
Saphenous nerve
... ligament lie in the front of the joint. it is inverted Y shaped. • 2Pubofemoral ligament it is triangular ligament lie in the lower anterior part of the capsule. • 3Ischiofemoral ligament it is spiral in shape lie posteriorly. • 4The transverse acetabular ligament it converts the notch into a tunnel ...
... ligament lie in the front of the joint. it is inverted Y shaped. • 2Pubofemoral ligament it is triangular ligament lie in the lower anterior part of the capsule. • 3Ischiofemoral ligament it is spiral in shape lie posteriorly. • 4The transverse acetabular ligament it converts the notch into a tunnel ...
1. The general name for an alternate pathway of blood flow in or
... will be unable to elevate her acromion. The dorsal scapular nerve innervates three muscles: rhomboideus major, rhomboideus minor, and the lower portion of levator scapulae. The rhomboids and trapezius retract the scapula toward the midline. So, if the dorsal scapular nerve is injured and rhomboids a ...
... will be unable to elevate her acromion. The dorsal scapular nerve innervates three muscles: rhomboideus major, rhomboideus minor, and the lower portion of levator scapulae. The rhomboids and trapezius retract the scapula toward the midline. So, if the dorsal scapular nerve is injured and rhomboids a ...
study questions for chapter four
... Define the concept of cellular polarity. * Discuss the structure and function of each of the following cellular structures: plasma membrane, nucleus, nucleolus, euchromatin, heterochromatin, polyribosome (polysomes), rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, golgi body, secretory ve ...
... Define the concept of cellular polarity. * Discuss the structure and function of each of the following cellular structures: plasma membrane, nucleus, nucleolus, euchromatin, heterochromatin, polyribosome (polysomes), rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, golgi body, secretory ve ...
Muscles and Fascia of Pelvic Wall
... The lateral pelvic walls: Have a bony framework formed by the hip bones, including the obturator foramen ; the obturator foramen is closed by the obturator membrane . Are covered and padded by the obturator internus muscles .Each obturator internus passes posteriorly from its origin within the ...
... The lateral pelvic walls: Have a bony framework formed by the hip bones, including the obturator foramen ; the obturator foramen is closed by the obturator membrane . Are covered and padded by the obturator internus muscles .Each obturator internus passes posteriorly from its origin within the ...
tot procedure
... • The needles are passed from the vaginal incision lateral to the urethra, following the posterior wall of the pubis, and crossing the fascia and the rectus muscle until the needle appears at the lower abdominal wall. • The sling is adjusted and the excess mesh cut of. ...
... • The needles are passed from the vaginal incision lateral to the urethra, following the posterior wall of the pubis, and crossing the fascia and the rectus muscle until the needle appears at the lower abdominal wall. • The sling is adjusted and the excess mesh cut of. ...
tot procedure
... • The needles are passed from the vaginal incision lateral to the urethra, following the posterior wall of the pubis, and crossing the fascia and the rectus muscle until the needle appears at the lower abdominal wall. • The sling is adjusted and the excess mesh cut of. ...
... • The needles are passed from the vaginal incision lateral to the urethra, following the posterior wall of the pubis, and crossing the fascia and the rectus muscle until the needle appears at the lower abdominal wall. • The sling is adjusted and the excess mesh cut of. ...
- Nottingham SCRUBS
... Name 2 muscles that attach to A - External anal sphincter, Bulbospongiosus muscle, superficial transverse perineal muscle, Anterior fibers of the levator ani, external urinary sphincter, deep transverse perineal muscle What nerve innervates B? – Dorsal nerve to clitoris ...
... Name 2 muscles that attach to A - External anal sphincter, Bulbospongiosus muscle, superficial transverse perineal muscle, Anterior fibers of the levator ani, external urinary sphincter, deep transverse perineal muscle What nerve innervates B? – Dorsal nerve to clitoris ...
THE MEDIAL COMPARTMENT OF THIGH
... POSTERIOR DIVISION Of OBTURATOR NERVE : • Emerges through obturator Externus and supplies it. ...
... POSTERIOR DIVISION Of OBTURATOR NERVE : • Emerges through obturator Externus and supplies it. ...
9.Axillary and Median Nerve2014-12-24 02:503.9 MB
... Hand looks flattened and “apelike”, and presents an inability to flex the three most radial digits when asked to make a fist. ...
... Hand looks flattened and “apelike”, and presents an inability to flex the three most radial digits when asked to make a fist. ...
Clinical Anatomy of the Female Pelvis - Figure B
... A small presacral subcompartment (see Table 1.1) is situated in front of the sacrum and coccyx. It is bordered by the caudal segments of the vertebral column dorsally and ventrolaterally, it is clearly demarcated by the pelvic parietal fascia (see Table 1.1) (Fig. 1.2), which is called presacral fas ...
... A small presacral subcompartment (see Table 1.1) is situated in front of the sacrum and coccyx. It is bordered by the caudal segments of the vertebral column dorsally and ventrolaterally, it is clearly demarcated by the pelvic parietal fascia (see Table 1.1) (Fig. 1.2), which is called presacral fas ...
Abdomen
... Between xiphoid process and pubic symphysis. the linea alba contains the umbilical ring. ...
... Between xiphoid process and pubic symphysis. the linea alba contains the umbilical ring. ...
Lower Limb 3: Gluteal Region
... iliac fosssa anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS): sartorius m. anterior inferior iliac spine (AIIS) : origin of rectus femoris m. posterior superior iliac spine posterior inferior iliac spine greater and lesser sciatic notch ...
... iliac fosssa anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS): sartorius m. anterior inferior iliac spine (AIIS) : origin of rectus femoris m. posterior superior iliac spine posterior inferior iliac spine greater and lesser sciatic notch ...
Anatomy of the Abdomen and pelvis
... • The superficial facia of the abdominal wall (subcutaneous tissue of the abdomen) is a layer of fatty connective tissue. It is usually a single layer similar to, and continuous with the superficial fascia throughout other regions of the body. However in the lower region of the anterior part of the ...
... • The superficial facia of the abdominal wall (subcutaneous tissue of the abdomen) is a layer of fatty connective tissue. It is usually a single layer similar to, and continuous with the superficial fascia throughout other regions of the body. However in the lower region of the anterior part of the ...
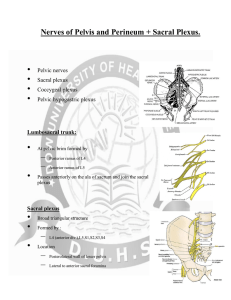
Sacral plexus and nerves of pelvis
... Sympathetic inhibits rectal peristalsis Stimulates contraction of internal genital organs producing ejaculation Parasympathetic stimulates contraction of rectum and bladder. Causes erection. ...
... Sympathetic inhibits rectal peristalsis Stimulates contraction of internal genital organs producing ejaculation Parasympathetic stimulates contraction of rectum and bladder. Causes erection. ...
File - Shabeer Dawar
... Formed by branches from med. Cut.nerve of thigh,the saphanous nerve and ant. Div. of obturator nerve. It supplies the overlying fascia lata &the neibouring skin. ...
... Formed by branches from med. Cut.nerve of thigh,the saphanous nerve and ant. Div. of obturator nerve. It supplies the overlying fascia lata &the neibouring skin. ...
Anatomy of anterior abdominal wall and hernia
... to cut the nerve supply to the rectus abdominis. Blood supply from the inferior epigastric artery also may be compromised. Inguinal incisions for repairing herniasmay injure the ilioinguinal nerve directly or it may be inadvertently included in the suture during closure of the incision. In such case ...
... to cut the nerve supply to the rectus abdominis. Blood supply from the inferior epigastric artery also may be compromised. Inguinal incisions for repairing herniasmay injure the ilioinguinal nerve directly or it may be inadvertently included in the suture during closure of the incision. In such case ...
To Elaborate Concept Of Sevani with The help Of Modern
... from Ayurveda, the aim of using these terms & functional unit of the body is cell. These also mentioned in it, that is meaning should cells came together to form tissue. These know everyone. To elaborate meaning of the tissue come together which have same work Ayuvedic terminology is necessary for i ...
... from Ayurveda, the aim of using these terms & functional unit of the body is cell. These also mentioned in it, that is meaning should cells came together to form tissue. These know everyone. To elaborate meaning of the tissue come together which have same work Ayuvedic terminology is necessary for i ...
Femoral Vein Anatomy
... medial border: adductor longus lateral border: sartorius apex: sartorius crossing the adductor longus muscle roof: skin subcutaneous tissue, the cribriform fascia and the fascia lata floor: adductor longus, adductor brevis, pectineus and iliopsoas muscles ...
... medial border: adductor longus lateral border: sartorius apex: sartorius crossing the adductor longus muscle roof: skin subcutaneous tissue, the cribriform fascia and the fascia lata floor: adductor longus, adductor brevis, pectineus and iliopsoas muscles ...
Document
... Mandibular nerve (CN V3) Auriculotemporal nerve Buccal nerve (inside cheek) Inferior alveolar n. Mental nerve (mental foramen) Lingual nerve (ant. 2/3 tongue) ...
... Mandibular nerve (CN V3) Auriculotemporal nerve Buccal nerve (inside cheek) Inferior alveolar n. Mental nerve (mental foramen) Lingual nerve (ant. 2/3 tongue) ...
Forearm and Hand [PPT]
... • Enters the palm by passing deep to flexor retinaculum in carpal tunnel • Breaks into medial and lateral branch • Lateral branch gives off recurrent branch that curve around distal border of FR to supply thenar muscles & 3 digital branches • Medial branch gives out 2 digital branches ...
... • Enters the palm by passing deep to flexor retinaculum in carpal tunnel • Breaks into medial and lateral branch • Lateral branch gives off recurrent branch that curve around distal border of FR to supply thenar muscles & 3 digital branches • Medial branch gives out 2 digital branches ...
ANATOMY OF THE FEMALE BONY PELVIS & FETAL SKULL
... Ischial spines are not prominent Subpubic arch accept 2 fingers Intertuberous diameter accept 4 knuckles on pelvic exam ...
... Ischial spines are not prominent Subpubic arch accept 2 fingers Intertuberous diameter accept 4 knuckles on pelvic exam ...
L6-pelvis & sacrum
... withstand the forces of the powerful muscles of locomotion and posture. Its secondary functions are to contain and protect the pelvic and abdominopelvic viscera (inferior parts of the urinary ,digestive tracts & internal reproductive organs); provide attachment for external reproductive organs and ...
... withstand the forces of the powerful muscles of locomotion and posture. Its secondary functions are to contain and protect the pelvic and abdominopelvic viscera (inferior parts of the urinary ,digestive tracts & internal reproductive organs); provide attachment for external reproductive organs and ...
Pelvic cavity and diaphragm 2013
... obturator internus, coccygeus, piriformis and levator ani are covered by fascia that is continuous superior with the transversalis and iliac fascia. Between the pelvic organs, the pelvic fascia mostly comprises a loose meshwork of connective tissue. However, it is condensed anterior to the rectum to ...
... obturator internus, coccygeus, piriformis and levator ani are covered by fascia that is continuous superior with the transversalis and iliac fascia. Between the pelvic organs, the pelvic fascia mostly comprises a loose meshwork of connective tissue. However, it is condensed anterior to the rectum to ...
Pelvic fractures
... internal pudendal arteries. The greater sciatic foramen is a common exit pathway for many pelvic vessels and any fracture involving this area incurs a higher risk of bleeding. The superior gluteal artery is at risk of laceration from the sharp fascia of the piriformis muscle as it enters the greater ...
... internal pudendal arteries. The greater sciatic foramen is a common exit pathway for many pelvic vessels and any fracture involving this area incurs a higher risk of bleeding. The superior gluteal artery is at risk of laceration from the sharp fascia of the piriformis muscle as it enters the greater ...
Vulva

The vulva (from the Latin vulva, plural vulvae, see etymology) consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals.The vulva has many major and minor anatomical structures, including the labia majora, mons pubis, labia minora, clitoris, bulb of vestibule, vulval vestibule, greater and lesser vestibular glands, external urethral orifice and the opening of the vagina (introitus). Its development occurs during several phases, chiefly during the fetal and pubertal periods of time. As the outer portal of the human uterus or womb, it protects its opening by a ""double door"": the labia majora (large lips) and the labia minora (small lips). The vagina is a self-cleaning organ, sustaining healthy microbial flora that flow from the inside out; the vulva needs only simple washing to assure good vulvovaginal health, without recourse to any internal cleansing.The vulva has a sexual function; these external organs are richly innervated and provide pleasure when properly stimulated. In various branches of art, the vulva has been depicted as the organ that has the power both to ""give life"" (often associated with the womb), and to give sexual pleasure to humankind.The vulva also contains the opening of the female urethra, but apart from this has little relevance to the function of urination.

















![Forearm and Hand [PPT]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000953850_1-fbf4b9850ae3ed83f7b082693c84a32e-300x300.png)



