Genetics - TeacherWeb
... • He also crossed 2 of the offspring of the yellow X green cross • The third generation had 6,022 yellow offspring to 2,001 green offspring; that’s a ratio of 3:1 ...
... • He also crossed 2 of the offspring of the yellow X green cross • The third generation had 6,022 yellow offspring to 2,001 green offspring; that’s a ratio of 3:1 ...
Document
... False Discovery Rate (FDR): Less conservative test that calculates the number of false positives within a set of significant values (P<0.05) and then calculates a new significance threshold , q. ...
... False Discovery Rate (FDR): Less conservative test that calculates the number of false positives within a set of significant values (P<0.05) and then calculates a new significance threshold , q. ...
Choose the correct option for each question.
... a. Loss of sensation, but preserved motor control b. Loss of both sensation and motor control c. Loss of motor control, but preserved sensation d. Unaffected sensation and motor control 8. Units of heredity that maintain their structural identity from one generation to another are: a. enzymes. b. mu ...
... a. Loss of sensation, but preserved motor control b. Loss of both sensation and motor control c. Loss of motor control, but preserved sensation d. Unaffected sensation and motor control 8. Units of heredity that maintain their structural identity from one generation to another are: a. enzymes. b. mu ...
True or False - University of Phoenix
... a. Loss of sensation, but preserved motor control b. Loss of both sensation and motor control c. Loss of motor control, but preserved sensation d. Unaffected sensation and motor control 8. Units of heredity that maintain their structural identity from one generation to another are: a. enzymes. b. mu ...
... a. Loss of sensation, but preserved motor control b. Loss of both sensation and motor control c. Loss of motor control, but preserved sensation d. Unaffected sensation and motor control 8. Units of heredity that maintain their structural identity from one generation to another are: a. enzymes. b. mu ...
Piecing Together an Identity
... • Since cells in a male contain a single X chromosome and cells in a female contain two X chromosomes, females contain twice as many copies of the genes on the X chromosome per cell as do males. To equalize the dosage of X chromosome genes between the two sexes, one of the two X chromosomes in each ...
... • Since cells in a male contain a single X chromosome and cells in a female contain two X chromosomes, females contain twice as many copies of the genes on the X chromosome per cell as do males. To equalize the dosage of X chromosome genes between the two sexes, one of the two X chromosomes in each ...
A Statistical Approach to Literature
... of the earlier literature-based method • In general, the new method is able to cover a large proportion of terms from GO enrichment analysis • Supplement with additional biological concepts, including many related genes • May be particularly useful for studying aspects not focused in GO, such as med ...
... of the earlier literature-based method • In general, the new method is able to cover a large proportion of terms from GO enrichment analysis • Supplement with additional biological concepts, including many related genes • May be particularly useful for studying aspects not focused in GO, such as med ...
Unit 3C - School District of Cambridge
... Heritability: variations among individuals that we can attribute to their differing genes If all schools were of uniform quality, all families equally loving, and all neighborhoods equally healthy, then heritability would increase because differences due to environment would decrease ...
... Heritability: variations among individuals that we can attribute to their differing genes If all schools were of uniform quality, all families equally loving, and all neighborhoods equally healthy, then heritability would increase because differences due to environment would decrease ...
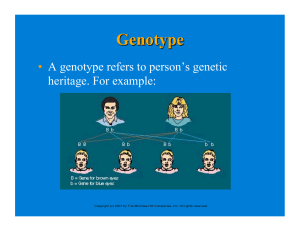
• A genotype refers to person`s genetic heritage. For example:
... traits are influenced by many pairs of genes in interaction with the environment. ...
... traits are influenced by many pairs of genes in interaction with the environment. ...
Human Heredity
... chance that some pairs of chromosomes will not split. – This causes the chance of Trisomy – ( 3 chromosomes of a certain chromosome ) – Karyotype is a picture of all the chromosomes. – It is determined by Amniocentesis, a sample of amniotic fluid from the uterus ...
... chance that some pairs of chromosomes will not split. – This causes the chance of Trisomy – ( 3 chromosomes of a certain chromosome ) – Karyotype is a picture of all the chromosomes. – It is determined by Amniocentesis, a sample of amniotic fluid from the uterus ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Lectures For UG-5
... response to stress, and the onset of disease, can thus be studied at the genomic level. • Instead of defining cell states using single markers, it is now possible to use clustering algorithms to group data obtained over many different experiments and identify groups of coregulated genes. • This prod ...
... response to stress, and the onset of disease, can thus be studied at the genomic level. • Instead of defining cell states using single markers, it is now possible to use clustering algorithms to group data obtained over many different experiments and identify groups of coregulated genes. • This prod ...
Lecture 14 - The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... results from a specific deletion in chromosome 5 • A child born with this syndrome is mentally retarded and has a catlike cry; individuals usually die in infancy or early childhood • Certain cancers, including chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), are caused by translocations of chromosomes ...
... results from a specific deletion in chromosome 5 • A child born with this syndrome is mentally retarded and has a catlike cry; individuals usually die in infancy or early childhood • Certain cancers, including chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), are caused by translocations of chromosomes ...
Biol
... AaBbCc) is crossed with a male fly that is homozygous recessive for all three mutant alleles. If the phenotypes of the most common offspring are ABc and abC, and the least common offspring are ABC and abc, then the order of the genes a b c on the chromosome is: A. B. C. D. ...
... AaBbCc) is crossed with a male fly that is homozygous recessive for all three mutant alleles. If the phenotypes of the most common offspring are ABc and abC, and the least common offspring are ABC and abc, then the order of the genes a b c on the chromosome is: A. B. C. D. ...
EVOLUTIONARY GENETICS (Genome 453) Practice problems for
... “third chimpanzee” hypothesis). Previously it appeared obvious that chimps, bonobos and gorillas must be most closely related because they all walk on their knuckles, while humans do not. How could this disagreement between genetics and morphology be explained? Note that knuckle-walking is not purel ...
... “third chimpanzee” hypothesis). Previously it appeared obvious that chimps, bonobos and gorillas must be most closely related because they all walk on their knuckles, while humans do not. How could this disagreement between genetics and morphology be explained? Note that knuckle-walking is not purel ...
070329Syl
... For each class two students will be asked to read all of the assigned papers and possibly an additional one. Each is then available to present the entire paper. Others are asked to read the assigned papers and may be questioned but are not penalized for ignorance. A standard way of reading and summa ...
... For each class two students will be asked to read all of the assigned papers and possibly an additional one. Each is then available to present the entire paper. Others are asked to read the assigned papers and may be questioned but are not penalized for ignorance. A standard way of reading and summa ...
Genetics
... • DNA- molecules of genetic material that holds information about an organism that is passed from parents to offspring. ...
... • DNA- molecules of genetic material that holds information about an organism that is passed from parents to offspring. ...
Text S2
... Functional analysis of the parent genes To explore if any functional preference exists among the parent genes, they were classified into various functional categories under the four major functional classes as defined in the clusters of orthologous groups for eukaryotes (KOGs) (1). This task was per ...
... Functional analysis of the parent genes To explore if any functional preference exists among the parent genes, they were classified into various functional categories under the four major functional classes as defined in the clusters of orthologous groups for eukaryotes (KOGs) (1). This task was per ...
The Living Environment Unit 4 Reproduction and Development
... • Replicates it’s DNA then divides in two. Sexual – TWO parents where offspring receives HALF the genes from each parent via GAMETES. • Gametes – Sex Cells such as Sperm and Eggs that carry half the genetic material. • Siblings are different due to unique combinations of genes TYPES OF CLONES Natura ...
... • Replicates it’s DNA then divides in two. Sexual – TWO parents where offspring receives HALF the genes from each parent via GAMETES. • Gametes – Sex Cells such as Sperm and Eggs that carry half the genetic material. • Siblings are different due to unique combinations of genes TYPES OF CLONES Natura ...