What is Cytogenetics?
... • Loss of a segment of chromosome • Invariably, but not always, results in the loss of important genetic material • In this example the area in the blue brackets is not present (deleted) in its pair designated by the red arrow= 46,XXdel(1)(q24q31) • Female with a deletion of chromosome 1 on the long ...
... • Loss of a segment of chromosome • Invariably, but not always, results in the loss of important genetic material • In this example the area in the blue brackets is not present (deleted) in its pair designated by the red arrow= 46,XXdel(1)(q24q31) • Female with a deletion of chromosome 1 on the long ...
arial: 16 bold, menggunakan huruf capital, line spacing : single
... As yet, laboratory staff and clinician have no guide in the reporting of this incidental finding. As this finding can raise ethical and legal concerns, it is essential to establish a guideline for laboratories and clinician in reporting and disclosing this unexpected result. On one hand, clinicians ...
... As yet, laboratory staff and clinician have no guide in the reporting of this incidental finding. As this finding can raise ethical and legal concerns, it is essential to establish a guideline for laboratories and clinician in reporting and disclosing this unexpected result. On one hand, clinicians ...
Gene Duplication, Gene Conversion and the Evolution of
... Nonrecombining chromosomes, such as the Y, are expected to degenerate over time due to reduced efficacy of natural selection compared to chromosomes that recombine. However, gene duplication, coupled with gene conversion between duplicate pairs, can potentially counteract forces of evolutionary deca ...
... Nonrecombining chromosomes, such as the Y, are expected to degenerate over time due to reduced efficacy of natural selection compared to chromosomes that recombine. However, gene duplication, coupled with gene conversion between duplicate pairs, can potentially counteract forces of evolutionary deca ...
Section 1
... reproductive cells join in a process known as fertilization to produce a new cell. In peas, this new cell develops into a tiny embryo encased within a seed. ...
... reproductive cells join in a process known as fertilization to produce a new cell. In peas, this new cell develops into a tiny embryo encased within a seed. ...
Document
... Mutations in the lac repressor (lacI): Also used partial diploid E. coli F’ strains, containing lac operon genes with normal promoters and normal operators. ...
... Mutations in the lac repressor (lacI): Also used partial diploid E. coli F’ strains, containing lac operon genes with normal promoters and normal operators. ...
Professor Anthony Monaco - AWARES, the All Wales Autism Resource
... •Evidence from twin studies suggests a monozygotic (MZ) to dizygotic (DZ) concordance rate of 60%:0% (Bailey et al., 1995) •Heritability estimates of >90% •The rate among siblings of an autistic proband is ~3% •Autism is one of the most strongly genetic of the childhood-onset psychiatric disorders b ...
... •Evidence from twin studies suggests a monozygotic (MZ) to dizygotic (DZ) concordance rate of 60%:0% (Bailey et al., 1995) •Heritability estimates of >90% •The rate among siblings of an autistic proband is ~3% •Autism is one of the most strongly genetic of the childhood-onset psychiatric disorders b ...
Package `TCGAbiolinks`
... query <- GDCquery(project = "TCGA-COAD", data.category = "Clinical", barcode = c("TCGA-RU-A8FL","TCGA-AA-3972")) GDCdownload(query) clinical <- GDCprepare_clinic(query,"patient") clinical.drug <- GDCprepare_clinic(query,"drug") clinical.radiation <- GDCprepare_clinic(query,"radiation") clinical.admi ...
... query <- GDCquery(project = "TCGA-COAD", data.category = "Clinical", barcode = c("TCGA-RU-A8FL","TCGA-AA-3972")) GDCdownload(query) clinical <- GDCprepare_clinic(query,"patient") clinical.drug <- GDCprepare_clinic(query,"drug") clinical.radiation <- GDCprepare_clinic(query,"radiation") clinical.admi ...
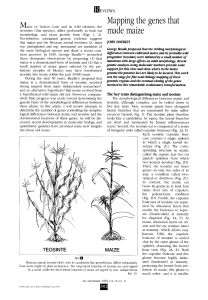
Mapping the genes that made maize
... maize-teosinte hybrids and reported that two traits were each under the control of a single major locus. He named Tr as the gene controlling the switch from the two-ranked ears of teosinte to the four-ranked ears of maize and pd as the gene converting the single spikelets of teosinte to the paired s ...
... maize-teosinte hybrids and reported that two traits were each under the control of a single major locus. He named Tr as the gene controlling the switch from the two-ranked ears of teosinte to the four-ranked ears of maize and pd as the gene converting the single spikelets of teosinte to the paired s ...
Chapter 4: EXTENSIONS OF MENDELIAN INHERITANCE
... are affected by a single gene that is found in two different alleles. In these cases, one allele is dominant over the other. This type of inheritance is sometimes called simple Mendelian inheritance because the observed ratios in the offspring readily obey Mendel’s laws. For example, when two differ ...
... are affected by a single gene that is found in two different alleles. In these cases, one allele is dominant over the other. This type of inheritance is sometimes called simple Mendelian inheritance because the observed ratios in the offspring readily obey Mendel’s laws. For example, when two differ ...
1903. - Sutton, Walter S. The chromosomes in heredity. Biological
... a number of able investigators. Further attention has already been called to the theoretical aspects of the subject in a brief communication by Professor E. B. Wilson.3 The present paper is devoted to a more detailed discussion of these aspects, the speculative character of which may be justified by ...
... a number of able investigators. Further attention has already been called to the theoretical aspects of the subject in a brief communication by Professor E. B. Wilson.3 The present paper is devoted to a more detailed discussion of these aspects, the speculative character of which may be justified by ...
Induced point mutations in the phytoene synthase 1 gene cause
... Tomato fruit are characterised by their red colour. Customer awareness that the red colour is associated with promoting human health is increasing (Fraser et al. 2009). Recent studies have shown the healthpromoting role of tomato consumption in preventing various cancers, cardio-vascular diseases an ...
... Tomato fruit are characterised by their red colour. Customer awareness that the red colour is associated with promoting human health is increasing (Fraser et al. 2009). Recent studies have shown the healthpromoting role of tomato consumption in preventing various cancers, cardio-vascular diseases an ...
Candidate gene resequencing to identify rare, pedigree
... Background: The Long Life Family Study (LLFS) is an international study to identify the genetic components of various healthy aging phenotypes. We hypothesized that pedigree-specific rare variants at longevity-associated genes could have a similar functional impact on healthy phenotypes. Methods: We ...
... Background: The Long Life Family Study (LLFS) is an international study to identify the genetic components of various healthy aging phenotypes. We hypothesized that pedigree-specific rare variants at longevity-associated genes could have a similar functional impact on healthy phenotypes. Methods: We ...
MS26/CYP704B is required for anther and pollen wall
... respectively. Comparison of the predicted amino acid sequences showed that the three homeologs are highly similar with 98–99% amino acid identity (Fig 1). The wheat Ms26/CYP704B proteins also show high similarity (96–97% identity) to putative Ms26/CYP704B from barley (BAK08270), while identity with ...
... respectively. Comparison of the predicted amino acid sequences showed that the three homeologs are highly similar with 98–99% amino acid identity (Fig 1). The wheat Ms26/CYP704B proteins also show high similarity (96–97% identity) to putative Ms26/CYP704B from barley (BAK08270), while identity with ...
Genetic quality and sexual selection: an integrated framework for
... Why are females so choosy when it comes to mating? This question has puzzled and marveled evolutionary and behavioral ecologists for decades. In mating systems in which males provide direct benefits to the female or her offspring, such as food or shelter, the answer seems straightforward — females s ...
... Why are females so choosy when it comes to mating? This question has puzzled and marveled evolutionary and behavioral ecologists for decades. In mating systems in which males provide direct benefits to the female or her offspring, such as food or shelter, the answer seems straightforward — females s ...
Document
... When will p̂ be on the interval between zero and one? In other words, when will there be a genetic polymorphism? (Show on the board.) step 1. Q: when is ...
... When will p̂ be on the interval between zero and one? In other words, when will there be a genetic polymorphism? (Show on the board.) step 1. Q: when is ...
Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium Vocabulary and Calculations Review
... dominant and one recessive for a particular trait. Let’s say our alleles are “A” and “a”. In this equation “p” represents the frequency of “A” (the dominant allele) expressed as a decimal in the range of 0-1. (For example: 0.4 means that 40% of the alleles found in the population are “A). “q” repres ...
... dominant and one recessive for a particular trait. Let’s say our alleles are “A” and “a”. In this equation “p” represents the frequency of “A” (the dominant allele) expressed as a decimal in the range of 0-1. (For example: 0.4 means that 40% of the alleles found in the population are “A). “q” repres ...
Insights into three whole-genome duplications gleaned
... closely related to the P. aurelia species group. P. caudatum shares only the most ancient of the three WGDs with the aurelia complex. We found that P. caudatum maintains twice as many paralogs from this early event as the P. aurelia species, suggesting that post-WGD gene retention is influenced by s ...
... closely related to the P. aurelia species group. P. caudatum shares only the most ancient of the three WGDs with the aurelia complex. We found that P. caudatum maintains twice as many paralogs from this early event as the P. aurelia species, suggesting that post-WGD gene retention is influenced by s ...
Interactions of Mitochondrial and Nuclear Genes
... expression is affected by the presence of nuclear fertility restorers and the information gained about these nuclear genes through recent map-based cloning efforts. We also describe the evidence that mitochondrial gene expression can affect the function of nuclear gene products that control floral d ...
... expression is affected by the presence of nuclear fertility restorers and the information gained about these nuclear genes through recent map-based cloning efforts. We also describe the evidence that mitochondrial gene expression can affect the function of nuclear gene products that control floral d ...
Centipede Hox genes - Development
... difficult to infer the full course of the evolution of these genes in the arthropods. Besides the importance of the myriapods’ phylogenetic position, they also have an interesting body plan. As noted, the myriapod body is divided into two tagmata, the head and trunk. The long trunk is typically fair ...
... difficult to infer the full course of the evolution of these genes in the arthropods. Besides the importance of the myriapods’ phylogenetic position, they also have an interesting body plan. As noted, the myriapod body is divided into two tagmata, the head and trunk. The long trunk is typically fair ...
Hox Genes: Let`s Work Together
... Sense and anti-sense long non-coding RNAs are detected from overlapping region of the BX-C (Bender, 2008; Stark et al., 2008; Tyler et al., 2008). The sense transcript is named as mir-iab-4 and antisense transcript is named as mir-iab-8. Further analysis of these two long transcripts showed that, th ...
... Sense and anti-sense long non-coding RNAs are detected from overlapping region of the BX-C (Bender, 2008; Stark et al., 2008; Tyler et al., 2008). The sense transcript is named as mir-iab-4 and antisense transcript is named as mir-iab-8. Further analysis of these two long transcripts showed that, th ...
View PDF
... the plant’s male reproductive cells, called sperm. Similarly, Mendel knew that the female portion of each flower produces reproductive cells called eggs. During sexual reproduction, male and female reproductive cells join in a process known as fertilization to produce a new cell. In peas, this new ce ...
... the plant’s male reproductive cells, called sperm. Similarly, Mendel knew that the female portion of each flower produces reproductive cells called eggs. During sexual reproduction, male and female reproductive cells join in a process known as fertilization to produce a new cell. In peas, this new ce ...
View poster
... genome sequencing (WGS) or targeted enrichment using exome or gene panels. Copy number variation (CNV) of genomic segments is a large category of structural variation and has been implicated in many Mendelian diseases and complex traits. The impact of CNVs on gene expression is not limited to only t ...
... genome sequencing (WGS) or targeted enrichment using exome or gene panels. Copy number variation (CNV) of genomic segments is a large category of structural variation and has been implicated in many Mendelian diseases and complex traits. The impact of CNVs on gene expression is not limited to only t ...
COP9: A New Genetic Locus lnvolved in Light
... Figure 2 shows cotyledon cross-sections of mutant and wildtype seedlings growing in the dark and light. The cotyledon expansion in dark-grown cop9 seedlings (Figure 2A) is similar to that of their light-grown siblings (Figure 28) and is significantly greater than that of dark-grown wild-type (Figure ...
... Figure 2 shows cotyledon cross-sections of mutant and wildtype seedlings growing in the dark and light. The cotyledon expansion in dark-grown cop9 seedlings (Figure 2A) is similar to that of their light-grown siblings (Figure 28) and is significantly greater than that of dark-grown wild-type (Figure ...