DNA (in 23 pairs) that virtually each cell of the human body contains and that, together, contain all the genes. Other species have more or fewer chromosomes. ...