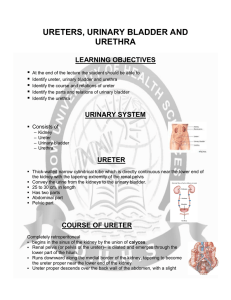
Ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
... Tube that connects the urinary bladder to the genitals for removal out of the body. In males, Urethra travels through the penis, and carries semen as well as urine. In females, the urethra is shorter and emerges above the vaginal opening. ...
... Tube that connects the urinary bladder to the genitals for removal out of the body. In males, Urethra travels through the penis, and carries semen as well as urine. In females, the urethra is shorter and emerges above the vaginal opening. ...
LAC.SYSTEM I-ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, CONGENITAL
... Situated near the medial end of each eyelid. Face slightly posterior in normal condition. slightly evert the medial end of the eyelid and the punctum will become visible. *Ampula: (Vertical canaliculus) The most proximal portion of the canaculus, ...
... Situated near the medial end of each eyelid. Face slightly posterior in normal condition. slightly evert the medial end of the eyelid and the punctum will become visible. *Ampula: (Vertical canaliculus) The most proximal portion of the canaculus, ...
anterior abdominal wall and inguinal area
... VIII. hernias - the protrusion of an organ, part of an organ, or other tissue through the wall of a cavity, which normally contains it A. inguinal hernias - located in the inguinal region; exits the body at the superficial inguinal ring 1. indirect inguinal hernia a. omentum or intestine enters the ...
... VIII. hernias - the protrusion of an organ, part of an organ, or other tissue through the wall of a cavity, which normally contains it A. inguinal hernias - located in the inguinal region; exits the body at the superficial inguinal ring 1. indirect inguinal hernia a. omentum or intestine enters the ...
The Cranial Nerves
... Greater petrosal nerve岩大神经: GVE fibers pass to pterygopalatine ganglion 翼腭神经节 and there relayed through the zygomatic and lacrimal nerves to lacrimal gland ...
... Greater petrosal nerve岩大神经: GVE fibers pass to pterygopalatine ganglion 翼腭神经节 and there relayed through the zygomatic and lacrimal nerves to lacrimal gland ...
1. A person receives a shallow knife wound just behind the
... superior belly of the omohyoid muscle. The carotid vessels and carotid sheath can be found in this triangle. The subclavian triangle is the same as the omoclavicular triangle. It is found in the posterior triangle of the neck. This triangle is bounded superiorly by the inferior belly of the omohyoi ...
... superior belly of the omohyoid muscle. The carotid vessels and carotid sheath can be found in this triangle. The subclavian triangle is the same as the omoclavicular triangle. It is found in the posterior triangle of the neck. This triangle is bounded superiorly by the inferior belly of the omohyoi ...
The Cranial Nerves
... Greater petrosal nerve岩大神经: GVE fibers pass to pterygopalatine ganglion 翼腭神经节 and there relayed through the zygomatic and lacrimal nerves to lacrimal gland ...
... Greater petrosal nerve岩大神经: GVE fibers pass to pterygopalatine ganglion 翼腭神经节 and there relayed through the zygomatic and lacrimal nerves to lacrimal gland ...
Pelvis - Lectures - gblnetto
... ischium. The two ligaments convert the greater and lesser sciatic notches into foramina, the greater and lesser sciatic foramina. The obturator internus muscle arises from the pelvis surface of the obturator membrane and the adjoining part of the hip bone. The muscle fibers converge to a tendon, whi ...
... ischium. The two ligaments convert the greater and lesser sciatic notches into foramina, the greater and lesser sciatic foramina. The obturator internus muscle arises from the pelvis surface of the obturator membrane and the adjoining part of the hip bone. The muscle fibers converge to a tendon, whi ...
Review of Pelvic Anatomy
... • The puborectalis forms a U-shaped sling, holding the anorectal anteriorly, blending with the deep fibres of the external anal sphincter • Anococcygeal raphe lies between the coccyx and the margin of the anus • Nerve supply, inferior rectal nerve and perineal branch fourth sacral Last 1984 ...
... • The puborectalis forms a U-shaped sling, holding the anorectal anteriorly, blending with the deep fibres of the external anal sphincter • Anococcygeal raphe lies between the coccyx and the margin of the anus • Nerve supply, inferior rectal nerve and perineal branch fourth sacral Last 1984 ...
Anterior abdominal wall and hernias (2)
... Abdominal Wall The posterior surface of the anterolateral abdominal wall is covered by fascia transversalis. Five umbilical peritoneal folds are seen. 1- Median umbilical fold: Extends from apex of urinary bladder to umbilicus, (obliterated urachus). 2- Two medial umbilical folds: Obliterated distal ...
... Abdominal Wall The posterior surface of the anterolateral abdominal wall is covered by fascia transversalis. Five umbilical peritoneal folds are seen. 1- Median umbilical fold: Extends from apex of urinary bladder to umbilicus, (obliterated urachus). 2- Two medial umbilical folds: Obliterated distal ...
Anterolateral Abdominal Wall And
... Abdominal Wall The posterior surface of the anterolateral abdominal wall is covered by fascia transversalis. Five umbilical peritoneal folds are seen. 1- Median umbilical fold: Extends from apex of urinary bladder to umbilicus, (obliterated urachus). 2- Two medial umbilical folds: Obliterated distal ...
... Abdominal Wall The posterior surface of the anterolateral abdominal wall is covered by fascia transversalis. Five umbilical peritoneal folds are seen. 1- Median umbilical fold: Extends from apex of urinary bladder to umbilicus, (obliterated urachus). 2- Two medial umbilical folds: Obliterated distal ...
Gluteal - Faculty
... Sciatic nerve (L4 - S3) Posterior thigh and all leg and foot compartments Tibial nerve (L4 - S3) Posterior leg and plantar foot Common fibular nerve (L4 - S2) Lateral/anterior leg and dorsal foot Pudendal nerve (S2 - S4) Pelvic perineum Identify the nerves from the entire lumbrosacral plexus (Nerve ...
... Sciatic nerve (L4 - S3) Posterior thigh and all leg and foot compartments Tibial nerve (L4 - S3) Posterior leg and plantar foot Common fibular nerve (L4 - S2) Lateral/anterior leg and dorsal foot Pudendal nerve (S2 - S4) Pelvic perineum Identify the nerves from the entire lumbrosacral plexus (Nerve ...
Anatomy Part
... The secondary functions: 1. Contain and protect the pelvic viscera (parts of the urinary tracts and the internal reproductive organs) 2. Protect inferior abdominal viscera (intestines), while permitting passage of their terminal parts (and, in females, a full-term fetus) via the perineum 3. Provide ...
... The secondary functions: 1. Contain and protect the pelvic viscera (parts of the urinary tracts and the internal reproductive organs) 2. Protect inferior abdominal viscera (intestines), while permitting passage of their terminal parts (and, in females, a full-term fetus) via the perineum 3. Provide ...
Surgical Anatomy of Urogenital Diaphragm and Course
... To report the surgical anatomy of the muscles of the urogenital diaphragm and the pattern of its vessels in the classic exstrophy bladder and incontinent epispadias. A total of 11 patients, 9 with unoperated classic exstrophy and 2 with incontinent epispadias, who were ⬎5 years old at presentation, ...
... To report the surgical anatomy of the muscles of the urogenital diaphragm and the pattern of its vessels in the classic exstrophy bladder and incontinent epispadias. A total of 11 patients, 9 with unoperated classic exstrophy and 2 with incontinent epispadias, who were ⬎5 years old at presentation, ...
7-Pelvis nd Sacrum2017-01-17 10:393.2 MB
... These are present on the anterior surface of the sacrum (which forms the posterior surface of the bony pelvis). Through these foramina pass the anterior rami of the sacral spinal nerves. Four on each side. ...
... These are present on the anterior surface of the sacrum (which forms the posterior surface of the bony pelvis). Through these foramina pass the anterior rami of the sacral spinal nerves. Four on each side. ...
19-Gluteal region2009-05-16 11:384.9 MB
... Course: passes through GSF, above piriformis, then divides into superficial branch between gluteus maximus & medius and deep branch between gluteus medius & minimus INFERIOR GLUTEAL Course: ...
... Course: passes through GSF, above piriformis, then divides into superficial branch between gluteus maximus & medius and deep branch between gluteus medius & minimus INFERIOR GLUTEAL Course: ...
15-Gluteal Region and Back of Thigh2017-01
... The four perforating branches of the profunda femoris artery (deep artery of thigh) provide a rich blood supply to this compartment. The profunda femoris vein drains the greater part of the blood from the compartment. ...
... The four perforating branches of the profunda femoris artery (deep artery of thigh) provide a rich blood supply to this compartment. The profunda femoris vein drains the greater part of the blood from the compartment. ...
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
... Lies below the inguinal ligament Divided into two groups; horizontal and vertical. A-The horizontal group lies below and parallel to the inguinal ligament. It divides into medial and lateral groups ...
... Lies below the inguinal ligament Divided into two groups; horizontal and vertical. A-The horizontal group lies below and parallel to the inguinal ligament. It divides into medial and lateral groups ...
Study Guide of the Facial Nerve Name the nerve which sends a
... At the end of the acoustic meatus the facial nerve enters the facial canal which descends to reach the stylomastoid foramen. The genicular ganglion communicates with the pterygoid ganglion through the greater petrosal nerve of facial nerve. The cervical branch of the facial nerve communicates with t ...
... At the end of the acoustic meatus the facial nerve enters the facial canal which descends to reach the stylomastoid foramen. The genicular ganglion communicates with the pterygoid ganglion through the greater petrosal nerve of facial nerve. The cervical branch of the facial nerve communicates with t ...
OLFACTORY AND OPTIC NERVE - part 2
... GVE fibers: arise from inferior salivatory nucleus and ralyed in otic ganglion, the postganglionic fibers supply parotid gland SVA fibers: arise from the cells of inferior ganglion, the central processes of these cells terminate in nucleus of solitary tract, the peripheral processes supply the taste ...
... GVE fibers: arise from inferior salivatory nucleus and ralyed in otic ganglion, the postganglionic fibers supply parotid gland SVA fibers: arise from the cells of inferior ganglion, the central processes of these cells terminate in nucleus of solitary tract, the peripheral processes supply the taste ...
Summary of Function of Cranial Nerves
... and go to the extrinsic eye muscles Functions in raising the eyelid, directing the eyeball, constricting the iris, and ...
... and go to the extrinsic eye muscles Functions in raising the eyelid, directing the eyeball, constricting the iris, and ...
Location of Suprarenal Glands
... promotes excretion of H+ in the urine; this removal of acids from the body can help prevent acidosis ...
... promotes excretion of H+ in the urine; this removal of acids from the body can help prevent acidosis ...
Gray`s Anatomy for Students , Third Edition
... Two levator ani muscles attach peripherally to the pelvic walls and join each other at the midline by a connective tissue raphe. Together they are the largest components of the bowl or funnelshaped structure known as the pelvic diaphragm, which is completed posteriorly by the coccygeus muscles. Th ...
... Two levator ani muscles attach peripherally to the pelvic walls and join each other at the midline by a connective tissue raphe. Together they are the largest components of the bowl or funnelshaped structure known as the pelvic diaphragm, which is completed posteriorly by the coccygeus muscles. Th ...
SALIVARY GLANDS
... facial artery passes behind the posterior digastric muscle and ascends vertically to lie posterior to the submandibular gland or is interposed between the deep and superficial lobes facial vein is found between the deep and superficial lobes at the lateral extent of the capsule. May also be supe ...
... facial artery passes behind the posterior digastric muscle and ascends vertically to lie posterior to the submandibular gland or is interposed between the deep and superficial lobes facial vein is found between the deep and superficial lobes at the lateral extent of the capsule. May also be supe ...
1. The entry of bacteria through which space could lead to an
... parasympathetic fibers that will eventually travel to the otic ganglion. The tympanic nerve lies on the promontory and creates the tympanic plexus, which gives rise to the lesser petrosal nerve. Given the clinical presentation, the patient must have an infection in the tympanic nerve, tympanic plexu ...
... parasympathetic fibers that will eventually travel to the otic ganglion. The tympanic nerve lies on the promontory and creates the tympanic plexus, which gives rise to the lesser petrosal nerve. Given the clinical presentation, the patient must have an infection in the tympanic nerve, tympanic plexu ...
Vulva

The vulva (from the Latin vulva, plural vulvae, see etymology) consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals.The vulva has many major and minor anatomical structures, including the labia majora, mons pubis, labia minora, clitoris, bulb of vestibule, vulval vestibule, greater and lesser vestibular glands, external urethral orifice and the opening of the vagina (introitus). Its development occurs during several phases, chiefly during the fetal and pubertal periods of time. As the outer portal of the human uterus or womb, it protects its opening by a ""double door"": the labia majora (large lips) and the labia minora (small lips). The vagina is a self-cleaning organ, sustaining healthy microbial flora that flow from the inside out; the vulva needs only simple washing to assure good vulvovaginal health, without recourse to any internal cleansing.The vulva has a sexual function; these external organs are richly innervated and provide pleasure when properly stimulated. In various branches of art, the vulva has been depicted as the organ that has the power both to ""give life"" (often associated with the womb), and to give sexual pleasure to humankind.The vulva also contains the opening of the female urethra, but apart from this has little relevance to the function of urination.