IB Biology--Chromosome Review Activity
... 4. Look @ the visuals from the BioNinja site and describe what appears to be the basic difference between active and less active genes? What is preventing the less active genes from ...
... 4. Look @ the visuals from the BioNinja site and describe what appears to be the basic difference between active and less active genes? What is preventing the less active genes from ...
Genetics Unit 2 – Transmission Genetics
... 1. Organisms inherit ____________________, one from each parent. 2. Some traits are _______________ and some are ________________. 3. Recessive traits show only when no ____________________ are present. ...
... 1. Organisms inherit ____________________, one from each parent. 2. Some traits are _______________ and some are ________________. 3. Recessive traits show only when no ____________________ are present. ...
Genit 1
... Genetics is the study of individual genes and their effect on the carrier and it controls health, growth, and disease. We will talk later about Genomics ( study of the human genome) ...
... Genetics is the study of individual genes and their effect on the carrier and it controls health, growth, and disease. We will talk later about Genomics ( study of the human genome) ...
Ch. 19 – Eukaryotic Genomes
... Extra copies of genes (like those for RNA) can be beneficial in the embryo Conversely it is also observed in cancer cells Transposons: regions of DNA that can move from one location to another…position effects this impact. 10% of human genome, 50% in some plants Retrotransposons : move with help of ...
... Extra copies of genes (like those for RNA) can be beneficial in the embryo Conversely it is also observed in cancer cells Transposons: regions of DNA that can move from one location to another…position effects this impact. 10% of human genome, 50% in some plants Retrotransposons : move with help of ...
Chapter 7 Note taking Form
... Widow’s peak Mendel’s rules of inheritance apply to autosomal genetic ________________________. An organism's ___________________________ represents the two alleles inherited for a given trait such as CC or cc. For an organism to be a ____________________, the genotype must include one copy of a r ...
... Widow’s peak Mendel’s rules of inheritance apply to autosomal genetic ________________________. An organism's ___________________________ represents the two alleles inherited for a given trait such as CC or cc. For an organism to be a ____________________, the genotype must include one copy of a r ...
Human Inheritance
... into the DNA of another organism. • Genetic engineering can produce medicines and improve crops. • Genetically engineered bacteria produce human insulin for diabetics. • Genetically engineered crops can resist pests or survive in cold temperatures or poor soil. ...
... into the DNA of another organism. • Genetic engineering can produce medicines and improve crops. • Genetically engineered bacteria produce human insulin for diabetics. • Genetically engineered crops can resist pests or survive in cold temperatures or poor soil. ...
Name Date Class
... 1. ________________ The body cells of humans contain 46 pairs of chromosomes. 2. ________________ A widow’s peak is a trait controlled by many genes. 3. ________________ In the case of sex-linked traits, only females can be carriers. 4. ________________ In females, a recessive allele on the X chromo ...
... 1. ________________ The body cells of humans contain 46 pairs of chromosomes. 2. ________________ A widow’s peak is a trait controlled by many genes. 3. ________________ In the case of sex-linked traits, only females can be carriers. 4. ________________ In females, a recessive allele on the X chromo ...
Gene Therapy: “Mr. Fix-it” for Cells
... Genes and Diseases • “faulty” or missing genes cause disease • Genetic conditions used to be considered a “life sentence” Is this still the case?? ...
... Genes and Diseases • “faulty” or missing genes cause disease • Genetic conditions used to be considered a “life sentence” Is this still the case?? ...
Implications of Biology
... • Chimp to Human is not so certain – Chimpanzees and humans are 95% related, in terms of common DNA – All human chromosomes, except the Y, first appeared (but were not fixed) about 2,000,000 years ago— during the time of Homo erectus, before Humans and Neanderthals split (600,000 years ago) ...
... • Chimp to Human is not so certain – Chimpanzees and humans are 95% related, in terms of common DNA – All human chromosomes, except the Y, first appeared (but were not fixed) about 2,000,000 years ago— during the time of Homo erectus, before Humans and Neanderthals split (600,000 years ago) ...
14-3 Human Molecular Genetics
... is replaced by a normal, working gene. - This way the body can make the correct protein or enzyme it needs, which eliminates the cause of the disorder. ...
... is replaced by a normal, working gene. - This way the body can make the correct protein or enzyme it needs, which eliminates the cause of the disorder. ...
GENETICS 310-PRINCIPLES OF HEREDITY
... MY OBJECTIVE: You will appreciate and be able to convey to others the many ways genetics impacts our daily lives. TEXT: (recommended) Human Genetics by Ricki Lewis (5th-10th) editions all OK EXTRAS: Lecture notes, study guides (learning objectives) and PDF versions of old tests with and without answ ...
... MY OBJECTIVE: You will appreciate and be able to convey to others the many ways genetics impacts our daily lives. TEXT: (recommended) Human Genetics by Ricki Lewis (5th-10th) editions all OK EXTRAS: Lecture notes, study guides (learning objectives) and PDF versions of old tests with and without answ ...
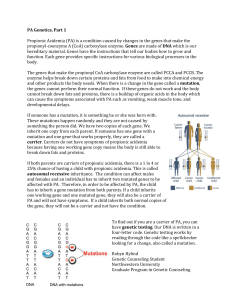
Propionic-Acidemia-G.. - Propionic Acidemia Foundation
... inherit one copy from each parent. If someone has one gene with a mutation and one gene that works properly, they are called a carrier. Carriers do not have symptoms of propionic acidemia because having one working gene copy means the body is still able to break down fats and proteins. If both paren ...
... inherit one copy from each parent. If someone has one gene with a mutation and one gene that works properly, they are called a carrier. Carriers do not have symptoms of propionic acidemia because having one working gene copy means the body is still able to break down fats and proteins. If both paren ...
b1_variation_and_control
... embryo before they become specialised, then transplanting the identical embryos into host mothers ■ adult cell cloning – the nucleus is removed from an unfertilised egg cell. The nucleus from an adult body cell, eg a skin cell, is then inserted into the egg cell. An electric shock then causes the eg ...
... embryo before they become specialised, then transplanting the identical embryos into host mothers ■ adult cell cloning – the nucleus is removed from an unfertilised egg cell. The nucleus from an adult body cell, eg a skin cell, is then inserted into the egg cell. An electric shock then causes the eg ...
Determinants of Gene Duplicability
... • The vertebrate genes homologous to fly homeotic genes are found in four clusters, tightly linked. • Vertebrate Hox genes are expressed in the same anterior-posterior order along the body axis as in flies ...
... • The vertebrate genes homologous to fly homeotic genes are found in four clusters, tightly linked. • Vertebrate Hox genes are expressed in the same anterior-posterior order along the body axis as in flies ...
BIOLOGY Chapter 10: Patterns of Inheritance Name: Section Goal
... A. Biologists worked out the processes of mitosis and meiosis in the late 1800s and observed the parallels between the behavior of chromosomes and the behavior of Mendel’s heritable factors B. The chromosome theory of inheritance states that genes are located on chromosomes, and the behavior of chro ...
... A. Biologists worked out the processes of mitosis and meiosis in the late 1800s and observed the parallels between the behavior of chromosomes and the behavior of Mendel’s heritable factors B. The chromosome theory of inheritance states that genes are located on chromosomes, and the behavior of chro ...
Mitochondrial genome
... • Recent African Origin Model suggests that our species evolved from a small African population that subsequently colonised the whole world • Coalescence analysis indicates that all mtDNA in modern humans can be traced back to a single female (~100-150,000 years ago) ...
... • Recent African Origin Model suggests that our species evolved from a small African population that subsequently colonised the whole world • Coalescence analysis indicates that all mtDNA in modern humans can be traced back to a single female (~100-150,000 years ago) ...
Unit 6: Mendelian Genetics
... 2 copies of allele = death at early age 1 copy of allele = brain cells produce only ½ the enzyme in it's proper form (other ½ is mutated form) ...
... 2 copies of allele = death at early age 1 copy of allele = brain cells produce only ½ the enzyme in it's proper form (other ½ is mutated form) ...
Human gene expression and genomic imprinting
... of alleles at certain gene loci dependent on the parent of origin • Uniparental disomy is pathogenic Some conceptuses have normal 46,XX or 46, XY karyotype but may have inherited two copies of the same chromosome from just one of the parents . This may result in abnormal phenotypes which are differe ...
... of alleles at certain gene loci dependent on the parent of origin • Uniparental disomy is pathogenic Some conceptuses have normal 46,XX or 46, XY karyotype but may have inherited two copies of the same chromosome from just one of the parents . This may result in abnormal phenotypes which are differe ...