Mendelian Genetics
... 1. Genes are material elements 2. These elements come in pairs. 3. These elements can retain their character through many generations (heritable). 4. That these element pairs separate during the formation of gametes.” ...
... 1. Genes are material elements 2. These elements come in pairs. 3. These elements can retain their character through many generations (heritable). 4. That these element pairs separate during the formation of gametes.” ...
Patterns of Inheritance
... In general, only genetic influences are inherited and the effects of the environment are not passed to the next generation In recent years, however, biologists have begun to recognize the importance of epigenetic inheritance, the transmission of traits by mechanisms not directly involving DNA sequen ...
... In general, only genetic influences are inherited and the effects of the environment are not passed to the next generation In recent years, however, biologists have begun to recognize the importance of epigenetic inheritance, the transmission of traits by mechanisms not directly involving DNA sequen ...
Topic 8: Quantitative Genetics
... Quantitative genetics: traits controlled by alleles at many loci Human phenotypic adaptations and diseases commonly involve the effects of many genes, each will small effect Quantitative genetics allows analysis of selection and genetic bases of quantitative phenotypic traits, such as height, weight ...
... Quantitative genetics: traits controlled by alleles at many loci Human phenotypic adaptations and diseases commonly involve the effects of many genes, each will small effect Quantitative genetics allows analysis of selection and genetic bases of quantitative phenotypic traits, such as height, weight ...
CA Breast cancer
... In 1994 scientists have discovered two tumor suppressor genes: 1. BRCA1 2. BRCA2 Any mutations in the above genes causes breast cancer. After 1994 many other genes were discovered that were linked to the cause of breast cancer. But these genes don’t directly involve in tumor formation. ...
... In 1994 scientists have discovered two tumor suppressor genes: 1. BRCA1 2. BRCA2 Any mutations in the above genes causes breast cancer. After 1994 many other genes were discovered that were linked to the cause of breast cancer. But these genes don’t directly involve in tumor formation. ...
Behavior lecture
... a) pass on genes directly to offspring b) assist relative (with your genes) to pass on their genes ...
... a) pass on genes directly to offspring b) assist relative (with your genes) to pass on their genes ...
The Mechanism of X inactivation
... The Sex-linked phenotypic effects may be due to 1. The expression of X-linked genes prior to embryonic X-inactivation 2. An imbalance in the expression of pseudoautosomal genes ...
... The Sex-linked phenotypic effects may be due to 1. The expression of X-linked genes prior to embryonic X-inactivation 2. An imbalance in the expression of pseudoautosomal genes ...
Conditions of existence
... 1. Conditions of existence: This view championed by Georges Cuvier and Charles Bell focussed on the differences between species that allowed each to adapt to its environment. Thus they believed that the hand of the human, flipper of the seal and the wings of the birds and bats were marvellous contri ...
... 1. Conditions of existence: This view championed by Georges Cuvier and Charles Bell focussed on the differences between species that allowed each to adapt to its environment. Thus they believed that the hand of the human, flipper of the seal and the wings of the birds and bats were marvellous contri ...
Probability
... process by which an offspring cell or organism acquires or becomes proposed to the characteristics of its parent cell or organism. ...
... process by which an offspring cell or organism acquires or becomes proposed to the characteristics of its parent cell or organism. ...
Name - Piscataway High School
... Recessive – the allele that is only expressed when two copies are present Answer the following questions in complete sentences. How are the terms genes, locus and allele related? All have something to do with a particular segment of DNA, or nucleotides. A gene is a region of DNA, a series of nucleo ...
... Recessive – the allele that is only expressed when two copies are present Answer the following questions in complete sentences. How are the terms genes, locus and allele related? All have something to do with a particular segment of DNA, or nucleotides. A gene is a region of DNA, a series of nucleo ...
Alleles - mykingbiology
... Traits – variations of a character. Ex) character: fur color possible traits: brown, black, red ...
... Traits – variations of a character. Ex) character: fur color possible traits: brown, black, red ...
Ch12b_Heredity
... Nondisjunction of the sex chromosomes is more often survivable than nondisjunctions of somatic chromosomes. As long as the fetus has at least one X chromosome, it can survive. ...
... Nondisjunction of the sex chromosomes is more often survivable than nondisjunctions of somatic chromosomes. As long as the fetus has at least one X chromosome, it can survive. ...
MUTATIONS
... Polyploid – 4 or more chromosomes Instead of 1n, gametes are 3n or 4n Common in plants Lethal in humans ...
... Polyploid – 4 or more chromosomes Instead of 1n, gametes are 3n or 4n Common in plants Lethal in humans ...
File
... Genetics and Heredity • The transmission of traits from one generation to the next is called heredity or inheritance. • However, offspring differ somewhat from parents and siblings, demonstrating variation. • Genetics is the study of heredity and variation. ...
... Genetics and Heredity • The transmission of traits from one generation to the next is called heredity or inheritance. • However, offspring differ somewhat from parents and siblings, demonstrating variation. • Genetics is the study of heredity and variation. ...
Summary - EUR RePub
... HS1-3 of the LCR seem to loop out. These data strongly suggest that the cis-regulatory DNA elements surrounding the β-globin genes create an erythroid-specific developmentally stable nuclear compartment dedicated to RNA polymerase II transcription. This spatial clustering of regulatory elements resu ...
... HS1-3 of the LCR seem to loop out. These data strongly suggest that the cis-regulatory DNA elements surrounding the β-globin genes create an erythroid-specific developmentally stable nuclear compartment dedicated to RNA polymerase II transcription. This spatial clustering of regulatory elements resu ...
Gene Counters Struggle to Get the Right Answer
... the right place for keeping up their gene pre- a set of benchdiction work. Steven Salzberg and his crew at marks it acquires The Institute for Genomic Research (TIGR) from existing inin Rockville, Maryland, have been improving formation. their programs for finding human genes “There are a since thei ...
... the right place for keeping up their gene pre- a set of benchdiction work. Steven Salzberg and his crew at marks it acquires The Institute for Genomic Research (TIGR) from existing inin Rockville, Maryland, have been improving formation. their programs for finding human genes “There are a since thei ...
Genetics - Biology Junction
... 13. Letter used to represent a dominant allele 14. Transferring pollen grains from anthers to the stigma of a flower 15. Cross involving two traits 17. stronger of two alleles which shows up most often 20. The weaker of two alleles in a pair that is often masked by the dominant allele 21. Male part ...
... 13. Letter used to represent a dominant allele 14. Transferring pollen grains from anthers to the stigma of a flower 15. Cross involving two traits 17. stronger of two alleles which shows up most often 20. The weaker of two alleles in a pair that is often masked by the dominant allele 21. Male part ...
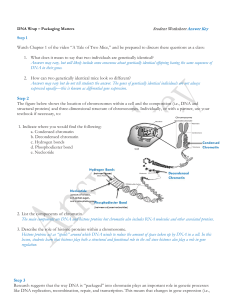
document
... transcribed into mRNA and then translated (conversion of mRNA sequence into amino acids) into a protein. An individual’s environment, even in the womb, can influence these factors and permanently alter the expression of genes in the adult. Alterations in epigenetic mechanisms lead to development of ...
... transcribed into mRNA and then translated (conversion of mRNA sequence into amino acids) into a protein. An individual’s environment, even in the womb, can influence these factors and permanently alter the expression of genes in the adult. Alterations in epigenetic mechanisms lead to development of ...
click here
... 1. Independent assortment is based on the fact that the genes are NOT linked. In a dihybrid cross, you would expect a 9:3:3:1 ratio if genes are not linked. The three ratios shown are all expected results of a dihybrid (AaBb x AaBb) cross- all show a 9:3:3:1 ratio, or a variant of it. Ans: all of th ...
... 1. Independent assortment is based on the fact that the genes are NOT linked. In a dihybrid cross, you would expect a 9:3:3:1 ratio if genes are not linked. The three ratios shown are all expected results of a dihybrid (AaBb x AaBb) cross- all show a 9:3:3:1 ratio, or a variant of it. Ans: all of th ...
Genetics and Sensorineural Hearing Loss (SNHL)
... How is SNHL inherited within families? Recessive Genes About 80% of cases of early onset SNHL are caused by alterations in ‘recessive’ genes. We have two copies of every gene, we inherit one copy from each parent. Everyone carries a few genes which have an alteration (spelling mistake) in the DNA co ...
... How is SNHL inherited within families? Recessive Genes About 80% of cases of early onset SNHL are caused by alterations in ‘recessive’ genes. We have two copies of every gene, we inherit one copy from each parent. Everyone carries a few genes which have an alteration (spelling mistake) in the DNA co ...
Introduction Thomas Hunt Morgan
... • Combined with other methods like chromosomal banding, geneticists can develop cytological maps. – These indicated the positions of genes with respect to chromosomal features. ...
... • Combined with other methods like chromosomal banding, geneticists can develop cytological maps. – These indicated the positions of genes with respect to chromosomal features. ...
Lecture 3A3 - Ms. RR Wingerden
... How linkage affects inheritance. A test crosses that Morgan preformed produced a much higher proportion of parental phenotypes than would be expected if the two genes assorted independently. Based on these result, he concluded that body color and wing size are usually inherited together in specific ...
... How linkage affects inheritance. A test crosses that Morgan preformed produced a much higher proportion of parental phenotypes than would be expected if the two genes assorted independently. Based on these result, he concluded that body color and wing size are usually inherited together in specific ...
Lecture 15 – PDF
... one crossover occurs per tetrad, one would not necessarily expect a crossover to occur between any two genes in any given tetrad a) If crossing over occurs randomly along a chromosome, the chance that a crossover will occur between any two genes should be a function of the distance between the genes ...
... one crossover occurs per tetrad, one would not necessarily expect a crossover to occur between any two genes in any given tetrad a) If crossing over occurs randomly along a chromosome, the chance that a crossover will occur between any two genes should be a function of the distance between the genes ...