Document
... Genome Size and Gene Number • Genome size has varied over evolutionary time; • Increases or decreases in size do not correlate with number of genes; • Polyploidy in plants does not by itself explain differences in genome size; • A greater amount of DNA is explained by the presence of introns and no ...
... Genome Size and Gene Number • Genome size has varied over evolutionary time; • Increases or decreases in size do not correlate with number of genes; • Polyploidy in plants does not by itself explain differences in genome size; • A greater amount of DNA is explained by the presence of introns and no ...
Chapter 13 Mutations (2)
... When lactose is present, the lactose molecules bind to the repressor, changing the shape of the repressor. The repressor molecule cannot bind to the operator, therefore, RNA polymerase CAN bind to the promoter and transcription does take place. The enzymes needed to digest lactose are created. ...
... When lactose is present, the lactose molecules bind to the repressor, changing the shape of the repressor. The repressor molecule cannot bind to the operator, therefore, RNA polymerase CAN bind to the promoter and transcription does take place. The enzymes needed to digest lactose are created. ...
Genetic Notes review page (blanks filled in except for
... 1. Which has 2 parents to create the new organism? __Sexual________ 2. Which only has 1 parent to create the new organism? __Asexual______ 3. Genes are carried from parents to their offspring on __chromosomes________. 4. Sperm carries which two chromosomes in sexual reproduction? __X Y__ 5. When the ...
... 1. Which has 2 parents to create the new organism? __Sexual________ 2. Which only has 1 parent to create the new organism? __Asexual______ 3. Genes are carried from parents to their offspring on __chromosomes________. 4. Sperm carries which two chromosomes in sexual reproduction? __X Y__ 5. When the ...
DNA Function - Grayslake Central High School
... What is the predicted ratio of females to males surviving to maturity from a cross between a carrier female and a normal male? What would have to be true for a female to express the disorder? ...
... What is the predicted ratio of females to males surviving to maturity from a cross between a carrier female and a normal male? What would have to be true for a female to express the disorder? ...
Chapter 6 Expanded Notes
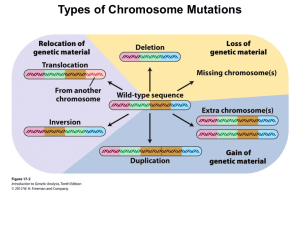
... In genetics, we often deal with what is referred to as the wildtype, a sort of generic, all-purpose version of an animal or plant. Something plain that contains the basic traits for that species being studied. A representative sample for that species. However, if there are members of a species with ...
... In genetics, we often deal with what is referred to as the wildtype, a sort of generic, all-purpose version of an animal or plant. Something plain that contains the basic traits for that species being studied. A representative sample for that species. However, if there are members of a species with ...
ANSWER KEY FOR PROBLEM SET #2
... -Involves 2 meiotic divisions over 64-78 days to form sperm cells -4 functional sperm produced from one primary spermatocyte -One or more billion sperm produced weekly ...
... -Involves 2 meiotic divisions over 64-78 days to form sperm cells -4 functional sperm produced from one primary spermatocyte -One or more billion sperm produced weekly ...
Supplementary Information
... Gene Pix 4000B scanner and signal intensities were extracted using GenePixPro 6.1 software. Probe intensities were corrected by subtracting background intensity and normalized using median array normalization, where each background-subtracted intensity was divided by the median intensity of all non- ...
... Gene Pix 4000B scanner and signal intensities were extracted using GenePixPro 6.1 software. Probe intensities were corrected by subtracting background intensity and normalized using median array normalization, where each background-subtracted intensity was divided by the median intensity of all non- ...
Full-text PDF
... EST sequences of the two stages in Dicty cDB. They were classified according to the expression stages (slug or vegetative) of the original ESTs, and 3,102 contigs were from the slug stage, 1,596 from the vegetative stage, and 1,085 from both. For functional prediction of each contig, we performed hom ...
... EST sequences of the two stages in Dicty cDB. They were classified according to the expression stages (slug or vegetative) of the original ESTs, and 3,102 contigs were from the slug stage, 1,596 from the vegetative stage, and 1,085 from both. For functional prediction of each contig, we performed hom ...
7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype
... • Female mammals have an XX genotype. – Expression of sex-linked genes is similar to autosomal genes in females. – X chromosome inactivation randomly “turns off” one X chromosome. ...
... • Female mammals have an XX genotype. – Expression of sex-linked genes is similar to autosomal genes in females. – X chromosome inactivation randomly “turns off” one X chromosome. ...
A unit of measurement on genetic maps is:
... My objective would be to identify a genetic marker that predicts the adverse side-effect. In this case, I would conduct a case-control genome scan with the 100,000 human tagging SNPs from the HapMap project, where the cases are as large a sample as I can find (at least 200) of patients who took the ...
... My objective would be to identify a genetic marker that predicts the adverse side-effect. In this case, I would conduct a case-control genome scan with the 100,000 human tagging SNPs from the HapMap project, where the cases are as large a sample as I can find (at least 200) of patients who took the ...
Glossary - Heart UK
... DNA testing This describes molecular genetic testing – testing that involves the analysis of DNA. Techniques can involve reading (sequencing) the code of the whole gene or testing for a known mutation. Family mutation This refers to the specific mutation that causes the genetic disease or condition ...
... DNA testing This describes molecular genetic testing – testing that involves the analysis of DNA. Techniques can involve reading (sequencing) the code of the whole gene or testing for a known mutation. Family mutation This refers to the specific mutation that causes the genetic disease or condition ...
Bioinformatics/Computational Biological Applications of
... (2) Large opportunity for selection bias to occur in feature selection. (3) Large multiple hypothesis correction problem. How to do this without being too conservative? • (Note: we will be talking about expression arrays; there are other array types such as SNP arrays that hybridize with genomic DNA ...
... (2) Large opportunity for selection bias to occur in feature selection. (3) Large multiple hypothesis correction problem. How to do this without being too conservative? • (Note: we will be talking about expression arrays; there are other array types such as SNP arrays that hybridize with genomic DNA ...
Exam101ANS
... 1. her mother must have been color blind. 2. her paternal grandmother was either color blind or was a carrier for color blindness….( the woman got a bad X chromosome from her Dad, who got it from his Mom) 3. her paternal grandfather must have been color blind. 4. her father may not be color blind. ...
... 1. her mother must have been color blind. 2. her paternal grandmother was either color blind or was a carrier for color blindness….( the woman got a bad X chromosome from her Dad, who got it from his Mom) 3. her paternal grandfather must have been color blind. 4. her father may not be color blind. ...
Presenter 18 - Florida International University
... adenine (A) forms a base pair with thymine (T) guanine (G) forms a base pair with cytosine (C) ...
... adenine (A) forms a base pair with thymine (T) guanine (G) forms a base pair with cytosine (C) ...
molecular approaches to cancer management in the postgenomic era
... Through the evaluation of large-scale expression profiles using microarrays, tumours can be classified and important molecular pathways discerned. One of the first studies that used gene expression data to supplement standard cancer histopathology studied the clinical heterogeneity of diffuse large ...
... Through the evaluation of large-scale expression profiles using microarrays, tumours can be classified and important molecular pathways discerned. One of the first studies that used gene expression data to supplement standard cancer histopathology studied the clinical heterogeneity of diffuse large ...
Chapter 12 Inheritance Patterns and Human Genetics
... (account for more than 200 human traits). Ex. Huntington’s Disease (HD) – AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT ALLELE – starts when people are in their 30’s and 40’s. Loss of muscle control, spasms, mental illness, death. HD is often unknowingly passed to offspring. Genetic Marker – short section of DNA that is kno ...
... (account for more than 200 human traits). Ex. Huntington’s Disease (HD) – AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT ALLELE – starts when people are in their 30’s and 40’s. Loss of muscle control, spasms, mental illness, death. HD is often unknowingly passed to offspring. Genetic Marker – short section of DNA that is kno ...
Psych 3102 Lecture 3 Gregor Mendel
... 2 alleles for each gene in each person alleles separate (segregate) during reproduction offspring receive 1 allele from each parent ...
... 2 alleles for each gene in each person alleles separate (segregate) during reproduction offspring receive 1 allele from each parent ...
1 - Acpsd.net
... 14. True Breeding: One that is homozygous for a trait (self pollinating) purebreeding Hybrid: one of each allele, heterozygous Ex. Hh 15. Male and female parts are located in the same plant, multiple offspring, fairly short generation times, traits are easy to tell apart. 16. Autosomal traits- found ...
... 14. True Breeding: One that is homozygous for a trait (self pollinating) purebreeding Hybrid: one of each allele, heterozygous Ex. Hh 15. Male and female parts are located in the same plant, multiple offspring, fairly short generation times, traits are easy to tell apart. 16. Autosomal traits- found ...
Mendel, Alleles, Punnentt squares Complex Punnett Squares VOCAB:
... Probability is the fraction of how many boxes contain the genotype of phenotype. Ratio (2:2) will always equal the number of boxes in the Punnett square and you count the boxes for the phenotypes or genotypes. Dihybrid Cross: A cross where you track 2 alleles. Boxes will have 4 letters. KEEP THE LET ...
... Probability is the fraction of how many boxes contain the genotype of phenotype. Ratio (2:2) will always equal the number of boxes in the Punnett square and you count the boxes for the phenotypes or genotypes. Dihybrid Cross: A cross where you track 2 alleles. Boxes will have 4 letters. KEEP THE LET ...
2017 - Barley World
... reproduction. However, only dioecious plants enjoy this advantage. a. T b. F 22. The synergids in the embryo sac of a diploid plant a. Are each “3n”. b. Give rise to 3n endosperm. c. Have no known function. d. Attract the sperm to the egg. 23. You have two homozygous diploid plants with perfect flow ...
... reproduction. However, only dioecious plants enjoy this advantage. a. T b. F 22. The synergids in the embryo sac of a diploid plant a. Are each “3n”. b. Give rise to 3n endosperm. c. Have no known function. d. Attract the sperm to the egg. 23. You have two homozygous diploid plants with perfect flow ...
Mammalian X Chromosome Inactivation
... 4. Telomeric and centromeric regions Features of Facultative Heterochromatin 1. Referred to as silent chromatin 2. Potential to become heterochromatic (Barr body) ...
... 4. Telomeric and centromeric regions Features of Facultative Heterochromatin 1. Referred to as silent chromatin 2. Potential to become heterochromatic (Barr body) ...
Section 11-3 Powerpoint
... • 14. There are some alleles that are neither dominant or recessive, and many traits: • Genetics tends to be a bit more complicated than that: – The majority of genes have more than two alleles, and important traits are controlled by many different genes. ...
... • 14. There are some alleles that are neither dominant or recessive, and many traits: • Genetics tends to be a bit more complicated than that: – The majority of genes have more than two alleles, and important traits are controlled by many different genes. ...
S1.Our understanding of maternal effect genes has been greatly
... many cases, the offspring will die at early embryonic or larval stages. These are called maternal effect lethal alleles. How would a researcher identify a mutation that produced a recessive, maternal effect lethal allele? Answer: A maternal effect lethal allele can be identified when a phenotypicall ...
... many cases, the offspring will die at early embryonic or larval stages. These are called maternal effect lethal alleles. How would a researcher identify a mutation that produced a recessive, maternal effect lethal allele? Answer: A maternal effect lethal allele can be identified when a phenotypicall ...