* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sacral plexus and nerves of pelvis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
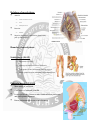
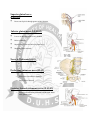
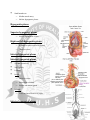
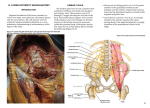
Nerves of Pelvis and Perineum + Sacral Plexus. • • • • Pelvic nerves Sacral plexus Coccygeal plexus Pelvic hypogastric plexus Lumbosacral trunk: • • At pelvic brim formed by – – Posterior ramus of L4 Anterior ramus of L5 Passes anteriorly on the ala of sacrum and join the sacral plexus Sacral plexus • • • Broad triangular structure Formed by : – L4 (anterior div.),L5,S1,S2,S3,S4 Location – – Posterolateral wall of lesser pelvis Lateral to anterior sacral foramina Relations of sacral plexus • • • Anterior – – – Lateral sacral arteries and veins Ureter Parietal pelvic fascia Posterior – Piriformis Superior gluteal artery and inferior gluteal artery pass up and below S1 Branches of sacral plexus Sciatic nerve (L4-S3) – – – – Largest nerve of body Converge on anterior surface of piriformis Enter greater sciatic foramen and pass out of pelvis Supply posterior aspect of thigh and entire leg and foot Pudendal nerve (S2,S3,S4) • • • • Main nerve of perineum Chief nerve of external genitalia Leaves pelvis thru Greater sciatic foramen below piriformis and sacrospinous ligament Enters perineum thru lesser sciatic foramen Superior gluteal nerve (L4,S1,S2) • Passes out of pelvis through greater sciatic foramen Inferior gluteal nerve (L5,S1,S2) • • • • Leaves out through greater sciatic foramen Below piriformis Superficial to sciatic and inferior gluteal artery Supplies gluteus maximus Nerve to Piriformis(S1,S2) Perforating cutaneous nerve(S2,S3) – – Pierces the sacrotuberous ligament Supply skin of buttock Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve (S1,S2,S3) – Passes backward below piriformis behind sciatic nerve enter gluteal region Nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus (L4,L5,S1) Leaves pelvis in front of sciatic nerve Nerve to obturator internus and superior gemellus (L5,S1,S2) Leaves pelvis lateral to pudendal vessels below piriformis Nerve to levator ani and coccygeus (S3,S4) Pelvic splanchnic nerves (parasympathetic) • • • • S2, S3, S4. S3 contributes the most in making the pelvic nerves Pass into the inferior hypogastric plexus and mix with sympathetic nerves to supply pelvic viscera. Distal colon Coccygeal plexus: • • Small network of nerve fibres Formed by • • • • • • • • – S4,S5,Coccygeal nerves. Location – Pelvic surface of coccygeus and levator ani Supplies – – – Coccygeus Levator ani Sacrococcygeal joint Annococcygeal branch Pelvic autonomic nerves Sacral sympathetic trunks Periarterial plexus – – – Ovarian Superior rectal Internal iliac arteries Hypogastric plexuses Pelvic splanchnic nerves Sacral sympathetic trunk • • • • • Smaller than lumbar Has 4 ganglia Descends on pelvic surface of sacrum on medial margin of anterior sacral foramen Converge in front of coccyx forming ganglia impar Posterior to rectum • Send branches to – – Median sacral artery Inferior hypogastric plexus Hypogastric plexus Superior hypogastric plexus – Inferior to bifurcation of aorta Right and left hypogastric plexus – – Descends on anterior surface of sacrum Lateral to rectum Inferior hypogastric plexus Inferior hypogastric plexus • • • • • 5cm anteroposteriorly 2cm vertically Location In male – – – Lateral to rectum Inferolateral to bladder Prostate and seminal glands In female – Cervix and lateral fornices of vagina Inferior hypogastric plexus Contributions to the plexus include: • • • Continuation of the hypogastric plexus on either side, in the form of the hypogastric nerve. Sacral splanchnic nerves, which emerge from the sympathetic trunk. Pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2, S3, S4) parasympathetic efferent fibers to the plexus. Functions • • • • Sympathetic inhibits rectal peristalsis Stimulates contraction of internal genital organs producing ejaculation Parasympathetic stimulates contraction of rectum and bladder. Causes erection. Injury to pelvic nerves • • During childbirth mother’s sacral plexus is compressed producing pain Obturator nerve is vulnerable to injury during surgery of removal of cancerous lymph nodes from lateral pelvic wall Obturator nerve (L2-L4) • • • • • • Branch of lumbar plexus Arises in abdomen comes down to pelvis and enter the obturator canal Lie highest in obturator foramen Divides into anterior and posterior parts Supply medial thigh muscle Gives no branch in pelvis