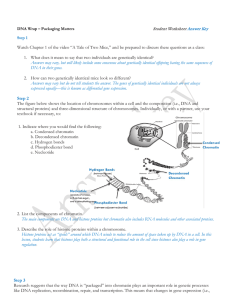
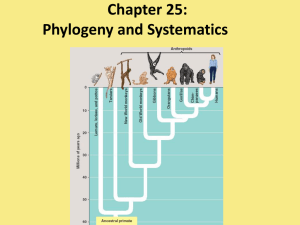
Document
... identifying bacterial pathogen genes more similar to host genes than you would expect based on phylogeny. The tool we developed investigates this, and is also useful for identifying cross-domain lateral gene transfer events (i.e. Trans - Bacteria, Archaea and Eukarya). Description: Proteins in a giv ...
... identifying bacterial pathogen genes more similar to host genes than you would expect based on phylogeny. The tool we developed investigates this, and is also useful for identifying cross-domain lateral gene transfer events (i.e. Trans - Bacteria, Archaea and Eukarya). Description: Proteins in a giv ...
Answer Key
... transcribed into mRNA and then translated (conversion of mRNA sequence into amino acids) into a protein. An individual’s environment, even in the womb, can influence these factors and permanently alter the expression of genes in the adult. Alterations in epigenetic mechanisms lead to development of ...
... transcribed into mRNA and then translated (conversion of mRNA sequence into amino acids) into a protein. An individual’s environment, even in the womb, can influence these factors and permanently alter the expression of genes in the adult. Alterations in epigenetic mechanisms lead to development of ...
ANSWERS Pitts` Biology 110 review: genetics 1
... 25. The number of genes present on a chromosome depends, in part, on the length of the chromosome and the length of each gene. Chromosomes, like books, differ in length. The number of genes present on a chromosome, like the number of pages in a book, may be small or large. 26. Some 50,000 to 100,00 ...
... 25. The number of genes present on a chromosome depends, in part, on the length of the chromosome and the length of each gene. Chromosomes, like books, differ in length. The number of genes present on a chromosome, like the number of pages in a book, may be small or large. 26. Some 50,000 to 100,00 ...
Gregor Mendel Mendel`s 7 Pea Plant Traits
... characteristic are called TRAITS. •Some forms are DOMINANT •Some forms are RECESSIVE ...
... characteristic are called TRAITS. •Some forms are DOMINANT •Some forms are RECESSIVE ...
Mendel/Punnet/pedigrees powerpoint mendel.punnett
... monk living in the 1800’s Interested in the causes of variation in plants – used peas to study inheritance Why Peas? • Short generation time • Large number of ...
... monk living in the 1800’s Interested in the causes of variation in plants – used peas to study inheritance Why Peas? • Short generation time • Large number of ...
outline21590
... 9. Study of previous abortus or stillborn 10. Molecular genetic analysis 11. Risk Estimate a. How big a risk is 25%? b. 25% risk means 75% normal which may sound good c. It depends on the prognosis (1) How will the offspring be different as an adolescent or as an adult? ...
... 9. Study of previous abortus or stillborn 10. Molecular genetic analysis 11. Risk Estimate a. How big a risk is 25%? b. 25% risk means 75% normal which may sound good c. It depends on the prognosis (1) How will the offspring be different as an adolescent or as an adult? ...
Genetics - TeacherWeb
... express its ____________ at the expense of an alternate allele; Generally the dominant allele will make a gene product that the recessive can not; therefore the dominant allele will ____________ itself whenever it is present ...
... express its ____________ at the expense of an alternate allele; Generally the dominant allele will make a gene product that the recessive can not; therefore the dominant allele will ____________ itself whenever it is present ...
Unit 2
... A sex-linked trait is a trait controlled by genes on the X or Y chromosome. Recall, female is XX and male is XY Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes. One set is the sex chromosomes, while the other 22 pairs are autosomes (non-sex chromosomes). If an allele is found on an autosome, it is called au ...
... A sex-linked trait is a trait controlled by genes on the X or Y chromosome. Recall, female is XX and male is XY Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes. One set is the sex chromosomes, while the other 22 pairs are autosomes (non-sex chromosomes). If an allele is found on an autosome, it is called au ...
Unit 07 - Lessons 4-6
... ! Sexual reproduction creates unique combinations of genes. • Sexual reproduction creates unique combination of genes. – independent assortment of chromosomes in meiosis – random fertilization of gametes • Unique phenotypes may give a reproductive advantage to some organisms. ...
... ! Sexual reproduction creates unique combinations of genes. • Sexual reproduction creates unique combination of genes. – independent assortment of chromosomes in meiosis – random fertilization of gametes • Unique phenotypes may give a reproductive advantage to some organisms. ...
Biology 4.7 Gene Types
... A ‘switched on’ gene is one that is transcribing mRNA, a ‘switched off’ gene is not producing mRNA. MICROARRAYS is a new technology that allows Scientists to study a large number of genes simultaneously and: ...
... A ‘switched on’ gene is one that is transcribing mRNA, a ‘switched off’ gene is not producing mRNA. MICROARRAYS is a new technology that allows Scientists to study a large number of genes simultaneously and: ...
Name
... A sex-linked trait has alleles on only one of the sex chromosomes—usually the X because it is much larger than the Y chromosome. 1. color blindness a. the inability to distinguish between certain colors caused by a X-linked recessive allele b. caused by defective version of any one of three genes as ...
... A sex-linked trait has alleles on only one of the sex chromosomes—usually the X because it is much larger than the Y chromosome. 1. color blindness a. the inability to distinguish between certain colors caused by a X-linked recessive allele b. caused by defective version of any one of three genes as ...
YyRr - s3.amazonaws.com
... • The process of making gametes (sex cells such as sperm and egg). • Purpose = to reduce the chromosome number in half! • 1 Diploid(2N) cell becomes 4 Haploid(N) cells. ...
... • The process of making gametes (sex cells such as sperm and egg). • Purpose = to reduce the chromosome number in half! • 1 Diploid(2N) cell becomes 4 Haploid(N) cells. ...
array CGH
... contains high-density coverage for ~500 targeted regions with an average oligo probe spacing of ~5 kb or at least 20 probes per gene. These targeted regions include clinically relevant haploinsufficient genes, X-linked intellectual disability genes, all recurrent microdeletion/microduplication syndr ...
... contains high-density coverage for ~500 targeted regions with an average oligo probe spacing of ~5 kb or at least 20 probes per gene. These targeted regions include clinically relevant haploinsufficient genes, X-linked intellectual disability genes, all recurrent microdeletion/microduplication syndr ...
17.1 Genes and Variation
... • Combination of genes from different parents • Half of the DNA comes from each parent. • Each offspring receives a unique set of genetic information. (Exception = Twins) • This is the result of crossing over and independent assortment during meiosis! ...
... • Combination of genes from different parents • Half of the DNA comes from each parent. • Each offspring receives a unique set of genetic information. (Exception = Twins) • This is the result of crossing over and independent assortment during meiosis! ...
Classic Methods of Genetic Analysis
... • People with hemophilia can bleed to death from seemingly minor cuts and may suffer from internal bleeding from bumps or bruises. • It can be treated by injecting AHF into the patients. ...
... • People with hemophilia can bleed to death from seemingly minor cuts and may suffer from internal bleeding from bumps or bruises. • It can be treated by injecting AHF into the patients. ...
COS 597c: DNA arrays Topics in Computational Molecular Biolo
... Interpreting the meaning and significance of 20,000 such numbers is a very big challenge, which becomes even more overwhelming because such a measurement is usually performed several times. The task of analyzing this amount of data is made easier by software packages. These packages are usually sold ...
... Interpreting the meaning and significance of 20,000 such numbers is a very big challenge, which becomes even more overwhelming because such a measurement is usually performed several times. The task of analyzing this amount of data is made easier by software packages. These packages are usually sold ...
Data Mining - functional statistical genetics/bioinformatics
... Graphical representation if relationship between ...
... Graphical representation if relationship between ...
Vigneshwaran Mani
... increased. Large amount of (Disease) sample DNA will hybridize to those spots on the microarray compared to (normal) control DNA hybridizing to those same spots. Those spots containing the sample DNA will fluoresce red with greater intensity than they will fluoresce green, indicating that the number ...
... increased. Large amount of (Disease) sample DNA will hybridize to those spots on the microarray compared to (normal) control DNA hybridizing to those same spots. Those spots containing the sample DNA will fluoresce red with greater intensity than they will fluoresce green, indicating that the number ...
View/print full test page
... Methylation Analysis (of chromosomes 14 and 15) is performed to detect imprinting abnormalities that can occur on these chromosomes. Imprinting disorders include: ...
... Methylation Analysis (of chromosomes 14 and 15) is performed to detect imprinting abnormalities that can occur on these chromosomes. Imprinting disorders include: ...
GENETICS
... Incomplete dominance – A form of dominance occurring in heterozygotes in which the dominant allele is only partially expressed, and usually resulting in an offspring with an intermediate phenotype. Alleles blend to create a new phenotype in the heterozygote! Example: In snapdragons, flower color can ...
... Incomplete dominance – A form of dominance occurring in heterozygotes in which the dominant allele is only partially expressed, and usually resulting in an offspring with an intermediate phenotype. Alleles blend to create a new phenotype in the heterozygote! Example: In snapdragons, flower color can ...
Document
... We all possess two alleles for each gene product – one from our mother and one from our father. In most genes the end result is the combination of these two alleles (eg handedness). In some genes, especially those related to growth one allele is permanently turned off. This occurs at or soon after f ...
... We all possess two alleles for each gene product – one from our mother and one from our father. In most genes the end result is the combination of these two alleles (eg handedness). In some genes, especially those related to growth one allele is permanently turned off. This occurs at or soon after f ...